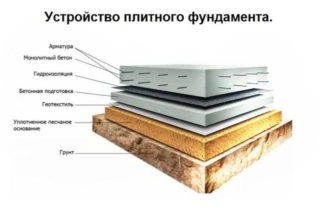
A reinforced concrete slab, buried in the soil or mounted on its surface, distributes the load generated by the building over a large area. Thanks to this, buildings do not deform, even on moving soils. In order for the foundation to be reliable and at the same time not to waste extra resources, it is important to correctly calculate the foundation slab.
- Benefits of a foundation slab
- Design advantages
- Structural features
- Calculation of the thickness of the foundation slab
- Sequence of operations for calculating the load on the base
- Sizing a concrete slab
- Calculation based on the determination of the bearing soil capacity
- Determination of the required volume of concrete solution
- Calculation of the required amount of reinforcement
Benefits of a foundation slab

When erecting low-rise buildings, the slab option has advantages over tape and pile structures. When implementing the work, you will have to spend money on concrete and reinforcement, but you can save on a number of other cost items. For example, since the slab surface serves as a subfloor for the lower floor, there is no need to install a floor. The preparation of shields for formwork here takes significantly less boards than when arranging a strip foundation.
Such a foundation is well suited for arranging a water heated floor - in this case, the system is laid inside the slab (instead of preparing a special screed for it).
From technical units for installation work, a concrete mixer will be required. You will not have to spend money on excavators and lifting machines during construction.
Design advantages

In addition to being economical, a big plus of this type of base is the significant surface area of the slab. Due to this, the pressure on each square centimeter of soil decreases, which prevents deformation processes and uneven settlement. Other advantages include:
- Possibility of installation on different types of soils, including those with increased mobility or high water rise. If you have to build a house on "uncomfortable" soils, slabs are an excellent option. However, it is difficult to make a reliable foundation of this type on a slope; it is better to choose piles here.
- Excellent insulation properties. If the foundation is made in accordance with the technology, good protection against heat loss is achieved. It also does not allow moisture to pass through.
- Durability: A solid slab can last for over a century without signs of deterioration.
- Rigid construction due to the reinforced frame, large dimensions and structure that does not provide for seam elements. This makes it suitable for buildings made of bricks, aerated concrete and other materials that react negatively even to minimal movements.
If the soil is very heaving, a solid slab with little or no deepening is well suited as a base. A pillow should be organized under it. The material is selected so that it levels the heaving of the soil.
Structural features
Such a foundation is not subject to local bends and is able to move with the soil without disturbing the structure.Due to this, it well neutralizes the disproportionate effects of the weight of the building, which can render the supporting structures unusable. When using an insulated plate, the unevenness of freezing under the house is also eliminated.
The foundation can be solid or composite. In the first case, when a monolithic slab is poured directly on the site, the base is more reliable, besides, the work is easier to perform. The second option assumes that the foundation consists of several elements of industrial production, combined at the construction site. Implementation will require the ordering of special machines to deliver and properly place the fragments, and the preparation of a tightening solution. This method is realized faster due to the absence of the need for formwork, reinforcement and long-term holding of the poured concrete for its drying.
Before starting construction work, it is necessary to investigate the composition of the soil and the surface relief. If there are pronounced slopes and other differences in height, it is better to prefer a pile foundation. Ideally, for mounting the slab, the surface should be as flat as possible.
If the soil is sufficiently "problem-free" (there is no need for a volumetric cushion and insulation structures), only a layer of a fertile surface is removed. Otherwise, the soil is removed in the required volume and a pad replacing it is organized. The material is usually crushed stone mixed with sand. Such a composition copes well with drainage, is not prone to heaving, and slightly compresses. Every 10 cm of the powder must be tamped using a vibrating plate.
The sandy pillow needs to be watered with water. The fraction used should not be too fine, otherwise unexpected shrinkage of the building is possible due to insufficient resistance to shrinkage. Usually a layer of sand is poured at 0.2-0.3 m.
Calculation of the thickness of the foundation slab
When calculating a concrete slab, the main challenge is the detailed modeling of bending loads and the most likely directions of roll. Based on such data, one can most accurately estimate the dimensions of the structure and say whether it needs to be reinforced. The highest quality calculations are obtained when using software systems sharpened for these tasks. To get them, you need to order the calculation of the slab foundation in a specialized company.
In practice, in private construction, this can be neglected, focusing on approximate values. The greatest danger is the situation with insufficient slab thickness: in this case, the bending moment is so high that the foundation may crack. Excessive size leads to resource overuse.
It often turns out that for a particular building, different values of the dimensions of the foundation are possible, if the reinforcement parameters are flexibly varied. For example, for a one-story house with a thickness of 0.2 m, additional strengthening of the areas bearing the greatest load is required, and at 0.3 m, a lot of concrete is consumed. In this case, in the second case, it will not work to save on reinforcing rods, but the slab can be made a little thinner without compromising the reliability of the structure. With an indicator of 0.25 m and a uniform density of the arrangement of the rods, the operational qualities will not suffer, and there will be no overexpenditure of resources.
Sequence of operations for calculating the load on the base
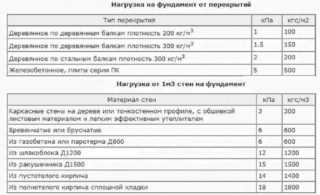
For the construction of a slab foundation, a calculation of thickness and reinforcement is required. This takes into account the building load and the local soil characteristics.
Sizing a concrete slab
The thickness of the slab is determined by the mass of the building, because the load on the base depends on it. In the general case, the optimal indicator for a country one-story house is 0.25-0.3 m.For a garage, bathhouse and similar light buildings, 0.15-0.2 m will be enough.If the house has two floors, a thicker foundation is needed, but the indicator should not exceed 0.5 m, otherwise the slab mobility is lost.
Bending load is also taken into account. It takes its maximum value in the central part of the building. If the building has a long length and few load-bearing walls, the base will bend. To prevent the occurrence of cracks, you need to make the foundation thicker. This applies to all cases of strong spacing of load-bearing walls.
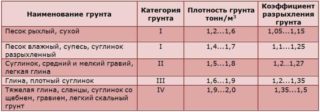
Calculation based on the determination of the bearing soil capacity
After finding out the thickness, the calculation of the foundation slab for the house is made, taking into account the bearing capacity of the soil. This is done to assess the condition of the soil and determine if it can support the total weight of floor walls and other structures. The increased pressure on the ground causes a strong settlement of the base with a shift of the underlying layers, which can cause the destruction of the building. That is why it is important to correctly calculate the key parameters.
The following expression is used to assess the reliability of the base area:
S> F * K1 / R * K2where:
- S - considered area (in square centimeters);
- F - weight of operational loads and floor components (in kg);
- R - design soil resistance (kg / cm²);
- K1 - coefficient of reliability;
- K2 - coefficient describing the construction conditions.
If the expression turns out to be correct, the operation of the building with such loads will be safe. When it is not fulfilled, you need to increase the area of the slab.
For the reliability indicator, a value of 1.2 is usually taken (when working on loam and fine sandy soils). If not a house is being built, but a light utility building, and there is a lot of soil in the soil, the figure can be increased to 1.4. When work is carried out on plastic clay soil, the parameter is equal to one.
The indicator describing the conditions characterizes the composition of the soil. Its meaning can be found in the table. The largest numbers are for clayey soils saturated with water, the smallest for silty sands.
Determination of the required volume of concrete solution

When calculating a monolithic foundation slab, you need to calculate how much concrete is needed for pouring. The volume of the base (in cm³) is determined by simply multiplying the values of thickness, length and width (all indicators are taken in centimeters). When the foundation is not a parallelepiped, but a complex configuration, it is mentally dissected into simple elements. Having calculated the volume of each of them, the values are added. When using stiffeners, separate calculations are carried out for them and the result is summed up with the general one.
Calculation of the required amount of reinforcement
When calculating reinforcement for a slab, the design dimensions of the building and the density of the frame are taken into account. Usually the grid spacing is about 0.2 m. Based on these figures, the amount of reinforcement and its mass are calculated. As a rule, the metal frame is 0.05-0.1 of the total weight of the foundation.
The design of the slab base ensures uniformity of the load and its reduction per unit area. When designing a foundation, it is important to make the right calculations.