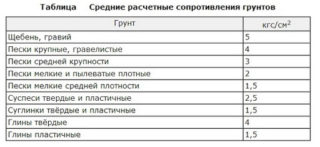
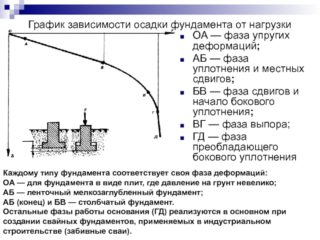
Deformations of the structure occur due to lowering, tilting or bending of the base. For warning, a calculation of the foundation settlement is made, at which the amount of subsidence, the curvature of the slope, the outlines of the area of subsidence are calculated. Based on the results of geodetic studies, graphs of deformation development, profiles of changes along the axes and levels of the building are drawn. To collect loads, diagrams are drawn, which are used in the calculation.
- The main causes of foundation settlement
- The influence of soils on the condition of the supports for the house
- Methods for determining the settlement of the foundation
- Layer-by-layer summation
- Equivalent layer
- Calculation for layered soil bedding
- According to Egorov's method
- Concrete placement recommendations
- Calculation of the foundation roll
The main causes of foundation settlement
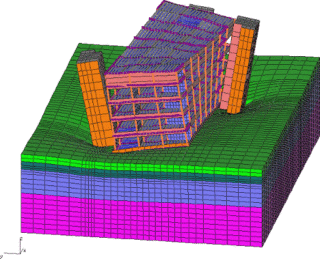
The soil under the sole is deformed when additional stresses are received, if they exceed the pressure from the own weight of the soil. As a result, the volume of the earth decreases due to a decrease in pores, distortions develop in space.
Causes of deformations:
- spasmodic compaction sediment;
- heterogeneous base under the foundation;
- intermittent voltage condition;
- uneven weight of the building during construction.
Residual subsidence exceeds elastic deformations, therefore soil distortions under the influence of uneven pressure are classified as compaction sediments. The indicator is not the same due to the diversity of soil conditions and uneven stress. The heterogeneity of the soil is caused by the presence of swelling layers, uneven bedding of layers and their different thicknesses.
The load is transferred unevenly, since the foundations perceive the load at different times of construction. The main pressure is received by vertical structures, the roof and from them the strip foundation, and floors with beams, partitions, equipment are loaded later. Some supports are made with a broadened sole in relation to others, therefore, an uneven settlement of the foundation occurs.
The influence of soils on the condition of the supports for the house
De-structuring of the ground also leads to the creation of hazardous areas. The risk arises when digging a foundation pit, trenches. This exposes the internal structure of the earth, and it is influenced by negative factors that were previously contained.
Soil settlement depends on the following conditions:
- earthwork method;
- the duration of the construction of the zero cycle;
- drainage device;
- measures to preserve the natural structure.
The structure of the soil is disturbed due to weather influences on open sections, dynamic stress from the operation of mechanisms, underground gases and moisture. Freezing increases the volume of the moistened layers and develops heaving forces, which sometimes exceed the settlement of the strip foundation from external influences. Bulging of the ground negatively affects the construction and operation of the building.
The influence of soils on the foundation is reduced by arranging the sole below the freezing mark and processing the sides of the support. Bitumen, diesel fuel are used, the filling of the sinuses is done with earth, which is not characterized by swelling.
Methods for determining the settlement of the foundation
There are 17 options for calculating drawdowns, but in practice, the calculation is carried out in several ways:
- layer-by-layer summation method;
- equivalent layer;
- accounting for layered soil strata;
- Egorov's method.
The structure of the structure experiences the greatest heel, bending or torsion with absolute subsidence at the end of the stabilization time. Deformations are called final or simply settlements, their value is determined as a result of calculations.
The foundation settlement shows an overall vertical movement due to the distortion of the basement soil, which slowly stretches over time. The subsidence of the soil layer indicates the magnitude of the reduction in obesity due to the deformation of the earth in this area. It will take a long time to analyze the calculation options, but a short description of the main methods looks acceptable.
Layer-by-layer summation
The formula is used R = (yc1 + yc2) / k (My K2 B + Mg D1 + (Mg - 1) db + Mc · Cn)where:
- yc1 and yc2 - coefficient of work factors, the first is taken as 1.1, the second - 1.0;
- k and k2 - coefficients equal to 1.0;
- b - bottom width of the foundation;
- cn - the calculated indicator of the specific adhesion of the soil, take 1 kN / m³;
- db - the depth of the basement walls;
- d1 - the depth of the laying of the building support;
- My, Mg, Mc - coefficients that depend on the angle of inclination of the foundation walls.
Diagrams of natural and auxiliary pressure are compiled, from which the values of the additional vertical load on the sole are taken. The formula is used to calculate the height of the elementary soil layer. For the stock, double the value.
Build a diagram of additional vertical loads from external factors of influence in the soil under the bottom of the pile and tape supports, for construction they take information from table No. 2 SNiP 2.02.01 - 1983. The lower edge of the compressible layer is found at the intersection of two diagrams. Settlement is determined by lowering the deformation module at the boundary of the layers. The calculation takes into account the average force in each layer and its height.
The average settlement as a result of calculating the settlement of the foundation by the layer-by-layer summation method should not exceed the maximum permissible standards for buildings of a certain type and type of soil.
Equivalent layer
The method assumes standard developed schemes for finding an equivalent layer in different parts of the base. This technique is used to determine the subsidence of supports, taking into account the impact of nearby foundations. The algebraic sum of the heights of equivalent soil layers in different areas gives an idea of the final settlement index.
The option is used for foundations of low height in urban construction conditions, when the foundations of existing structures are nearby. The method works well in stable soils with small deformations during compressibility.
Calculation for layered soil bedding
Calculation in unstable soils involves determining the depth of the base so that it is below the freezing mark. Flowing and soft-plastic clays, as well as loams and silty sands swell.
Calculation of sediment in stratified soils is carried out in two ways:
- finding the average compressibility of the layer;
- by summing the distortion of individual layers.
The second option increases the complexity of the calculations. Approximate averaging is allowed because the low accuracy of finding the values of compressibility is taken into account. The regulation takes into account the strength of individual layers in a stressed state. Standard formulas are used to calculate the seal performance as a first approximation. Averaging is carried out within the calculated compressibility index.
According to Egorov's method
Practical observation of the subsidence of buildings showed the correctness of Egorov's method. The results were analyzed and it was concluded that for supports with a foot width or radius of less than 10 meters, all options give similar settlement results. The exception is clay subsidence.
Concrete placement recommendations
Monolithic structures are concreted in a collapsible formwork from unified parts. The method of laying and transporting the mixture is chosen taking into account the minimum number of overloads.
Concrete is served in several versions:
- lifting mechanisms in tubs;
- dump trucks on overpasses or in formwork;
- transport belts;
- concrete pumps.
Moving by crane is convenient because it is used regardless of the volume of the foundation and at the same time supplies reinforcement for the frame. Concrete is laid in hard-to-reach areas with light removable conveyors or vibrating chutes.
Calculation of the foundation roll
The deformation modulus and Poisson's ratio are taken into account:
- sandy loam and sands - 0.3;
- clays - 0.42;
- loam - 0.35.
The distortion modulus is taken according to special tables for a certain type of soil. The width and area of the base of the foundation are taken into account, the absolute and additional pressure on the base is calculated. The calculation is carried out for the side of a rectangular structure in relation to which the bending moment works. If no deformation rotation is expected in the above-ground part, the roll calculation is not done.