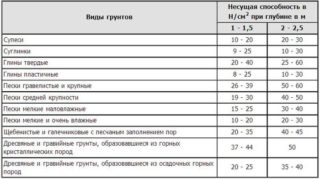
Piles are made of concrete, reinforced concrete, metal and are hollow or solid rods, which are laid obliquely or vertically into the ground. The elements are installed under the structure and transfer compressive, torsion and shear loads to the ground from the ground part. The bearing capacity of the pile depends on the material of manufacture and the type of soil.
Dependence on support materials and soil types

The pile is in contact with the earth layers, so its ability to withstand loads depends on the soil category. The required number of pile elements is calculated based on the characteristics of the material and soil.
In the construction of private houses, types of foundations have become widespread:
- on driven piles;
- on screw supports;
- with bored casings.
The bearing capacity of the soil is taken into account when determining the type of pile foundation. It characterizes the pressure that the conditional area of the layer can withstand. This value is lower than the similar characteristic of the pile rod and depends on the type of formation, its saturation with water and density. Geodetic surveys are carried out to determine the properties of the land layer in the field of construction.
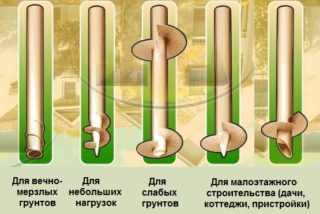
Reinforced concrete piles are placed under buildings with heavy loads, industrial enterprises. They work well in compression and bending, since they have a metal frame inside. Steel elements resist shear, dynamic impact and torsion, therefore they are used under buildings with similar loads. Wooden rods are used in stable soils and absorb pressure from small private buildings.
Determination of the bearing capacity of the foundation
The mass of the house consists of the weight of the elements:
- vertical barriers (walls, partitions);
- interfloor and basement ceilings;
- rafter, truss and roofing systems;
- exterior trim with layers of insulation;
- equipment, communications, technology, people;
- snow and wind pressure;
- foundation.
All components are carefully calculated, then added, the strength factor is applied and the total load on the base is obtained. If extensions are assumed over time, the pressure from them is also taken into account when finding the bearing capacity.
If the obtained value is less than the calculated one, the option is accepted and the construction is carried out according to the plan. Otherwise, the method of broadening the pile base or increasing the number of rod elements is used. Expansion of the support part is better for screw piles, when it is possible to significantly increase the diameter of the blades.
For reinforced concrete elements, use the method of drilling with a drill-expander or make camouflage piles. The method of soil injection maximizes the load-bearing properties when a solution of sand and cement is fed into the space between the pile rods 1.5 - 2.0 meters below the pillar support.
Calculation methods
Shells undergo several tests at the construction site.The number of control studies is chosen by the author of the project, taking into account the field conditions, the structure of the building, the design capacity of the piles according to the recommendations of the construction GOST for the survey of soils. Revision tests are performed at the beginning of the immersion so as not to overuse concrete and metal and to fully utilize the design strength.
Control surveys are carried out by methods:
- static pressure on the pile;
- dynamic action;
- studying the soil when immersing the reference rod;
- the study of the soil with a static probe.
1% of the number of piles on the site is subjected to static testing, the result depends on the complexity of the soil, the format of the loads and the number of types of vertical supports. 2% of the number of rods is subjected to dynamic load, but not less than 6 - 9, depending on the class of the structure.
The bearing characteristics of the pile and soil can be calculated using the formulas in a theoretical, dynamic and trial way.
Theoretical
The qualitative result of calculating the interaction of piles and soil is obtained taking into account the plasticity of the soil layer, the compressibility of the foundation rod. Local areas of ultimate stress and redistribution of tangential loads are determined. The minimum distance between the screw elements is taken in the amount of double blade diameter, and the maximum is selected according to the ability of the grillage and support to resist pressure.
The span between the pillars is considered as a rigidly fixed beam from two ends, the load is determined so that deformations do not occur, and the central deflection is not more than the standards.
Theoretically, the calculation of the bearing capacity of the pile is expressed by the formula W = H / dwhere:
- H - design bearing characteristic of the bar;
- d - coefficient of strength, taking into account the margin of pressure resistance.
The quantity H is determined by multiplying the area of the support or by the calculated resistance of the soil where it is laid in the ground. For common soil layers, such indicators are given in construction tables, provided that the depth is more than 1.5 meters. When immersed, the earth loses its density, the initial characteristics take a long time to recover. The maximum distance between the supports is assumed to be at the level of three meters. If the calculation results in large gaps, add several bars to reduce the span.
Dynamic
The technology of the dynamic method consists in the fact that when the column is deepened, the resistance of the soil layer increases. The relationship between the impact force during immersion and the bearing characteristic of the element is taken into account. Driving reveals weak points of the pile field and shells to calculate the diameter and length of the support pillar.
Dynamic surveys do not require expensive equipment and high costs, they are suitable for testing different standard sizes. The downside is the fact that the changing load sometimes overestimates the strength indicator, and an inaccuracy appears in the calculation. Dynamic testing is carried out by experienced technicians; unstable or loose substrates are not suitable for this method.
The type of piles is selected according to the properties of the layer, which is located under the tip of the rod. Rack piles are mounted if low-compressive rocky soils are used. In other versions, friction piles (pinched in the ground) are placed. The length is chosen taking into account the fact that the rod is embedded in the body of the grillage by 5 - 10 cm with a vertical load.
Trial
The process of trial deepening is accompanied by technical documents, where the size, type and design load on the pile are affixed. For carrying out, a detailed plan of the foundation is required with the given sounding pits, which were investigated by geologists.The passage of communications and electrical cables is indicated.
Test driving is carried out in the case of:
- the presence of weak soils, man-made fill plots;
- the number of piles is more than 2 thousand;
- construction of high-rise buildings over five floors;
- if there are doubts about the correctness of the theoretical part of the calculation.
The immersion is accompanied by technical documents indicating the design loads, the type of shells. The test results are recorded in a log, which describes the damage received, the category of the hammer and the number of blows before the final immersion.
Calculation of the bearing capacity of piles in specific conditions

The bearing properties of driven reinforced concrete rods are calculated as the sum of the soil resistance under the sole and lateral obstruction F = y (Fd + Fr)where:
- Fd = u Σ y Fl Hl;
- u - the outer perimeter of the post;
- y - coefficient of functioning;
- Fl - lateral resistance of the earth;
- Hl - the thickness of the soil layers in the contact area;
- Fr = y R S;
- R - soil resistance under the tip according to the norm;
- S - support area at the bottom.
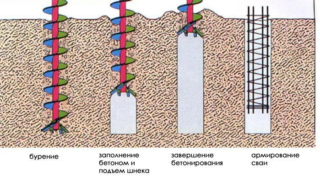
The calculation is also carried out for bored casings. For such piles, the bearing capacity is calculated by the formula F = R S + u ∫ y Fl Hlwhere:
- R - soil resistance under the tip according to the norm;
- S - support area at the bottom;
- u - the outer perimeter of the post;
- y - coefficient of functioning;
- Fl - lateral resistance of the earth;
- Hl - the thickness of the soil layers in the contact area.
The formula for calculating the indicator for a screw pile differs from the previous expressions, since other characteristics are required: F = yc ((a1 c1 + a2 y1 h1) D + u G (h - d))where:
- yc - coefficient of functioning;
- a1 and a2 - tabular coefficients;
- c1 - coefficient of linearity of the soil for sand or specific cohesion for clay;
- y1 - the specific gravity of the earth above the blade;
- h1 - the amount of deepening;
- D is the diameter of the blades minus the diameter of the pile itself;
- u - pile base perimeter;
- G - lateral soil resistance;
- h - the length of the pile;
- d Is the diameter of the support screw.
The bearing capacity after dynamic, static research and probing is checked by calculating the loads and actions of the material resistance. If one of the types of testing does not confirm the calculated indicators, such piles are not allowed to be installed.










