The weight of the building, furniture, units acts on the base, the support of the structure perceives the pressure of wind and snow. Under these conditions, the correct calculation of the load on the foundation is essential to ensure strength. The area of the base is calculated, which transfers forces to the soil, taking into account the properties of the soil and its bearing capacity. The calculation determines the depth of the laying, the configuration of the reinforcing cage in concrete and the diameter of the rods.
Required parameters for calculating the load on the foundation

The purpose of the calculation is to select the dimensions of the base and its spatial position in the soil to limit shifts, displacements of the foundation and ground structures. The choice of the foot area and the depth of the filling affects the operating conditions of the structure without subsidence, rolls, changes in the design marks of structural elements.
Before calculating the load on the foundation, you need to take into account the parameters:
- the structure of the building and its purpose;
- the height in the ground of the foundations of adjacent buildings, the depth of laying pipes of passing communications;
- relief of the construction area;
- geological conditions of the site, taking into account possible dynamics: soil properties, presence of weathering caverns and karst cavities, location and thickness of layers;
- the possible impact of the construction and operation of a building on changes in soil characteristics;
- the likelihood of soil erosion near the piles of structures erected in the aquatic environment;
- the depth of soil freezing and the mark of the standing of ground moisture.
The strength of the foundation and its resistance to cracking are checked by calculation, which is performed on the basis of the collection of loads from the aboveground part. The height of the base and the degree of immersion in the ground are selected by comparing the technical and economic indicators with other options.
Calculation of the load on the foundation
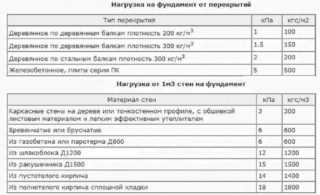
The slab section contains the summed mass of panels, beams, finishing materials. The load is added from home furniture, people, equipment, temporary and permanent partitions. The weight of the house includes a lot of plumbing devices, as well as communication pipes.
The weight of the floor of the first level of the structure is taken into account when collecting efforts, transition coefficients are applied, for which the principle of its structure is taken into account:
- on the ground;
- with support on walls or foundations.
In the section of vertical elements, the mass of load-bearing walls, columns, bay windows, balconies and other frame structures of the building is taken into account. To calculate the weight of the walls, you need to determine their volume and multiply by the volumetric weight of the material of manufacture.
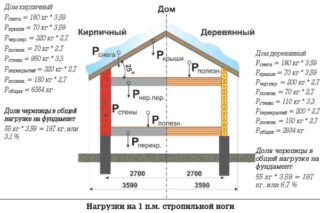
The total forces are transferred to the base and depend on the load area. For walls, the indicator is calculated according to the area of one running meter of the wall, then multiplied by the load in kg / m² - the mass is obtained, which is transferred to the foundation.
Strip foundation
The total load is determined by the final summation of the efforts, while the sides on which the roof rests are experiencing the greatest pressure. According to the tables of SNiP 202.01-1983, the conditional permissible soil resistance (kg / m²) is taken and compared with the obtained actual value of the mass per unit area (kg / m²), while the first indicator should be greater than the second.
The area of the sole is found by the formula S> a F / (b R)where:
- S is the calculated indicator of the footing area of the strip foundation, cm²;
- a - the safety factor is equal to 1.2;
- F - load on the base from the building;
- b - the coefficient of service conditions, depends simultaneously on the type of land and the type of building (in the tables);
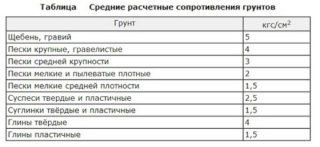
- R - calculated soil resistance, kg / cm².
The last indicator is used unchanged if the foundation is buried 1.5 - 2.0 meters. For a shallower dive, the table value is converted by the formula Rm = 0.005 R (100 = h / 3), where h is the depth of placement, and R taken from the table.
If the load does not correspond to the type of soil, the project is adjusted by replacing heavy materials with light ones. Otherwise, the width of the sole of the base is increased. Changing the material of the covering or walls entails the transformation of a number of parameters and coefficients. They often resort to the second method, taking into account the labor costs for the production of the zero cycle.
Column foundation

The load from such a base is considered one support and multiplied by the number of pillars. The support volume is found as a result of the product of the sole area by the length of the vertical element. The result is multiplied by the volumetric weight of the material (more often, concrete). Add the mass of the metal frame to the base.
The total load (calculation of the mass of the house) is compared with the table value of the soil resistance. If the foundation does not meet the requirements, more posts are made or the cross-sectional area of the support is increased.
The formula is used S = 1.3 P / R to calculate the total area of the soles of the pillars, where:
- 1.3 - safety factor;
- P - weight of the structure with the base, kg;
- R - calculated soil resistance, obtained from the SNiP tables, kg / cm².
At the surface of the earth, the bearing capacity of the soil decreases, and the tabular value shows the value at a depth of 1.5 - 2.0 m, therefore, an adjustment is made. The number of pillars and their cross section are determined after the final calculation of the total area for all pillars. Heavy buildings put an unbearable load on weak and unstable soils, therefore, the cross-section of the foot of the support increases significantly.
For an extension, the number of pillars is considered separately, so the foot area and the number of elements differ from the main structure.
Pile foundation
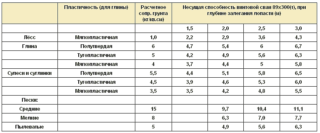
The pile volume is found by multiplying the base area by the length of the element. The section of a rectangular bar is calculated by multiplying the width and length, and for a round pile is found by the formula S = r 3.14 (r - circle diameter). The cubic capacity of one support is multiplied by the number of elements and the total volume of the pile foundation is obtained. The weight is found as the product of the cubic capacity and the volumetric weight of the pile material.
The rods can be connected by a grillage or hold a monolithic slab. The weight of these elements is calculated in the same way and added to the weight of the piles. The load per 1 cm² of soil is determined by dividing the mass of the building (with foundations) by the supporting cross-sectional area of the base. The resulting value is compared with the normative table index.
The formula is used D = S Rwhere:
- S - the total area of the pile soles;
- R - design earth resistance at the level of the vertical bar.
Determine the ability of the rod to resist forces and to what extent it can be loaded. The parameter depends on the type of pile and soil category. The standard size of the elements is kept strictly, and it is much more difficult to assess the characteristics of the soil, sometimes a technical specialist is invited for this.
The calculation of the load of the screw pile for the foundation is expressed by the formula W = D / kwhere:
- W - the value of the operational force that the vertical element can withstand;
- D - the calculated indicator of the element's ability, taken from the table;
- k - strength factor.
The section and length of the pile is selected taking into account the stability of the soil. In some regions, the solid foundation lies deeper than three meters, and the base of the rod may not reach it. In this case, hanging piles are used after geological exploration of the land.
Soil analysis
The main types of soils:
- rocky;
- frozen with splashes of ice;
- dispersed;
- technogenic with fill and alluvial areas.
You can independently determine the category of soil by digging wells at the corners of the future house. It must be remembered that overconsumption of materials causes unnecessary waste, but a weak base causes the destruction of the structure.
A handful of soil is moistened with water and rolled into a rope, the diameter of which is about 1 cm. The resulting sample is rolled into a ring.
Results:
- the tourniquet disintegrates - sand;
- rolls down, but rather fragile - sandy loam;
- the cord is obtained, but does not fold into a ring - light loam;
- bends into a circle, but there are cracks on the surface - heavy loam, close to clay;
- the sticky tourniquet does not crack when bent - clay.
The ground liquid level is determined by the water marks on the walls of the basement at the neighbors. The freezing depth is taken from the reference for the construction area.
Determination of the bearing capacity of the soil
The type of soil can be determined by yourself, but its bearing capacity is regulated in the reference tables of regulatory documents. The land under the house can consist of several layers, therefore, they accept the category that prevails over the rest of the layers.
Humidity is determined by eye. If water does not arrive in a dug well or hole and does not accumulate there, the soil is classified as dry. The appearance of moisture at the bottom indicates that the ground liquid level is approaching, and the earth is considered moisture-saturated.
The density of the soil varies with depth, because the soil presses on the underlying layers and compresses them. The ground at a depth of 1 m is considered to be dense when examining the bearing capacity. If there are no geological exploration data and tabular indicators, the ability to withstand loads at the level of 2 kg / cm² is assumed.