Concrete slows down the setting at low temperatures slightly above zero, and negative values destroy the structure of the artificial stone. Pouring concrete in winter leads to the fact that the water does not have time to react with cement, freezes and increases its volume. The stresses arising inside destroy the concrete, which has not gained strength. With the arrival of heat, the water defrosts and the setting continues. But in the body of the material there are destroyed structures that reduce the bearing capacity.
Features of pouring concrete at sub-zero temperatures

An optimal environment is needed for concrete hardening, if the air has not warmed up more than + 5 ° C, or the values are reduced to negative values. Humidity-temperature conditions are created to reduce the curing time and strength gain in the early stages.
Acceleration methods:
- heating due to the internal heat of the concrete mass;
- heat supply to the structure from the outside.
The first method is used for fast-hardening varieties, high-strength mixtures, fine-grained varieties of cement. This group includes astringents with a low degree of fluid intake. Concreting at low temperatures is carried out with the addition of plasticizers to reduce the volume of required water, and chemical antifreeze additives accelerate the setting.
The temperature inside the product depends on the amount of energy that is produced during the exothermic process of attaching water molecules. Such energy is not enough to obtain the strength of the breaking level, and in frost conditions this degree cannot be achieved without additional measures.
- massive structures - not less than + 5 ° С;
- thin-walled structures - not less than + 20 ° С.
Sometimes a sufficient amount of energy can be supplied from the outside to the product with negative indicators. The internal heat reserve in concrete is increased by heating aggregates and liquids. For this, a certain technology for preparing the solution at the construction site is observed, which requires additional labor and energy costs.
Things to Consider When Placing Concrete in Winter
During the preparation of the mixture, the concrete components are protected from snow drifts, icing and freezing. The binders are stored in closed containers or bags made of moisture resistant material. In factories, components, aggregates and water are heated for distribution to vehicle mixers. The solution is prepared in a heated room, so a mass of the required temperature is obtained at the exit.
Sand and crushed stone are heated with registers in the form of heat exchangers, through the body of which steam or water, heated to + 90 ° C, passes. The liquid receives the temperature in the water heaters, from there it is supplied to the supply tanks. The tanks are placed not far from the place of preparation and equipped with a device for dosed draining.
The temperature of the mass can rise if the mixture is prepared in electric mixers, inside of which steam heating is provided. The mixture is transported in heated car mixers, insulated containers are used.
Pouring concrete at sub-zero temperatures is carried out in dump trucks, where the body temperature rises due to exhaust gases during exhaust. The car body is covered with heat-insulated shields, wooden caps or tarpaulins. The mixture is delivered to the site without additional overloads on the way, so as not to reduce the amount of internal energy.
Hoses and concrete pipes are warmed up before being fed into the formwork, and at the end of the work they are cleaned with scrapers. It is not allowed to wash out with water, so that ice does not appear inside the pipe.
The use of additives when pouring concrete
Antifreeze components:
- sodium nitrite;
- sodium chloride + calcium chloride;
- sodium nitrite + calcium chloride;
- urea + calcium nitrate;
- calcium nitrate-nitrite + urea;
- calcium chloride + urea;
- potash.
Additives are selected depending on the design, the amount of fittings, the presence of eddy currents, and the ambient weather. Antifreeze components cannot be added when pouring structures with thermally hardened metal reinforcement. Modifiers are not used when concreting structures, where electrification will subsequently occur and eddy induction currents will appear.
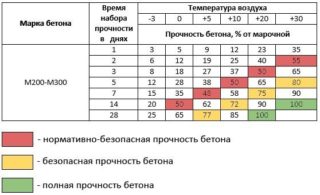
Antifreeze additives slow down the achievement of strength compared to the setting time in a normal environment and without additives. Potash leads to the fact that at -50 ° C the concrete will only harden by 75% in 28 days, whereas under normal circumstances the mixture would have gained 100% strength.
The effect of additional components on the mechanical and technological properties of the solution, for example, plasticity, workability, is taken into account. Concrete with urea should not be heated above + 40 ° С, since the additive is destroyed. Chloride salts create a whitish coating on the surface, which impairs the appearance of the structure. The concrete mix must not contain undissolved salt particles.
Electro-porous concrete technology
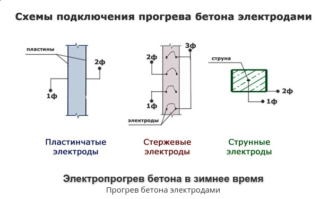
Electrodes supply electric current, heat is released, which is spent on increasing the temperature of the shell and concrete mass and compensates for the energy losses in the surrounding room. The heating of concrete is determined by the amount of energy produced, the mode is selected depending on the heat loss in frost.
Heating formwork transfers heat from its area by heat transfer, the following elements are used:
- mica plates;
- cables;
- Heating elements;
- carbon-graphite fabric;
- heating nets.
This method is optimal for foundations (SNiP 303.01 - 1987) and foundations for the installation of equipment, it is used for columns, girders, monolithic sections of floors.
Infrared heating is an increase in the temperature of concrete from emitters of corresponding waves, directed at the surface of a reinforced concrete product.
Used for the following works:
- warming up frozen soils and concrete, formwork, reinforcement;
- reduction of setting time in sliding formwork;
- obtaining a thermal curtain in places inaccessible for electric heating.
The phasing circuit determines the way of current exchange in the structure. If opposite electrodes are connected to different poles, the current flows through the entire concrete mass. If adjacent plates are connected to different poles, the current heats the edges of the concrete, and the inner layer heats up due to the initial heat content.
Heat insulation of concrete
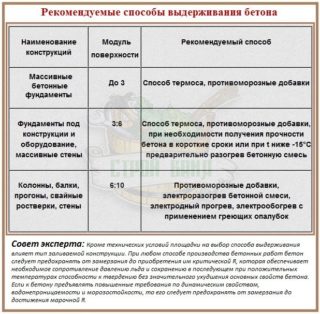
There are methods for maintaining the mixture:
- thermos;
- thermos using mass setting accelerators;
- a thermos with the use of combined substances, which simultaneously accelerate hardening and improve plasticity.
Thermal insulation is an economical option for pouring concrete at sub-zero temperatures. The energy obtained during the hardening of the mixture is used, which is stored inside the mass due to the warm formwork. The mass is gaining power on time, despite the cold season.
The thermos is used to pour the solution into any structure, as well as in case of high requirements for the quality of concrete in terms of water permeability and frost resistance. Warmed holding of the mixture eliminates the appearance of stresses in the mass and the occurrence of cracks. The choice of insulation parameters depends on the massiveness of the structure, weather conditions, wind, and the activity of the binder.
Internal and external concrete heating
The temperature of the solution without anti-freezing modifiers should not be lower than + 5 ° C, and the additives increase the working range to -10 ° C. Concrete structures can be loaded and further work performed only after reaching 100% compressive strength.
The heated concrete mass is mixed in winter 25% more time compared to preparation in the warmth. The base for laying is heated if there is a risk of freezing from contact with old concrete or metal embedded parts. Vibration of concrete for distilling bubbles takes longer 25% of the time.
External insulation is organized using lightweight formwork materials, for example, wall panels of three layers, the outer part of which is made of asbestos cement, metal, plywood, and the inner layer is polyurethane foam.
Internal heating uses energy from the switch cabinet through cables. Infrared irradiation assumes full automation with periodic switching on and off of the device according to a given program.