The walls are made of various thicknesses depending on the purpose, the structural elements are arranged in a certain order. The correct calculation of bricks for masonry is needed to find out the volume of material for individual parts of the building, for example, a basement, vertical fences, partitions. A full count is done to determine the total volume per house and the purchase price.
Types and properties of bricks

Cellular or hollow ceramic bricks are characterized by low heat conductivity, allows to reduce the width of the masonry, and reduces the weight of the structure by 25 - 30% compared to solid ones. Used for pillars, walls, arches, smoke channels. Solid stone resists moisture, shows high indicators of frost resistance, strength, is used for foundations, walls, columns, furnaces.
Silicate options are available in full-bodied and hollow. The material conducts heat, is durable and dense. They are not used for laying the basement and foundations due to hygroscopicity; they are used for the construction of external walls and internal partitions.
Bricklaying methods
The thickness of the wall is taken as a multiple of the size of the stones. The elements are laid on preparation from the solution, the seams are filled completely for the front masonry or they are made in a wasteland for tiling.
Brick parts:
- a horizontal wide plane is called pastel;
- the lateral long side is called a spoon;
- the end short part is called a butt.
The stones are laid by hand, scaffolding and scaffolding are erected for work at height. The brick resists compression well, but reacts poorly to bending, therefore, the laying is carried out with bandaging of horizontal and vertical seams. Distinguish between single-row, three-row and multi-row overlapping systems.
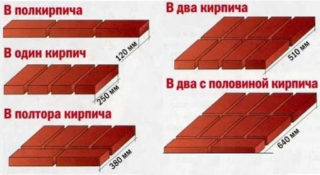
Half

The thickness in the calculation of a brick wall 1/2 masonry is half the length of the element, this masonry option is popular due to the simplicity of execution. Work in half-brick is carried out when installing partitions and outbuildings, where there is no heavy load from the floor and roof.
Used in cases of construction:
- gazebos, separate garages, terraces and verandas;
- fences, flower beds, parapets;
- stove heating elements (ceramics).
They are reinforced with a mesh for stability after 4 rows, starting from the third row, the thickness of the seam is obtained from 14 mm. If necessary, the nets are connected along their length with an overlap of the edges by welding or wire.
Single

Single-brick laying is used in the construction of outbuildings and load-bearing walls with wooden beams. The width of the fence is 250 mm (the length of the stone per spoon). The complexity of the work increases in comparison with half-laying, because dressing of sutures is carried out in two directions.
The main part of the elements for single laying is placed along the wall, turning the spoons to the outside. Dagger rows are placed after the third or eighth row, they also start and finish the work. Vertical seams should not overlap in subsequent rows.
One and a half

The one and a half brick option is common when building walls up to two stories high. Structures withstand the load of concrete slabs and roof trusses. The width of the wall is 380 mm (250 mm - brick, 120 mm - ½ stone, 10 mm - joint thickness).
Three-quarters, halves and quarters of small-sized elements participate in the masonry. Attention is paid to the dressing of the seams and the arrangement of the corners of the structure, on which the reliability and durability of the operation of the house depends. Not only horizontal sections are reinforced, but the joints of partitions and corner joints, therefore, the calculation of a brick for a basement or wall takes into account the widening of the seam due to metal inserts.
Double

The width of the double-brick wall is 510 mm (500 mm - 2 blocks, 10 mm - intermediate joint). Standard masonry can withstand high compressive and tensile forces and is used most often in the construction of multi-storey buildings.
A complex system of bandaging horizontal and vertical sutures is used. There are methods of lightweight masonry, when closed wells are left inside. They are backfilled with concrete, mortar, brick fighting, or leave air gaps.
Two and a half bricks

Such walls are installed in buildings with increased stress or in cold regions. Many incomplete parts of the stone are used, which the bricklayer prepares at the place of work by the method of chopping off. Small-sized brick blocks that were damaged during transportation or unloading are used.
The felled elements are placed inside the wall, and only factory-made spoons and pokes look out from the outside. Oversized stones must be selected correctly, otherwise the system will be disrupted.
For bricklayers, drawings have been developed indicating the ordinal installation of wall elements, corners. A multi-row stacking system is used, and the columns are laid out in a three-row pattern.
Important parameters for calculating bricks for masonry
Building elements differ in size in height, and the length and width are always the same, therefore, the calculation differs for walls made of different types of bricks in that they take into account their different number in the same cubic capacity.
Wall thickness
The thickness of the fence is calculated by the designers taking into account various loads. Horizontal forces are transmitted from expansion by trusses and by the action of the wind. Vertical pressure consists of the weight of the wall, beams, floor slabs.
The width of the vertical fence is always a multiple of the length and width of the small-sized element, so it is quite easy to calculate the number of stones. Vertical gaps are not reinforced with reinforcement, therefore their width is taken at the level of 8 - 10 mm. If the wall consists of separate partitions with insulation between them, then each vertical fence is calculated separately, and the results are summed up.
Wall area
The square of the fences is considered in fact, i.e. subtract from the result the area of doors, windows and other openings.
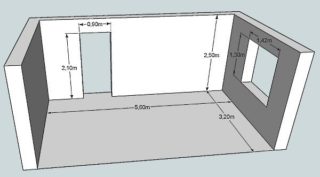
An example of calculating brickwork 3 x 5 m, 2.5 m high, there is a 1.5 x 1.5 m window and a 0.8 x 2.1 m door:
- find the perimeter of the room - (3 + 5) 2 = 16 p / m;
- determine the square of the walls - 16 · 2.5 = 40 m²;
- calculate the area of the openings - 1.5 · 1.5 + 0.8 · 2.1 = 4.02 m2;
- the final square of the fence is 40 - 4.02 = 35.98 m².
The resulting value is multiplied by the width of the wall to get the volume of the intended masonry.
Brick size
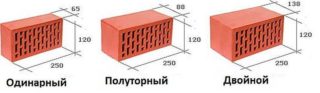
Wall stone dimensions in millimeters:
- single size - 250 x 120 x 65
- one and a half brick - 250 x 120 x 88;
- double - 250 - 120 x 138.
Facade clinker is available in sizes 250 x 65 x 60 mm (half, 0.5 NF), 250 x 120 x 65 (single, 1NF), 250 x 65 x 85 (European 0.7 NF). Cladding blocks are solid or with through voids.
Calculation of bricks for masonry
The calculation of the brickwork is carried out taking into account the thickness of the mortar or without it.In the second case, material overruns are obtained in an amount of up to 30%. The first option is preferable, but the final total is multiplied by a factor of 1.1 to take into account the battle in the process of transportation and rigging.
Find the number of bricks in the square of the wall:
- calculate the squaring of the butt side - 0.12 · 0.065 = 0.0078 m2;
- calculate the number of elements in 1 square - 1 / 0.0078 = 128 pcs.;
- for a wall of 2 bricks, the quantity is multiplied - 128 2 = 256 pcs.
The number of elements in one square is multiplied by the area of the vertical fences and the volume of material for the construction of the structure is obtained.
Walls
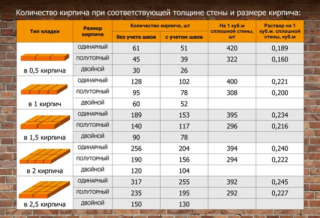
Single brick consumption for walls:
- 1 m³ of fences - 394 pcs. taking into account mortar gaps, 512 - without them;
- 1 m² of masonry in 1/2 stone - 51 and 61 pieces, respectively;
- 1 m² of walls in 1 room - 103 and 128 pieces;
- 1 m² of 1.5-level fencing - 154 and 189 pcs.;
- 1 m² of brickwork in 2 rooms - 205 and 257 pieces;
- 1 m² in 2.5 rooms - 255 and 318 pcs.
Similar ready-made calculations of the number of elements depending on the size and width of the wall are in construction reference books. They can be used if the wall is a straight enclosing structure without many turns.
On the base
For a floor buried in the ground, ceramic brick elements are used to avoid moisture absorption. They should be solid to prevent water from entering through the voids. You can calculate the number of bricks per plinth according to standard rules, while taking into account the thickness of the wall and the size of the ceramic block.
The thickness of the vertical structure of the base can be 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 bricks, the height is taken from the project. The brick has dimensions of 250 x 120 x 65 mm. In the basement, vents of 150 x 150 mm are arranged, their size is neglected and the area of the ventilation openings is not subtracted from the total square of the wall.
Final settlement
The house has a variety of brick structures, including partitions of varying thickness, load-bearing outer walls, basement, and sometimes brick foundations and retaining walls. The number of bricks is counted for each part of the building, taking into account the characteristics of the structure.
After that, the volume of material for each structural element is added. As a result, a picture of the need for brick for the construction of the building is obtained.