The retaining wall is being erected on an area with uneven terrain for the purpose of zoning, preventing soil leaching and the occurrence of landslides and avalanches. Also, a device of this design allows you to make the landscape view more interesting. When designing retaining walls, it is important to adhere to technology, correct foundation and drainage.
Retaining wall design and calculation

Before making a wall project, you need to evaluate the factors that can affect its sustainability. These include seismic events, winter soil swelling, vibrations (for example, from railroad tracks), rain washing. The thickness of the structure is chosen according to the height and characteristics of the soil. For example, a high retaining wall on relatively soft soil should be thick enough. It is necessary to erect the structure on a stable ground of crushed stone, gravel or clay. The freezing depth should not exceed 1.5 m. The groundwater must not rise higher than 1-1.5 m below the surface.
If the height of the building is more than 2 m, the strength of the wind also affects its stability. Such walls are especially demanding on the accuracy of calculations, requiring attention to a number of factors: soil mobility, density of building materials, susceptibility to cracks. They should be carried out by specialists, relying on professional guidance. With your own hands, you can mount low structures (no more than 1.4 m of the aboveground part).
The slope at the rear of the structure is steep and gentle. The shape of the structure from the side is usually a rectangle or a trapezoid. Sole dimensions should be 50-70% of the wall height. The thickness is selected depending on the characteristics of the soil. If it is plastic and consists mainly of sand and clay particles, the support should be massive. In this case, the thickness is equal to half the height. For hard soils (quartz, feldspar and similar), the ratio of the parameters will be 1: 4, for intermediate options - 1: 3.
Effective loads and stability

Calculation of retaining walls requires an understanding of the loads acting on the structure. They influence the choice of building materials and the arrangement of the base. Permanent loads are divided into horizontal and vertical. The former include the soil pressure behind the structure and the friction force in the areas of their contact. The second group includes the mass of the wall, pressure on its upper part and backfill.
In addition to constant loads, there are temporary ones:
- seismic loads;
- water leaks;
- vibration (railway or track);
- wind impact (especially in relation to high walls);
- swelling of soil layers in winter.
To prevent shifts and increase stability, a slight tilt towards the elevation can be arranged. This reduces soil pressure on the rear of the structure.
Weight distribution is assisted by a console device in the front area. It is advisable to make the side facing the ground non-smooth. For structures made of brick, stone or blocks, protrusions are provided. Monolithic walls are chipped.
Well-designed drainage also increases stability.To reduce the vertical pressure, you can fill the gap between the soil and the back of the wall with expanded clay or similar building materials with a hollow structure.
Retaining wall device
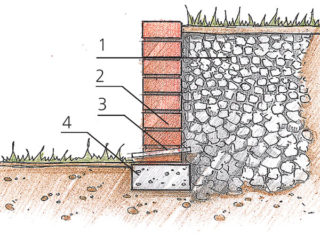
The structure includes a foundation, main body and drainage system. Almost all wall options are a configuration of these three elements. Their performance can be different and is determined by the purpose, soil characteristics and available resources.
Foundation
It is equipped for any walls, the height of which exceeds 0.3 m. The structural features depend on the soil on which the work is carried out, as well as on the characteristics of the body. If there is a lot of clay in the soil, they make a choice in favor of a strip foundation formed from blocks. On soft soils containing a lot of sand (especially "floating"), the base is organized on piles. Low walls (0.3 m or less) are buried in the soil without a foundation.
The depth of the bookmark depends on the height of the above-ground part. If it is small (0.3-0.8 m), the foundation has dimensions of 0.2-0.3 m.For walls of 0.8-1.5 m, the depth will be 0.3-0.5 m, for higher (but not more than 2 m) - 0.7 m. With a high mobility of the soil or a close location of groundwater (less than 1.7 m), a deepening is performed, 1.5 times greater than the width.
Body
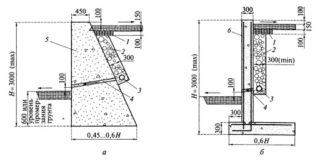
This is the part of the fortification that rises above the ground. For a structure to be stable, it must be heavy enough. This explains the attention to wall thickness. Before you start laying out the body, you need to prepare a drawing in advance.
Some versions of the walls are characterized by high rigidity. This includes brick and masonry, monolithic concrete, buildings from blocks connected with cement mortar. Other types of walls are resilient. They are able to withstand slight deformations without cracking. These are gabion and dry stone masonry. The tops of such configurations should be at least 0.45 m wide.
The amount of inclination of the front part depends on the features of the structure. If the structure is firmly fixed, and the total height of the body and foundation is less than 1.5 m, there is no need to make a slope for this face. In larger buildings, a slightly pronounced slope (within 15 degrees) contributes to the visual perception of the wall as vertical, and also increases stability.
The angular value of internal friction depends on the type of soil and its porosity. The smallest angle is for clay, and the largest is for gravelly soil.
Drainage and drainage
The functions of this system are the accumulation and removal of excess liquids of various origins (ground, rain, melt water). This helps prevent wall erosion and flooding. Structures are transverse, longitudinal or mixed.
Retaining walls made of various materials
The main parameters when selecting a material for construction are its water resistance, immunity to aggressive environments, ease of accessibility and the chances of a long service life. The height of the building is also important.
Made of wood

Wood retaining walls are attractive in appearance, but the material is not among the most durable. To improve performance (to achieve resistance to decay and moisture), logs and beams are treated with special compounds. The sides from which the structural elements will be buried are exposed to burning or coating with liquid bitumen. The tree is suitable for the construction of low buildings (no more than 1.5 m).
Vertical and horizontal arrangement of logs in the reference object is possible. In the first case, the digging depth is one third of the beam length. A 0.15 m layer of crushed stone is poured into the prepared trench, which is then tamped. The logs are placed tightly one to one and reinforced with wire.To make the structure more stable, the trench is poured with a mixture of cement and sand. The back part is covered with a sealant (for example, roofing material) and covered with soil.
When arranging a horizontal configuration, support pillars are first buried. The distance between them is 1.5-3 m. The smaller it is, the more reliable the structure will be. Horizontal elements can be placed in the grooves previously cut in the posts, or to their backs. In the second case, you need to lay out the waterproofing material in advance, since the first beam will be placed on the ground. The logs are attached to the support posts with wire ties or nails.
Concrete

The concrete retaining wall is mounted on piles (bored or screw) or on timber formwork. The first case is preferable if you have to deal with unreliable soil or if the wall consists of several blocks. A ready-made monolithic slab of industrial production is installed in a pre-dug trench by means of a forklift. In this case, it is not required to prepare the foundation if the soil is not loose and unreliable. A console made at a slight angle towards the embankment (10-15 degrees) will make the wall more stable.
Step-by-step instructions for installing concrete reinforcement:
- A trench of sufficient depth is prepared, which includes space for a cushion of gravel and sand. In front of the future wall, you need to leave 0.3 m of space, for the back edge - 0.5 m. The soil to create a slope is removed manually. The slope is checked when preparing the formwork and filling it with concrete and straightened as needed.
- Reinforcement of the foundation is in progress. The metal rods that protrude from the concrete must be at least 0.5 m high. The sole is left to anchor for about a month. No work needs to be done before this period has elapsed.
- For the manufacture of formwork, plywood material treated with a composition that provides water resistance is used. Dimensions - 244 * 122 * 15 cm. 3 sheets are spent on one workpiece: one for each face and the third, cut for the sides.
- Reinforcement helps to prevent the divergence of the seams. Upon completion of the pouring, holes are drilled in the side zone into which the rods are inserted. You can arrange them in the form of a chessboard. The distance between adjacent elements is 0.4-0.5 m, the length of outgoing tails is 0.3-0.4 m.
- Metal corners are suitable for creating bonds between faces. Along the perimeter of the formwork, beams of 5 * 5 cm can be nailed. Reinforcing supports are installed on three sides.
You can cover the surface of the slab with a stone. In order to reduce costs, instead of concrete blocks, they sometimes use expanded clay and foam concrete, as well as slag and aerated blocks. Doing so is not recommended due to the insufficient strength of the materials.
Of stone

Such a building will have an attractive appearance and will fit well into the landscape. The material is suitable for creating low (less than 1.5 m) configurations. Laying can be done wet or dry. The latter method requires more skill from the manufacturer - he will need to adjust the elements in size so that they fit together in the best possible way.
The type of foundation is organized by tape. If the solution is not used when erecting the wall, the seams can be filled with soil, into which the seeds of crops with a fibrous root system can then be planted. This will make the structure more aesthetically pleasing and more durable.
From gabions

This option is attractive because of its flexibility and moisture permeability - you don't have to drain it. You will need large crushed stone or river rounded stones. The assembled boxes are mounted on leveled soil and covered with filler. Between them, you can fill the ground with seeds. The sections are connected with wire ties treated with an anti-corrosive compound.
Brick
You can independently make a wall up to 1 m high, otherwise use the services of a master. The material is a well-fired red brick, laid on the mortar in a sling. Use a strip foundation with a depth of at least a meter and a width three times greater than that of the wall. At the bottom, a crushed stone or gravel backfill of 0.2-0.3 m is made, and on top - a sand layer of 0.1-0.15 m. Laying in a single brick is suitable for fortifications with a height of less than 0.6 m. For larger walls it is done in one and a half to two units, while the lower area will be wider.
Drainage system
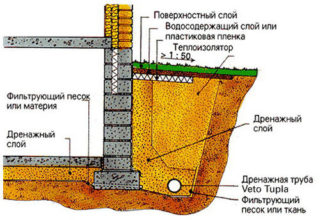
Transverse drainage is organized by placing pipes with a diameter of 50 mm in the wall thickness or arranging holes with a diameter of 100 mm. The distance between adjacent holes is 1 m. Another option is not to cement any of the vertical joints in the lower rows of stone or brick masonry.
With the longitudinal method, a flexible drainage tube with a corrugation is placed along the length of the structure on the foundation. It must first be wrapped in geotextiles.
Special approaches taking into account the landscape
The aesthetic qualities of most of the materials used and the structure of the building itself make it possible to make it an element of the landscape. It is possible to plan the execution of the retaining wall in an area with a slope in accordance with the characteristics of the terrain. On a small area with a fence, a low wall (up to 0.6 m) will look good. If it is decided to erect a structure of large dimensions, in order to harmonize the appearance, the landscape should be saturated with elements (benches, steps, an alpine slide, etc.). You can decorate the wall with moss or climbing plants. Surface finishing can be done with different facing materials - small stones, natural or artificial stone, tiles.








