Foundations and foundations are designed to be stable and durable. The calculation of the foundation is done taking into account the bearing capacity and the deformation of the soil to determine the optimal structure and dimensions. The support under the action of loads is somewhat displaced, which is unacceptable according to the standards for the operation of the building. Because of this, the foundations are calculated by the limit state method, so that a small increase in efforts leads to destruction.
- Influence of soil on the depth of the foundation
- What does the foundation calculation include?
- Calculation of the bearing capacity of the soil
- Calculation for soil deformation
- The main stages of the calculation
- Determination of the weight of house structures
- Determination of the dimensions of the foundation
- Correcting the dimensions of the foundation
- How to determine the type of soil on the site yourself
- An example of calculating a strip foundation
Influence of soil on the depth of the foundation
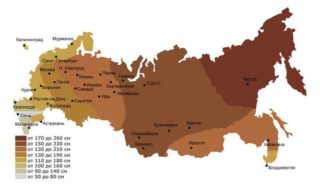
The depth into the ground depends on the type of structure and its structure. For the calculation, the loads acting on the base are collected. Geological conditions, the degree of soil heaving, sedimentation and freezing are important indicators for calculating the foundation. The depth of laying is taken not less than 0.5 m (excluding rocks).
In each case, the deepening is calculated according to individual rules so as to take the minimum value to reduce the volume of excavation, to reduce the work on restructuring the soil below the base of the excavation. Water disposal from the site is simplified when choosing the optimal degree of deepening the base into the ground.
Laying depth rules:
- the sole sinks into the thickness of the bearing layer by 10 - 15 cm;
- the presence of a small thickness under the base of the base is not allowed if its technical characteristics are inferior to the properties of the underlay;
- the bookmark is made above the level of the ground fluid rise to exclude dewatering work during construction.
The size of the deepening of the foundations is assigned without taking into account the degree of freezing under the inner walls in buildings with heating, if the soils are protected from moisture from the beginning of construction until commissioning.
What does the foundation calculation include?
The designer collects the loads from the ground structure and selects the base structure. The underground part of the building works in conjunction with the soil, so the characteristics of the soil are also taken into account, for example, its ability to withstand extreme forces.
The foundation calculation consists of the following parts:
- calculation of resistance to loads (bearing capacity);
- calculation for soil deformation.
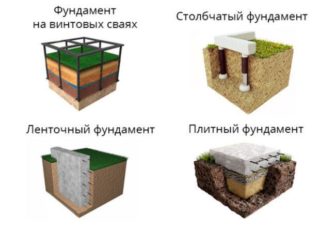
Design takes place in a separate phase or as part of a turnkey project. The following foundation designs are used:
- tape (monolithic or precast reinforced concrete);
- columnar with or without beams;
- pile;
- from slabs;
- other types.
Before the start of the calculation, the designer must have construction conditions for the construction, geodetic and engineering characteristics of the object site, climatic indicators in the area. The specialist works with architectural drawings and detailed sections of units, uses information about the technological and design features of the structure.
The designer gives a list of loads perceived by the foundation, and in writing offers options when choosing its type. The project includes general and detailed drawings with a description of the base, depth marks, and overall dimensions. The specification of materials, the calculation of concrete for the foundation, requirements for reinforcement and the design of the support are given.
Calculation of the bearing capacity of the soil
Formula S H> Pwhere:
- S - sole area, m²;
- H - bearing capacity, kg / m²;
- P - mass of the structure with all loads, kg.
The calculation of the foundation for the house is carried out according to the following method:
- the indicator of soil resistance to loads is determined;
- the total weight of the structure is calculated;
- the amount of pressure on the soil is found;
- the load and bearing capacity of the earth are compared, corrections are made to the dimensional parameters.
The snow mass on the roof can be calculated by the specific gravity of the cover. For example, in the middle lane, the figure is 100 kg / m². If there is a non-standard object in the building, for example, a swimming pool, its weight is added to the total mass.
The weight of people for a country house, apartment in the city and a cottage is calculated by the formulaRl. = 400 kg / m² · Sp., where:
- Rl. - weight of people, kg;
- SP. - the area of the house, m².
As a result, the right balance of indicators is chosen to ensure the stability and strength of the house. The calculation excludes the shift of the sole and the overturning of the structure.
The design takes into account the direction of the loads, such as inclined, vertical or horizontal. For this, the coefficients are used that are in the reference books of the designer and designer.
Calculation for soil deformation
Some meanings:
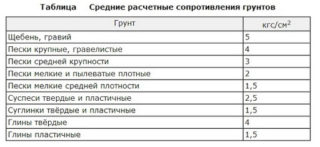
- gravel with sandy or clay-silty aggregate - 4 - 5 kg / cm²;
- crushed stone with a similar filler - 4.5 - 6 kg / cm²;
- coarse and medium sands of medium and high density - 2.5 - 4.5 kg / cm²;
- dusty and fine sands with low moisture and damp - 1.5 - 2 kg / cm².
- sandy loam (porosity 0.3 - 0.7) - 2 - 4 kg / cm²;
- loam - 1 - 4 kg / cm²;
- clay - 1 - 9 kg / cm².
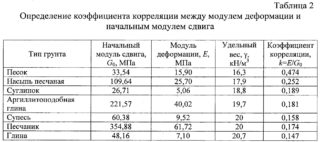
If the foundation deepens less than 1.5 m, the density below the lower boundary will differ. The formula is used for the calculation R = 0.005 Ro (100 + h / 3)where:
- Ro - value from the table for a depth of 1.5 m;
- H - estimated depth.
Deformations of building supports are sedimentary and subsidence. The first type includes the concepts: full, average or additional subsidence under load, which is determined by the number of changed sections. Additional deformations are caused by wetting with rain and melted snow, with an incorrectly executed blind area around the house. The foundations settle due to the dynamic action of the equipment, sewage leaks, water supply.
Subsidence - failing deformations, in which the soil will change radically. To prevent them, loess-like and loose sandy soils are compacted, frozen soils are thawed.
The main stages of the calculation
When designing, it is assumed that the load from the weight of the structure is distributed evenly over the support area. In moist loamy and clayey soils, the liquid freezes quickly, the soil swells. This feature of these types negatively affects the bearing capacity.
A high elevation of soil waters acts similarly if the freezing depth is much lower. The unevenness of this process leads to a distortion of the foundation and the appearance of cracks, as a result, the house requires repair in 2 - 3 years.
The calculation of the strip foundation involves the following stages:
- finding the mass of a building by collecting useful and harmful loads on the structural elements of the house;
- choice of support sizes;
- adjustment of dimensions after the final calculation and verification of parameters.
Design errors lie in the fact that the depth of the abutting foundation is made deeper than the sole of the existing structure support.The strength of the foundation suffers if it is made at a shallow depth (50 cm) from the level of aerated concrete floor, which is often found in a garage or similar structures. It should not be allowed that efforts are redistributed to the base of the house, which are greater than the bearing characteristic of the supporting part.
Determination of the weight of house structures
To begin with, the type of soil and the height of the standing soil water for the construction region are determined. The materials that are used for the construction of the building frame, roof, exterior and interior decoration are taken into account. The layout of the building, its number of storeys and the type of roof is taken from architectural and construction drawings.
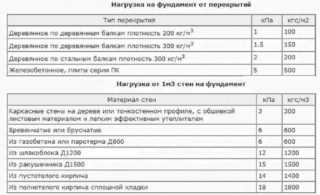
The approximate mass of the house is made up of permanent and temporary loads. The constant includes the own weight of walls, roofs, ceilings. The pressure of the earth and soil water on the side walls of the base is taken into account.
The live load is:
- long-term;
- short-term;
- special kind.
Long-term pressure refers to the force transmitted from the equipment, the effect of the weight of materials stored in the warehouse, furniture. A short-term force occurs when people are found, the load includes the weight of lifting mechanisms in production halls, the effect of snow and wind on the roof.
A special type includes emergencies, seismic effects, changes in efforts during soil subsidence from mine workings. It is possible to correctly calculate the strip foundation only after collecting loads in the most unfavorable combinations, which show the most dangerous positions.
Determination of the dimensions of the foundation
The size of the foundation is taken as standard (500 mm) for two-story or one-story summer cottages, because the load from the building is small and the soil does not settle over time. Experts recommend columnar supports without significantly increasing the horizontal dimensions. If it is required to increase the bearing capacity, the lower part of the support expands and the post takes the form of an inverted glass.
In other cases, the dimensions of the base depend on the thickness of the walls of the house and the depth of freezing of the soil in winter. For a heavy building of brick walls (500 mm) and reinforced concrete floors, a strip monolithic foundation with reinforcement is made or prefabricated blocks are used. In a building with a basement, a tape type is also made, but the base is deepened below the underground. The thickness of the tape is made similar to the size of the wall.
Correcting the dimensions of the foundation
Correction and sizing is done to select the most profitable option in order to correctly calculate the concrete for the foundation according to the selected base dimensions. If the obtained bearing capacity exceeds the design load from the structure by 15 - 20%, in order to save the dimensions of the support, you can reduce it.
The corrected dimensions in width and length are checked by a new calculation. The fact is taken into account that when collecting loads, one should take the changed cubic capacity of the foundation and its reduced weight.
The final calculation is carried out according to the formula H> kP / (dR)where:
- H - bearing capacity, depends on the size of the base;
- to - the coefficient for calculating the reliability is constantly equal to 1.2;
- R - the load of the house, calculated as the collection of efforts;
- d - tabular coefficient, depends on the type of soil and type of structure;
- R - soil resistance, taken from the table.
The sole area of the base strip is considered to be the multiplication of the strip width by the total length of the structure. When correcting the length of the support tape, it will not be possible to reduce, therefore, they work with a size in width. Correction of a columnar type means selection of the number of glasses and changing their dimensions.
How to determine the type of soil on the site yourself
Visual determination method:
- Clay soil, when rubbed in a dry state, gives a feeling of powder, clods are difficult to crush. Moistened clay remains soft and plastic, smears on fingers, rolls into a sausage. The flat cake when squeezed is obtained without edge cracks.
- Loams in dry form give the feeling of sandy grains, lumps easily crumble upon impact. The wet mass rolls into the sausage, but when bent, it cracks, and the cake is obtained with cracks at the edges.
- Sandy loam soil in a dry state resembles flour or dust. The wet mass forms lumps of low strength, which crumble. The wet mass lacks plasticity, it does not roll into a ring, does not flatten into a cake.
Sand is a loose mass with no connection between fine particles. In a dry state, it wakes up between the fingers, and in a wet state, there is no plasticity, stickiness and cohesion.
An example of calculating a strip foundation
For the calculation, a section with a length of 1 m is selected. The forces acting on this piece are determined by dividing the total load from the building by the required area. As a result of the calculation, the width of the base will be obtained, the ratio of the specific pressure on the soil under the section of the tape and the resistance of the earth will be checked.
Example: The load of a building is calculated by collecting efforts. The indicator of the design resistance is contained in the DBN B.1.2 table. - 10 - 2009. The total mass of the structure is 238 t divided by the base area of the belt section of 21.4 m2 and the pressure under the sole is 11.12 t / m2. It can be seen from the table that a similar calculated soil index is 20.0 t / m2, which means that the foundation with the selected dimensions will work reliably and will not settle under load, while the required margin of safety is set.