The durability of the building erected on it directly depends on the choice and correct arrangement of the support system. In the private sector, construction is sometimes necessary in the most difficult conditions, where a bored foundation may be the best option in almost all areas. Structures of this type can rightfully be called universal, since they are applicable on almost any soil and relief. An undoubted advantage is that bored columnar foundations can be erected with your own hands without the involvement of special equipment.
Features and structure of the bored foundation
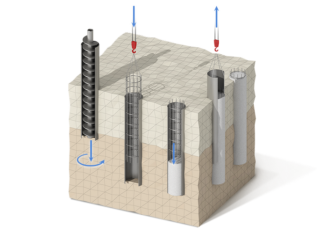
The filler foundation is one of the varieties of pile support systems. The difference lies in the fact that the supports are made directly at the construction site, or rather, in the ground. The technology for arranging such bases is quite simple. First, a well is made, and then concrete is poured into it.
Support device:
- Substrate. It is poured into the bottom of the hole for drainage and compensation of soil vibrations. Sand, crushed stone or gravel is used.
- Formwork. It is made to protect the walls of the borehole from crumbling, as well as to protect concrete from contact with aggressive reagents. Plastic, steel and asbestos-cement pipes, cellophane and roofing material can be used.
- Steel frame. Serves to give the support a slight flexibility and solidity, resistance to bending and twisting. Depending on the diameter, the pipe is made in the form of a triangular prism from 10-16 mm reinforcement. The top of the reinforcement is used for fastening to the general harness.
- Concrete. High strength grades are used, resistant to frost and dampness.
A prerequisite for laying the foundation on bored piles is to lower it to a depth 15-20 cm higher than the level of soil freezing.
Application area

The scope of application of bored support systems is practically unlimited. As a rule, they are installed in places where the arrangement of classic strip and slab monolithic foundations is impossible or economically inexpedient.
Indications for installation may be as follows:
- Cramped conditions. The limited area of the construction site, the lack of the possibility of supplying piles and fragments of foundation pits.
- The presence of underground communications. In most cases, it is technically impossible or too expensive to change the sewerage or water supply line.
- High groundwater table. In such places, heavy slabs should not be laid, as they may squint due to blur.
- Unstable and heterogeneous soils. In such areas, it is unprofitable to make deeply buried foundations due to the high consumption of material.
- Rugged terrain. Installation of self-made piles allows you to avoid time-consuming earthworks. By varying the size of the supports, it is possible to compensate for the height differences in the area.
- Engineering restrictions. Cutting through unrecoverable fragments of previously dismantled structures.
In private construction, do-it-yourself bored piles are installed during the construction of frame and wooden houses, baths, sheds, terraces, summer kitchens. They make such bases for gate and fence supports.
Pros and cons

Structures are very popular in private construction, if the owners do not have professional skills and do not have sufficient funds to attract hired labor and equipment.
Bored technology has the following advantages:
- versatility in terms of density, moisture and acidity of the soil on the site;
- simplicity of making supports, even novice developers can easily handle;
- affordable cost of materials and necessary equipment;
- short terms for the production of a pile field, even for a large building;
- the ability to carry out the work in stages, mixing the solution and installing supports at intervals necessary to rest or restore the weather.
Cons of designs:
- limited strength, which is significantly inferior to screw and reinforced concrete factory counterparts;
- lack of the possibility of arranging a basement;
- the need for high-quality and expensive thermal insulation of the floor;
- arrangement of strapping or grillage is required.
Bored foundations are a reliable and budget option for low-rise construction.
Varieties of foundations on bored piles

The choice of technology for erecting a pile foundation is determined by the weight of the building and the type of soil. In addition, the probability of flooding the site with flood, melt and storm water is taken into account.
There are such types of foundations on bored piles:
- With a grillage. This element is designed to connect the supports into a single system, thanks to which they acquire additional stability. The grillage serves as a support for the beams, on which floorboards and walls are then laid. This design is used when conducting construction on unstable and heaving soils, as well as on areas where there is a risk of flooding. Depending on the degree of heaving, the grillage is understood to be 5-20 cm above the ground. If necessary, the clearance increases, but this entails an increase in the diameter of the supports or a decrease in the step of their installation, which means additional costs.
- Strip foundation. This option is chosen when the construction of massive structures made of bricks or reinforced concrete blocks is carried out. The tape is poured after the installation of the supports and goes deep into the ground to a depth of 30-50 cm. Thanks to this solution, part of the load is removed from the supports, and they themselves perform the functions of anchors, holding the building in the ground when it freezes. When choosing a combined system, it is necessary to have accurate data on the composition of the soil. Its arrangement can only be carried out on stable soils that are not subject to heaving.
The calculation of the number of supports, their installation locations and the interval between fragments is carried out after determining the bearing capacity of the soil and the weight of the building after its improvement. It is recommended to place piles in corners, under walls and in places where there will be an increased load on the base.
Well drilling features

Do-it-yourself drilling under the foundation piles is a rather laborious process. To save energy, it is better to rent a motor-drill, which will greatly simplify and speed up this work.
In addition to the drill, you will need the following tools:
- roulette;
- shovel;
- level;
- compass;
- mixer for mixing the solution;
- ax;
- welding machine;
- Bulgarian;
- deep vibrator;
- paint brush;
- device for tying wire.
General regulatory requirements for the arrangement of bored foundations are set out in SNiP 3.02.01-87 and 2.02.03-85, SP 24.13330.2011.
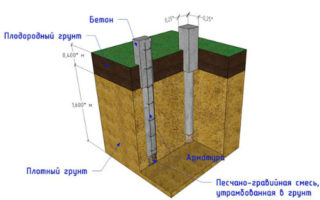
Step-by-step instructions for making a belt-type support system:
- Determine the location of the building, focusing on the cardinal points and buildings.
- Clear vegetation and debris from the construction site.
- Carry out the markings using stakes and a cord, check the correct size and their compliance with the project.
- Dig a trench around the perimeter of the building and along the lines of the interior walls. The depth is calculated taking into account the filling.
- Outline the location of the supports. Drill holes there. It is necessary to accurately maintain the vertical, otherwise the column will not be stable.
- Lower the formwork into the well. Roofing material is best suited, which, after twisting, is pulled together with an elastic band or soft wire.
- Pour 10 cm of sand into the holes, and then 10 cm of crushed stone. Tamp and level the material.
- Make a reinforcing cage. The frame is made of triangular cross-section, attached to the frames with knitting wire. Lower the frame into the formwork, fixing it exactly in the center. If necessary, fix a head for fastening with a grillage on it.
- Make a formwork in a trench, fill it with drainage, put reinforcement and tie it to the frame of the supports.
All that remains is to mix and pour concrete along the edge of the formwork. At rest, the structure must stand for at least 28 days, after which you can continue construction.








