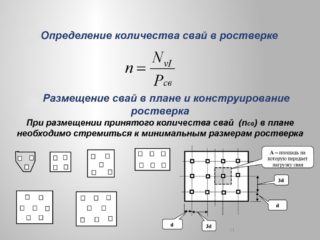
The reliability of pile and columnar foundations directly depends on the number of supporting elements. When designing and marking the foundation field, it is necessary to determine the distance between the piles so that the load from the building is distributed evenly between all the supports. Before starting work, it is necessary to study the requirements and recommendations of regulatory documents.
Foundation design

The main governing document governing the design of foundations is the Code of Rules 24.13330.2011. "Pile foundations".
Section 4 of the document obliges, when designing, to take into account:
- engineering survey results;
- information about seismic hazard in the construction area;
- data on the purpose, design features of the structure and operating conditions;
- loads acting on the foundation;
- existing development and the impact of new construction on it;
- environmental requirements;
- technical and economic comparison of possible design solutions;
- condition of groundwater;
- technical specifications issued by authorized organizations.
Based on the results of the analysis, design decisions are made about the required number of piles and the method of their distribution.
Types of piles

The number of supports required depends on the type and size, installation method, base area.
In industrial and civil construction, the following types of piles are used:
- Driven in, reinforced concrete or steel. When installed, the mechanized hammer strikes, deepening the support. The soil around the pile is compacted, and part of the load will subsequently be absorbed by the side walls.
- Bored. For piles, a hole of the required depth and diameter is drilled. The reinforcement frame is mounted in the pit and the hole is poured with concrete. When arranging holes, it is possible to expand the lower part of the shaft, thereby increasing the cross-sectional area. Based on this, the distance between bored piles can be greater than that of other types.
- Vibro-submersible sinks without large shock loads. The pile is given vibration, and it pushes the soil under its own weight. The method is used for hollow pipes of large diameter, the earth squeezed into the inner cavity is removed and removed from the construction site.
- Screw bases are more often used in the construction of frame or wooden residential buildings, since the installation of the support can be carried out without the use of heavy equipment. The blades are welded to the lower part of the structure, which significantly increases the support area. Therefore, the distance between screw piles can be greater than with other types of construction.
- The push-in type is suitable for small buildings and fences. For installation, special equipment is required.
Reinforced concrete, metal, wood are used as material.
For optimal load distribution, the piles are connected with strapping or grillage. A special case is the combination of a pile field and a strip foundation.
Gathering information for design
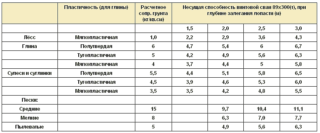
Critical indicators affecting the number of required support elements are the bearing capacity of the soil and the loads acting on the foundation.
Theoretical calculation of piles on the ground
For the analysis, prospecting excavations are carried out at the construction site. According to clause 5.5. Of the Code of Rules, if the load on the pile cluster exceeds 3 Nm, then the borehole is drilled to a depth of 5 meters below the bearing end.
On light soils - bulk, sandy, slightly clayey and swelling - drilling is carried out to the underlying dense rocks, on which the piles will rest.
It is not always possible to make an independent calculation of the number of supports "on the ground", for this you need to have engineering knowledge.
The formula looks like this: F = Yc * (Ycr * R * A + U * ∑ Ycri * f * l).
Parameter designations:
- F - load bearing capacity;
- Yc, Ycr, Ycri - coefficients from the tables of the Code of Rules;
- BUT - support area;
- U - the perimeter of the pile walls;
- F - the frictional force of the side walls;
- R - the bearing capacity of the soil, obtained from the table or as a result of field tests;
- L - pile length.
Substituting the required values in the formula, they calculate what load one support can withstand.
Instrumental measurement of soil parameters
Static load method consists in carrying out the following complex of works:
- At the construction site, test foundation racks are installed, withstand time for strength gain, if the pile is bored.
- Apply a load from a stepped jack to the support.
- Accurate measuring instruments measure the shrinkage after a load is applied.
- The bearing capacity is calculated using a special algorithm and tables.
According to the experience of builders, this method is considered the most accurate.
Dynamic loading method provides shock loads on the control pile with simultaneous measurement of the base shrinkage after each impact. Based on the results, the desired value of the maximum possible load is obtained.
Sounding with the help of a test pile and sensors installed to it, it allows obtaining data on the resistance of each soil layer, if they are inhomogeneous.
Calculation of load
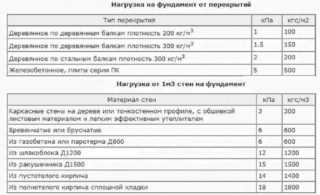
The total load on the foundation is determined by calculation.
Add up:
- a mass of piles and grillage;
- weight of walls, floors, roofs;
- snow, wind and operational load.
The specific weights of building materials can be obtained from reference books and manufacturer data.
The snow load is taken based on the results of long-term observations in the region of construction. The values are reflected in the construction manuals.
For regions with strong winds, the pressure of the air currents is significant. It is impossible to neglect them when calculating, especially for roofs with steep slopes.
The operational load is understood as the mass of people living or staying in the house temporarily. Add weight to pieces of furniture and household electrical and plumbing fixtures.
The resulting load when calculating the foundation must be increased by 10-15%. Planned and unforeseen situations often arise, for example, there is a desire to sheathe the house with plastic or metal siding, which will increase the load on the foundation.
Determining the number of piles
Sequence of calculations:
- The total load in kg is divided by the bearing capacity of the soil, measured in kg / cm2. The result is the total required area of the supports.
- Calculate the area of one support.
- By dividing the required area of the foundation into the cross-section of one support, their required number is obtained.
If a large number of piles are produced, it is better to use supports with a larger base area.
Area distribution
When placing the stop, take into account the minimum and maximum allowable distances.
The distance between the driven piles cannot be less than 3 diameters of the support, otherwise there is a negative mutual influence.
When distributing supports over the foundation field, the requirement for uniform distribution of loads is taken into account.
Be sure to mount piles in the corners of the building and the intersection of any walls with each other. A larger number of supports are mounted under heavy capital walls.
The difference in weights between the most and least loaded piles should not be allowed to exceed 15%. Permanent support loads should not differ by more than 5% and short-term loads by more than 20%. This is important, for example, for the foundation for a garage built into the house.
The maximum spacing of the piles is due to the presence or absence of a grillage. In most cases, piles should not be more than 1.5 m apart.
Allocate installation methods:
- single;
- bush;
- tape;
- solid field.

The choice of the option depends on the previously made calculations, the configuration of the building, the places of maximum and minimum loads.
Single piles are designed for the installation of lighting poles or small structures.
Bushes are mounted at high loads per unit area, for example, under the walls of multi-storey buildings.
Straps in one row are most often used in the construction of long retaining walls.
For private two-story houses and in general buildings of a large area, foundation fields are installed, with a pile pitch calculated based on the load.
Light buildings
For structures of light weight, for example, terraces and sheds with animals, a simplified method of calculation and installation is used. It is enough to install piles in the corners of the building and make a strapping with a bar.
On such a foundation, you can put frame structures filled with OSB slabs.
It is better to entrust the correct calculation of the foundation in the absence of special education to a specialized organization. The strength of the entire structure and safety of use depend on the correct project. Before starting construction, it is advisable to study the basic requirements that will come in handy for monitoring the contractor.