At the stage of building design, external influences are taken into account. One of the dangerous phenomena is frost heaving of the soil. Unevenly expanding soil puts pressure on the base of the house. Deformation of the foundation leads to damage to the walls and roof.
- What is frost heave of soil
- What types of soil are heaving
- Why soil heaving is dangerous for the foundation
- Ways to protect the foundation from frost heaving of the soil
- Drainage and drainage
- Replacement of soil
- Installation of insulated blind area
- Construction and structural methods
- Construction of a pile foundation
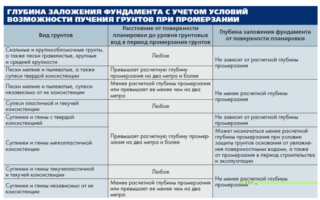
- Correct laying depth
- Construction processing
What is frost heave of soil

Uneven rise and increase in the volume of soils due to freezing of the moisture in them is called frost heaving. The process is typical for moist soil containing fine particles. With the onset of the seasonal cold snap, when the temperature drops below 0 ° C, the water turns into ice. In this case, its mass does not change, but its density decreases. The volume increases according to the law of physics. Experts estimate the possible expansion of the soil - plus 9% to the original value.
The pressure of the frozen water causes the formation to be ejected vertically. Part of the soil bulges out, rising above ground level. During thawing and thawing in spring, reverse processes occur - the water turns into a liquid state, subsidence occurs. Such ground movements are the most dangerous for buildings, they cause deformation of the foundation.
The main factors contributing to ground movement are:
- High humidity - saturation of the soil with water from a close occurrence of groundwater or a large amount of precipitation.
- Temperature and duration of the cold period - the stronger and more prolonged the frost, the greater the volume of the earth is shackled into the total movable mass.
- Type and structure of soil - dispersion or shape and size of mineral particles, fine fractions bind water, they are most prone to swelling.
The swelling process is characterized by unevenness. This is due to the heterogeneity of the soil, different amounts of moisture, the presence of heat-insulating coatings (plants, snowdrifts), and solar activity.
What types of soil are heaving
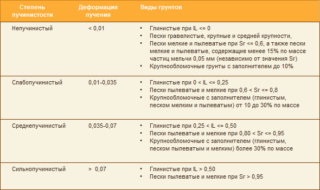
The heaving mechanism is related to the amount of water contained in the soil. This indicator is influenced by the inflow of liquid from the underground layers and the granulometric composition of the soil. In the structure of soil or rock, particles of different diameters or fractions are distinguished. A large number of dusty particles provokes an increase in the degree of heaving of the soil. Such soils are called frost-hazardous or heaving. According to the degree of heaving, they are divided into several categories:
- potentially heaving;
- slightly puffy;
- medium porous;
- strongly bulging;
- excessively heaving.
The following types of soil are prone to heaving in the cold season:
- clay of medium density and plastic;
- loam;
- sandy loam with a content of rock particles from 30%;
- silty sandstone with a high level of groundwater.
Non-rocky soils include:
- rock formations;
- gravelly sands;
- hard clay.
If the site contains coarse and rocky rocks, sand of a coarse and medium fraction, you can arrange any base. Such layers pass water well into the depths, and the remaining moisture has room for expansion when freezing.
Why soil heaving is dangerous for the foundation

When designing buildings, it is necessary to take into account the magnitude and intensity of heaving. These factors are important for regions where the freezing layer reaches considerable depth. To calculate the base of the house and choose the appropriate type of foundation, it is necessary to conduct an engineering-geological survey of the site. For study, a hole is dug and soil is taken. The composition of the soil, its properties, and bearing capacity are evaluated.
The frozen soil is firmly attached to the base of the house. Its effect on the side of the foundation is called the tangential heaving force. An increase in the size of the contact surface and the growth of a frozen layer can lead to the movement of the base along with the soil. Lateral pressure results in horizontal shear.
The vertical force causes the structure to rise. After defrosting, movement resumes in the opposite direction. If the foundation is built without taking these factors into account, for several seasons the walls are covered with cracks, the floors are deformed, the roof is warped. The house is in disrepair.
At risk are light wooden and frame-panel buildings. Their load is inferior to the applied natural heaving forces. The destructive effect is clearly noticeable when constructing monolithic strip foundations and columnar foundations without reinforcement. The tape can crack, break, and the pillars can bend. On heaving soils, experts advise be sure to arrange a reinforcing frame that reinforces the base.
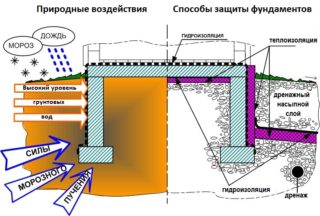
Ways to protect the foundation from frost heaving of the soil
Drainage and drainage
The decrease in humidity occurs with the help of engineering and reclamation measures. At the stage of building the foundation, work is being carried out on the arrangement of storm sewers, drainage, drainage trays. Atmospheric precipitation, melt water and groundwater are removed from the site through a system of ditches or drainage pipes. Trenches are dug with a slope, perforated pipes wrapped in geotextiles are placed in them. Crushed stone serves as a filling.
A waterproof blind area with a slope of 3-5 ° is arranged along the perimeter of the building. Moisture is discharged into the centralized sewage system, the nearest body of water or outside the site. To prevent replenishment of aquifers near the house, it is impossible to dig out reservoirs, sources of moisture should be at least 20 m.
Replacement of soil
The creation of a cushion of non-porous materials and backfilling of pits helps to minimize the negative impact. After excavation of the earth, when digging trenches and pits, a layer of clean sand or a mixture with rubble is poured onto the flat bottom. Sand is taken of medium and coarse fraction, without clay impurities. The size of the pillow is 20-30 cm. The layer is carefully compacted to give strength.
The backfill ensures an even distribution of the load on the base. When constructing a pile foundation, a larger well is drilled, the free space is filled with sand. Over the years of operation, sand or crushed stone is silted up with clay particles. Geotextiles are laid to prevent pollution.
Installation of insulated blind area
Soft blind area technology:
- a trench is dug with a slope from the house;
- a layer of sand 15 cm is poured;
- geotextile is covered, one edge is put on the foundation, the second into the drainage ditch;
- a layer of crushed stone, expanded clay or gravel is poured;
- paving stones give a decorative look, a curbstone is installed to support the structure.
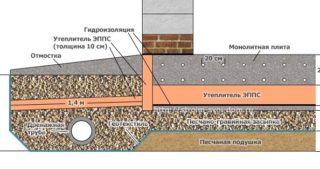
Rigid blind area:
- crushed stone is poured at the bottom of the trench, then a layer of sand to level the base;
- sand is covered with a waterproofing sheet;
- formwork is installed;
- insulation is laid (penoplex or polystyrene);
- reinforcing contour are mounted;
- concrete is poured;
- finishing with tiles or stone is performed.
Plate insulation is the best option when installing a blind area. The material is waterproof, durable, and has high thermal insulation characteristics. The thickness of the slabs is 80-100 mm.
You can temporarily insulate the soil with the help of materials at hand: straw, sawdust, leaves, dry peat, slag or gravel. The thickness of the layer depends on the climatic conditions. Thermal insulation is performed before the onset of cold weather. Another simple temporary measure is soil salting. This will require table salt or potassium chloride. Product consumption 30 kg per cubic meter. m, the depth of salting is 50-100 cm.
Construction and structural methods

Swelling can be dealt with by adapting the foundation structure to difficult conditions. Such measures are justified when it is impossible or very expensive to cope with the heaving effect in other ways.
Construction of a pile foundation
A pile foundation is a common option for frost-hazardous soils. Supporting elements for it are metal, concrete and reinforced concrete. By the method of installation, they are divided into:
- screw;
- hammered;
- stuffed.
The piles are installed to a depth below the freezing point, which eliminates the effect of vertical swelling. The most widespread are screw elements, which differ in their affordable cost and installation speed.
Correct laying depth
Construction processing
The side surface of the columnar base and basement walls is covered with a special compound that reduces soil freezing. It can be bituminous mastic, substances that form a polymer film, roofing material. A smooth surface without roughness is less prone to adhesion to the ground. The procedure allows you to reduce the tangential effect of heaving forces.
Frost swelling negatively affects the structural parts of buildings, causing deformation and damage. To reduce repair costs, it is necessary to take measures in advance to protect the foundation from heaving soil.