The foundation base (foundation) is the basic element of any building under construction. Thanks to him, each structure erected evenly transfers its weight to the soil and is kept in a static position. Therefore, special attention is paid to the construction of the foundation of the house.
Varieties of foundations, their features and structure

The reliability of a private house as a whole depends on the correct choice of the foundation. Before proceeding with the construction of the foundation for a private house with his own hands, the developer must take into account the type and total weight of the building, the type of soil, the depth of groundwater and freezing of the soil.
Strip foundation
The tape structure is a tape of reinforced concrete or made of stone materials of equal cross-section along the entire length. It is laid under all (external and internal) walls of the building being erected. In practice, there are two types of such a foundation:
- Shallow, in which the lower level of occurrence is at a depth of no more than 75 cm. On this basis, light wooden structures are installed or structures are erected from aerated concrete.
- Buried, having a depth of at least 20 cm below the freezing point of the soil. Such a foundation is used in the construction of heavy houses with stone walls and ceilings, which have a basement and / or a semi-underground garage.
It is forbidden to use the strip foundation on heaving and saturated with a large amount of moisture soils.
Monolithic tape bases, subject to all building codes and regulations, serve 70 or more years.
Columnar and pile foundations

The columnar foundation is based on stone or concrete pillars, which are installed at a distance of no more than 2.5 m from each other. They are placed in places of the greatest weight load: building corners, junction and intersection of walls, etc. The depth of the pillars, as a rule, does not exceed one meter.
Having installed the pillars, the outer gaps between them are closed with basement insulating walls, and the free space under the house is poured with rubble and poured with unreinforced concrete.
Columnar foundations are not laid on heaving and peaty soils with a high level of groundwater. They are used in the construction of light frame structures.
Neatly laid columnar bases last at least 40 years.

Arrangement of the pile foundation begins with the installation of solid piles, immersed to a dense layer of soil. The parts of the piles protruding above the ground are connected to each other by a metal or reinforced concrete grillage, on which the erected structure will then rest.
A pile is a reinforced concrete or steel pillar sharpened on one side. The most powerful of them are capable of withstanding a load of up to 5 tons.
In the construction of private houses, steel screw piles are most often used, which can be manually screwed into the ground. To drive a reinforced concrete pile into the ground, you will need special equipment.
The service life of pile structures is determined by the material from which the grillage elements are made - reinforced concrete beams or metal structures (channel or I-beam).
The foundation on screw piles lasts from 50 to 70 years.Buildings built on reinforced concrete piles can last for over 100 years.
Slab foundation

The slab foundation is a monolithic reinforced concrete slab, slightly larger than the base of the building being erected. It is located directly on the surface of the soil and is used in the construction of small houses on any type of soil. At the same time, the depth of soil freezing and the occurrence of groundwater does not matter.
The presence of the base plate does not require the arrangement of a high base and allows it to be used as a floor.
The design of the slab base guarantees its trouble-free operation for at least 50 years and depends on the mobility of the soil and the depth of the groundwater.
DIY construction

Self-production of the foundation does not require any special skills. The only requirement that must be observed when building a foundation with your own hands is strict adherence to the order of work:
- Preparatory work - clearing the site from debris, roots, etc.
- Layout of the site for the foundation according to the project, for which you will need a level, tape measure, cord and pegs prepared in advance.
- Excavation work, during which they dig trenches and prepare places for poles.
- The preparation of a sand cushion for the foundation involves laying and tamping clean sand, in which there are no clay impurities. The layer of such a pillow should be at least 20 cm.
- The arrangement of the formwork is carried out from boards having a width of 10-20 cm and a thickness of 2.5 to 4 cm. Opposite formwork boards, as well as its corners, must be rigidly fixed.
- The reinforcement frame is knitted with a special knitting wire. As reinforcement, metal rods with a diameter of 12-14 mm (horizontally laid) and 8-10 mm (vertically stacked) are used. The connected frame is laid in a trench.
- The concrete is poured from the corners, after which the resulting voids are filled. For concrete, cement of the M200-M400 brand is used, which is mixed with sand and thoroughly mixed. To expel air from concrete, it must be vibrated with a deep vibrator or bayonet method.
- Alignment of the resulting surface is carried out immediately after pouring. If the concrete “grasps” and begins to crumble, the leveling should be stopped.
Each type of foundation has its own characteristics for carrying out preparatory work and pouring concrete.
Thermal insulation and waterproofing of the base
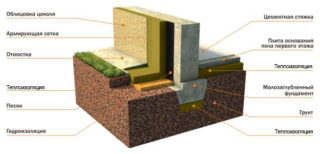
The foundation of any house during operation is exposed to aggressive environmental influences: soil movement, groundwater, a sharp change in temperature, etc. To protect the foundation of a house with your own hands from this harmful effect, help:
- drainage;
- waterproofing;
- insulation.
Waterproofing can be coated or glued. Depending on the place of application, vertical or horizontal waterproofing is used. The choice of the type of waterproofing and the method of its application depends on the soil, the properties of the foundation and the area where the building is being erected.
To divert excess water from the building, which can accumulate on the site and adversely affect the foundation, a special drainage system is used. Depending on the design of the house, drainage can be:
- wall-mounted (for houses with basements);
- circular (in the absence of basements);
Insulation of its foundation with heat-insulating materials helps to avoid large heat losses and protect the house from dampness. The foundation is insulated, as a rule, from the outside, which helps to protect it from sudden temperature jumps, and the house from freezing of the walls and falling into the basement of groundwater. If it is impossible to insulate the foundation from the outside, it is insulated from the inside.
Common mistakes when laying the foundation

The main mistake inexperienced developers make is trying to save money.Effects:
- the use of low-quality materials, which will lead to the instability of the foundation to external influences;
- uneven load distribution;
- cracking or deformation of the base;
- subsidence and even destruction of the structure.
Unpleasant consequences can be caused by the construction of a foundation without formwork or a sand cushion, improper reinforcement or violation of the geometric dimensions of the foundation.








