The soil swells if the liquid in it freezes. Ice is less dense than water and tends to occupy a larger volume. Expansion leads to shear of soil particles and swelling of the earth layers. Heavily soils contain a large amount of moisture, so the construction of foundations in such layers becomes risky if you do not take measures.
Features of heaving soils

Frost heaving is the deformation of moisture-saturated soils within the volume. Cryogenic swelling of non-rocky soils occurs due to crystallization of drops and decompaction of organic components. Ice inclusions in non-rocky rocks take the form of polycrystals, interlayers, lenses. The silty-clayey layers swell from the rise of moisture from the underlying layers to the freezing area.
Heaving options:
- if moisture is distributed evenly along the vertical of the soil, swelling appears at the level of 3%;
- flow movement or uneven freezing leads to an increase in swelling up to 10-25%.
The structures of the foundations rise from the swelling of the soil, but in spring, during thawing, they cannot settle together with the ground in the opposite direction, the effect of buckling of the supports (pillars, monolithic and prefabricated belts) arises. Long-term swelling mounds appear in peatlands, which are formed in different ways.
During the winter thaw, water flows migrate, which subsequently freeze. This phenomenon repeats itself many times and leads to the appearance of volumetric ice balls. Bumps grow at a rate of up to 10 - 20 cm per year. Loose soils freeze into the body of the dug-in foundation in winter, and raise it in the spring. The cavity under the support is filled with liquid or liquefied soil. The process is repeated for several years and leads to the collapse of the house.
The non-rocky category includes clastic rocks and rocky soils. Fragments are obtained when mining rocks are destroyed, crushed stone, gravel and other materials with large grains in the composition fall into the group. This also includes sands of medium and large fraction.
An increase in structural particles leads to a decrease in the degree of heaving. Foundations in such layers are buried regardless of the freezing mark and the level of standing of the soil liquid.
How to determine the type of soil

Field surveys of the ground include instrumental studies and observation of the behavior of anchored depth markers (benchmarks). Instruments (beam gauges) are used, which contain in the structure a heat-insulating container for soil with a support sample and shear measurement sensors.
The tendency of the soil layer to swell is called the degree of frost heaving. It is found by the formula F = (R - r) / rwhere:
- F - the degree of heaving;
- R - the height of the swollen layer;
- r Is the height of the sample before freezing.
Heaving soils include soils, the indicators of which are more than 0.01, such rocks increase the volume by more than 1 cm at a freezing depth of 1 m.
The assessment consists of examining a test foundation with anchoring elements to counteract heaving. The measuring device has a springy element, the deformations of which indicate the level of swelling. The linear dimensions of the shift are fixed by sensors and detectors.
There are methods for determining the degree of heaving without violating the integrity of the samples under the influence of deformation forces. Informative sensors are not inserted into the ground, the devices do not come into contact with the soil layer.
Such studies include:
- gammascopy;
- ultrasound x-ray;
- laser method.
Such devices record shifts and displacements of mineral particles during deformation at a distance, but reading and working with indicators requires special technical knowledge and skills.
When building a private house, a laboratory study of a sample of the land layer on the site is ordered. The analysis takes some time, but as a result, an official conclusion and a certificate on the composition and properties of the soil at the construction site are issued.
There is a rough estimate, which, according to the granulometric structure, will certainly determine the non-porous soil. Average testing is carried out according to the formulas. An accurate result is obtained from a field survey or laboratory study.
Classification of soils by the type of swelling
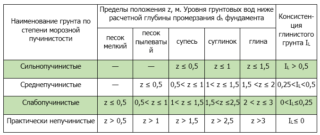
In winter, the swelling is so powerful that it raises the support base together with the building, while in the spring the raised structure does not return to its usual position. The density of ice inclusions is 916 kg / m3, the same indicator of water is 1000 kg / m3. This suggests that the volume of ice is 9% greater than the cubic capacity of water, therefore, an additional load is created on the structure of the earth layer. The soil moves under the action of the pressure force, but cannot move the deep-lying layers, but raises the upper part together with the building.
Classification of heaving soils:
- non-porous;
- slightly puffy;
- medium porous;
- strongly puffy.
The list is based on the size of the flow rates and the moisture content ratio. Weak liquid have a yield point of 0 - 0.25, a water content coefficient - 0.6 - 0.8. The category includes coarse rocks with sandy filler, which should be no more than 30% of the mass.
The medium-porous group includes clays, sandy loam with a fluidity value of 0.25 - 0.5, silty and fine sand - fluidity 0.8 - 0.93, and rock fragments in which there is more than 30% sand filler. Heavily heaving is represented by soils with a clay fluidity of more than 0.5, a heaving degree of more than 0.07 and moisture-saturated sands with a water coefficient of more than 0.95.
Frost swells the most of the clays, which increase the volume up to 15%. Sands, especially of rocky and stony rocks, practically do not swell when freezing. The difference is that the clay holds the water inside the structure, while the sand allows it to pass between the fine particles.
The tendency to bloat depends on the chemical and mineral composition. Kaolinite rocks are less mobile than monorillonite soils. Soils with a high potassium content are a good base for foundations.
Ways to combat soil heaving
Methods for reducing soil moisture that will maintain soil stability and prevent bad effects:
- laying of drainage collectors for the removal of ground moisture;
- vertical planning with a wall slope of at least 5% for water to leave the surface;
- reduction of the level of occurrence of supports by replacing the unstable foundation with solid soil;
- the device of waterproof blind area around the perimeter of the building;
- regular activities to reduce water;
- compaction of the earth for backfilling the foundation cavities;
- elimination of threats of water supply and sewerage breakthrough;
- remoteness of the foundation from wells, a reservoir, washing stations, communications.
Soil dehydration as a result of the installation of a drainage system is important. The site is drained by installing a sand bed and installing perforated pipes.Drainage is arranged along the perimeter, and not far from the pit (0.5 m), a hole is dug with a depth at the level of the foundation. An insulated pipe with a slope is taken out into the ditch and sprinkled with coarse gravel or sand.
The smooth surface of the roofing material under the foundation sole will smooth the vertical uplift and cause a sliding effect. The same effect is exerted by smoothing the soil surface under the heel of the foundation. Unstable soil is replaced with solid soil, for example, coarse gravelly sand. The pit is dug below the freezing mark, the heaving earth is removed, and a new layer is poured and tamped in its place. This is an effective method, but it involves a large volume of land work.
How to secure the foundation of a building

The foundation is laid below the freezing mark - so the pressure from heaving will not act on the base. As for the lateral surface, soil particles will freeze to the support and lift the foundation when swollen. Therefore, deep laying is used only for heavy buildings with reinforced concrete floors and walls made of bricks and concrete.
Soil warming is used as a method of reducing the influence of the soil during the construction of shallow supports for a house made of light materials. Freezing of the ground is excluded, and moisture does not swell the soil. An insulating layer is laid on the ground, the width of the tape corresponds to the freezing height. The thickness of the insulation is taken by calculation depending on the properties of the material and the climate in the region.
The foundation is protected by the introduction of special additives, for example, the soil is salted. This temporary effect is used during the construction of the house. Potassium chloride or technical sodium chloride is used at the rate of 30 kg per cubic meter of earth. It is mixed with backfill soil and injected into the space around the base of the house. It is done at a depth of 0.5 to 1.0 meters.
The soil is impregnated with an oil-based solution. Two layers are made on the border with the lateral surface of the foundation with backfilling of the sinuses. The composition includes bitumen, calcium oxide, anionic active components, water. The amount of the solution is taken at the level of 5 - 10% of the mass of the soil. Polymer modifiers are used for mixing with the ground, which retard icing.









