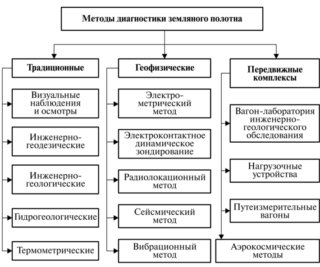
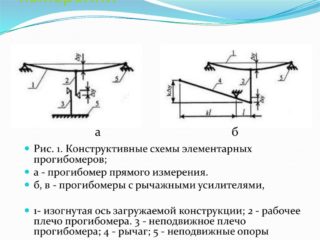
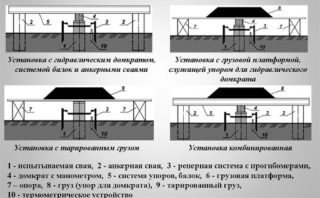
Field investigation of piles helps to study the mechanical and physical properties of elements, measure the level of resistance and determine typical deformations directly under construction conditions. The quality of the survey depends on the use of instruments and special devices. Static tests of piles are carried out by accredited firms, where there are specialists of the required profile and the necessary equipment.
Why and when are piles tested?

Experimental driving of the support posts is carried out on a special technical installation to determine the pulling out, pressing loads and tensile forces. The unit in the form of a platform with a standard load includes a pile pressure mechanism, a crane for lifting. The device is equipped with a support installation made of metal trusses or reinforced concrete beams, through the system of which the vertical load is transferred to the tested element.
Measurement of actual soil parameters is important to prevent sudden subsidence and destruction of the structure. Soil testing using pile driving technology is done during the construction of a new building and during the reconstruction or re-equipment of an existing structure.
The test evaluates soil uniformity, bedding, quantitative composition, physical characteristics of each row. Check the compliance of the design loads with the real resistance of the bar. The degree of pile displacement during testing is recorded by measuring sensors, detectors, controllers, which differ in measurement accuracy up to 0.1 mm. Field studies are carried out taking into account the requirements of general standards, which are supplemented by relevant regional and industry documents.
What information does the test give
Stamp research in the field is carried out to determine:
- precise structure and bearing capacity of the support bar;
- the possibility of deepening the rack to the design depth;
- the relationship between the subsidence of the pile in the ground and the load in an extended time interval.
Sometimes a house is built on an old pile foundation, then static tests are carried out to assess the true state of the soil around the existing elements. This is how they choose the type of pile required, the material, its diameter, and decide on the drilling and installation of additional rods.
The hydraulics transfer the load to the die through the strut. Reactive stress is perceived by the anchor working to pull out the pile element. The soil in the cased bore is loaded with a device attached to the pipe. The pressure is controlled by the weight of the loads on the platform, and the verticality is controlled by the guide skids.
What is included in the field test program
The method by which the test is carried out at the construction site:
- static research;
- dynamic check;
- soil diagnostics with a reference element;
- soil control by static sounding.
The number of piles to be checked depends on various factors, but should not be less than 1% of the total number of mounted racks. The choice of the number of test samples is influenced by the complexity of the conditions, the size of the transmitted voltage and the variety of standard sizes of the support rods.
Test specific areas for the entire construction site and check for areas with weakened performance. The results are recorded in a journal, drawn up in the form of graphs of the relationship of load and displacement of the rack. The relationship between the number of blows and the number of burial failures is taken into account.
Regulatory documents
The standard for testing bored piles, as well as screwed, pressed and driven elements is GOST 56.82-2012. The rules of the document regulate research on the construction site, and describe the methods of control checks of pile racks. There is SNiP 2.02.03-85 and SP 50.102-2003, which standardize the survey of foundations and the design of pile supports for new construction and reconstruction.
Static tests of the ability of piles and soil are expensive, they are carried out within a day (the time depends on the size of the object), but they are classified as accurate tests with flawless results.
Research is allowed at different stages of construction:
- geological surveys;
- before the start of the design;
- during the installation of pile supports;
- during the acceptance of the zero cycle.
Test technical documents describing the elements are handed over to the pile installers. In the papers there is a plan with a tie-in of wells along the axes, points of test static and dynamic sounding, the location of communications at the facility, buildings are indicated. The terms of reference for testing the piles and the conclusion of geologists on the conditions of construction, as well as the estimate for the work, are transferred.
Features of dynamic tests
The test uses deflection meters. Before the load, the first zero result is recorded, then the second reading is taken and measurements are taken sequentially for 30 minutes (4 in total). The pile is considered stabilized if the settlement is not more than 0.1 mm in the last hour.
The load is brought to the calculated one when immersed in dense clayey, coarse-grained soils and sands, but the value should not be less than 1.5 indicators of the bearing characteristic of the pile.
Features of static tests
Ultimate resistance is determined by the value of the load, after which the pile deepening stops. The method is simple, but it takes time and technical equipment. The principle of static testing is that the element is pressed on, and not dropped from a height.
A hydraulic jack is used that presses down on a metal beam welded to the pile test piece and connects it to adjacent anchor posts. The distance from the control pile to the anchor pile is made at least 2 m or five diameters (in elements with a section of up to 80 cm).For control elements, the gap is made at least three diameters, but not less than 1.5 m. The reference umbrella-pile is placed at a distance of at least 1 meter.