Membrane materials are needed to protect the foundation from penetrating moisture. During construction, it separates the base from the soil, walls and porous layers of material that are saturated with water. Contact with water is dangerous for most building materials - the liquid penetrates into the pores, after which the material freezes with the formation of cracks, the binding components are washed out, and the corrosion of the reinforcement is accelerated. Porous materials of walls with increased thermal conductivity, when saturated with moisture, reduce thermal insulation properties, microcracks and fungus appear, and bearing capacity decreases. The waterproofing membrane allows moisture to pass through only in one direction - from the room.
Definition and characteristics

A membrane for waterproofing is called a material for protecting the foundation, floors, roofs, and other structures from moisture penetration. Some species can last half a century. Membrane waterproofing often has a single layer that can be reinforced. It is made of polymeric materials with one-sided moisture transmission. The material provides waterproofing, does not allow moisture to pass from the outside, but does not interfere with the removal of water vapor from the structure.
Depending on the type of moisture source, there are:
- Moisture insulation. It is a lightweight form of insulation against surface moisture, preventing penetration from external sources and internal capillary suction.
- Heavy to medium waterproofing. Prevents penetration of surface moisture to building structures and foundations. It is used when there is a danger of soil watering.
Waterproofing materials are used for roofing, insulation of basements, foundations. Each type of material has its own characteristics - thickness, layering, moisture protection. Correctly selected insulation can ensure reliable operation of the facility for many years.
Types of waterproofing membrane
The fabric structure consists of a non-woven fabric. It is homogeneous, with microperforation throughout the entire plane. Such a surface "breathes", letting in steam, air outside from the insulation. Films are also perforated, but then their strength indicators are reduced.
By external signs, membranes are:
- Flat. For their manufacture, low or high pressure polyethylene, polyoethin, PVC are used. The thickness of such insulation reaches 2 mm. The waterproofing membrane for the foundation is taken from 0.5 mm and thicker. A film thinner than 0.5 mm is used for insulating flat floors. These types of membranes are used in waterproofing and moisture insulation works. Some types of materials have a corrugated surface for better adhesion to the mortar.
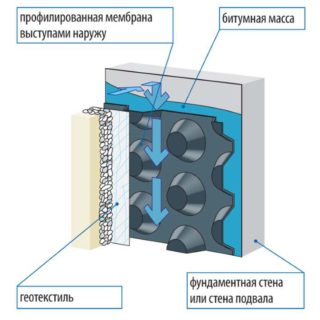
- Profiled type. HDPE is used in the manufacture. The appearance resembles sheets with spikes or projections on one side. Such fabric can be single-layer or multi-layer. It is also used with geotextile elements. The thickness of the profiled membrane is 0.5-1 mm, the length of the projection is 8-20 mm. The canvases are fixed directly to the wall.The profiled membrane is used for waterproofing the foundation if the groundwater is above the basement of the building. This type of insulation retains the water pressure for a long time, subject to correct installation.
Film membranes are made from modified polyvinyl chloride, a mixture of rubber with propylene, and synthetic rubber. A membrane for a foundation made of such a material is called "lightweight". The film is laid without gaps and additional joints.
Diffusion membrane
It has a more complex design than a film. The pores of the material resemble small funnels that pass moisture only in one direction, and from the inside they perfectly conduct steam and water. During installation, the narrow part of the pores faces the roof, the wide part - towards the insulation. Such materials are fragile - they tear easily. They require clearance when mounted on both sides, otherwise their holes are easily clogged.
Super diffusion membrane

This type of material is used when working with structures that have direct contact with moisture - a facade, attics, temporary roofs.
Superdiffusion membrane properties:
- do not need preparation before laying;
- have long-term protection of insulation, structures, materials from moisture, dust;
- vapor permeability;
- durability;
- withstand UV radiation for a long time;
- incombustibility, environmental friendliness.
Roofing fabrics can be multi-layered. Up to 4 layers of polypropylene are used for manufacturing. Such material is durable, flexible, easy to stretch. Layers serve a different purpose. The upper protects against UV radiation, wind, water, external factors. The inner one releases air, steam.
Supermembranes do not require leaving gaps during installation, since the steam removal rate is much higher than that of diffusion materials. They are mounted on insulation without lathing, which reduces the labor intensity of the work. This is economical as it reduces wall thickness during construction.
Superdiffusion waterproofing is not used for laying under euro-slate, profiled sheet, metal tile. Heavy condensation forms when using these roofing materials.
Anti-condensation membrane
Some types of coatings are sensitive to moisture from indoor areas. This is a metal tile, a professional sheet. Anti-condensation film solves this problem, since it does not release excess moisture outside, but from the inside it retains it with the smallest fibers. The collected moisture is then removed from the inside of the room by ventilation.
Waterproofing membrane Ondutis D (RV)
Ondutis D (RV) is used as a temporary roof. It is a gray fabric with an added layer of UV protection. This protection can withstand up to 1.5 months. direct sunlight. For ease of installation, adhesive tape is applied to the base of the material. Ondutis D (RV) is also used for waterproofing basements, semi-basements.
Application area

Diffusion membranes are used for ventilated facades, on walls with external insulation, in ceilings, insulated roofs with a slope angle of more than 35 degrees. Installed on insulation under the roof, facade cladding.
Strong superdiffusion materials are used for waterproofing insulated walls, on frame ventilated facades, and pitched insulated roofs. Thanks to good protection against ultraviolet radiation, it can be used as a temporary roof.
The scope of application of anti-condensation material is insulated and non-insulated metal roofs. They reliably protect the attic and attic from leaks, provided there is ventilation.
Installation of waterproofing PVC membrane for the foundation has the following advantages:
- UV resistance;
- long period of operation, reaching 50 years;
- resistance to rodents, aggressive environments;
- safety due to the absence of oxidation processes;
- elasticity;
- no corrosion formation.
Profiled membrane waterproofing of the foundation is expensive, but it pays for itself by the low labor intensity of the installation, the duration of operation.
Selection rules

The main function of the waterproofing membrane is moisture protection. Therefore, the most important parameter is water resistance, which is measured in mm of water column and should be at least 250 mm. The higher the value, the more efficiently the waterproofing retains water, protects floors, walls, thermal insulation, and the foundation from moisture.
Tensile strength is important during installation. The durability of the material is a complex characteristic that depends on the lateral and longitudinal breaking load. Good performance starts at 140 N along, 100 N across. This indicates the necessary mechanical strength and reliability of the barrier.
An important factor when choosing is resistance to weather conditions: temperature drops, fluctuations in humidity, precipitation, wind load, ultraviolet radiation. Critical temperature fluctuations should not destroy the insulation, contribute to the release of toxic elements.
The complexity of installing moisture protection should also be taken into account. Installation of diffusion films is the most laborious, because it is necessary to provide gaps for moisture removal. The use of superdiffusion membranes is justified to separate facades from thermal insulation to save space. Without the lathing, the waterproofing layer is thinner.
The most convenient materials are those with an adhesive layer, which reliably seals the formed strips of material. A sample of such products is Ondutis "Smart".
The cost of film waterproofing is more expensive than polyethylene, roofing felt, glassine, but much cheaper than the materials being fused.
The cheapest types of waterproofing films are of the diffusion type. Superdiffusion is somewhat more expensive due to the difference in structure. The most expensive are anti-condensation films.
When comparing prices, you should rely on the cost per square meter, not the cost of the roll. The amount of material on a roll may vary.
Membrane mounting technology
Vertical waterproofing can be carried out on a building under construction or finished. For proper installation, it is necessary to provide access to the structure by expanding the trench to 0.8 m. The surface of the foundation is cleaned from sharp protrusions that can damage the film. The membrane is fastened with strips and hangs freely vertically.
The convenience of vertical fastening of the profile material is that it does not need to be glued, primed, or heated.
Installation technology:
- install profile strips along the top of the foundation;
- fix the membrane inside with thorns with overlapping sheets, fasten with locks;
- fasten the sheets at the bottom with dowels with hermetically sealed washers;
- glue the membrane on the outside with geotextile.
The membrane under the foundation slab is installed horizontally. Work technology:
- A pit 50 cm deep comes off.
- Drainage is being prepared.
- The soil is compacted, leveled, insulated with polystyrene plates.
- Geotextiles with a density of more than 110 g / m² are laid on polystyrene foam.
- Membrane cloths are applied with an overlap of at least 5 cm, thoroughly cleaned.
- The edges are welded with a construction hairdryer or welding.
- Geotextiles with a density of at least 110 g / m² are laid on top to protect them from damage during concrete work and reinforcement.
After welding, the quality of the material obtained is controlled. For control, a piece of 5 * 15 cm is cut out with a seam in the middle and stretched. The destruction of the material should occur along the fabric, not the seam. The cut place is sealed. In a similar way, the membrane is laid for the foundation blind area.