The basis for the stability and durability of any building is a well-planned and correctly constructed support system. A monolithic concrete foundation is rightfully considered the most reliable option, suitable for almost all conditions in which construction is carried out. This design is not particularly complex and may well be made on its own. However, it is necessary to take into account a number of nuances that are inherent in this particular technology.
The device and features of a monolithic foundation
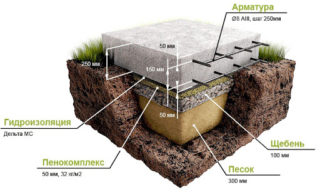
A standard monolithic foundation has such a device:
- Geotextile lining. Prevents erosion of the base by groundwater.
- A pillow made of sand and rubble. The thickness of the substrate varies between 10-30 cm. The stone acts as a drainage, and the sand dampens ground vibrations.
- Thermal insulation. Polystyrene based boards are commonly used. A layer of insulation retains the cold coming from the ground and contributes to the creation of a comfortable and healthy microclimate in the house.
- Formwork. During the construction of a monolithic foundation, temporary or permanent formwork can be used. The first is used when pouring the slab, the second - when arranging a buried tape system.
- Steel frame. It is assembled from reinforcement 12-16 mm by twisting rods with metal wire. It is laid over the entire area of the structure with reinforcement elements in the corners.
- Concrete. The best option is a mixture of the M200 brand, with a mobility index of P-3, water resistance W8 and frost resistance F200.
The prefabricated support system is faster, but more expensive. The strength indicators of such a structure are lower than that of a monolithic one.
Varieties of a monolithic foundation

There are several ways to make a monolithic support system. Each of them has its own characteristics, pros and cons.
In private construction, the following types of foundations can be used:
- Tape. Suitable for buildings of any size and weight. Set up on all types of soil, except quicksand and permafrost. According to the degree of immersion in the ground, it is subdivided into buried, shallow and not buried. In all cases, the tape forms a closed loop, inside which a basement can be equipped.
- Plate. It is a slab made by casting formwork or a prefabricated structure of several segments. It is used for construction on unstable clay and loamy soils. The monolithic structure ensures an even distribution of the load on the ground.
- Columnar. This design is used on dense and stable soils that are not subject to heaving. Supports are cast on site or finished products are exhibited. After alignment, the pillars are covered with plates, and only then they are tied with steel pins. So the structure becomes monolithic.
- Pile.Popular technology for construction on slopes, uneven areas and near bodies of water. The formwork, the frame is lowered into the pre-drilled wells, concreting is performed. The piles are connected into a single system with a reinforced concrete grillage.
The basis for choosing a base is data on the state of the soil, the availability of groundwater, the depth of freezing of the earth and seismic activity in the region.
Advantages and disadvantages

Like any engineering system, a monolithic base has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Design advantages:
- high bearing capacity;
- simple and affordable manufacturing technology;
- applicability to almost all types of soil;
- long service life;
- vibration resistance;
- even distribution of the vertical load on the ground;
- the ability to use as a subfloor.
Cons of the design:
- high consumption of building materials and a decent cost;
- low elevation above ground level;
- erection is associated with significant physical stress during construction with your own hands;
- the impossibility of arranging the basement.
Monolithic slabs are the most reliable foundation for residential and utility structures.
Preparatory work

The initial stage of construction is design. At this phase, a site survey is carried out, drawing up drawings, calculations of the need for materials and tools.
If we take as a basis the device of a monolithic foundation slab according to GESN 81-02-06-2017 (collection 6), you can accurately determine the construction estimate.
It includes the following costs:
- delivery of equipment and materials, organization of their storage;
- excavation;
- installation of formwork, including preparatory actions;
- arrangement of the working site; installation of equipment;
- fabrication of a reinforcing cage;
- mixing and pouring concrete solution, caring for the foundation;
- removal of the formwork;
- backfilling.
In some cases, additional activities may be carried out.

As a rule, such devices will be enough for work:
- concrete mixer;
- level;
- Bulgarian;
- roulette;
- shovel;
- hacksaw;
- a hammer;
- ax;
- scissors.
It is recommended to build a foundation in the warm season, when the earth has warmed up and dried out well. It is advisable to have a favorable weather forecast for at least a week.
Monolithic foundation construction
There are such norms for a monolithic foundation:
- 20 cm - sheds, garages, gazebos, summer kitchens, light frame houses;
- 30 cm - one-story buildings made of bricks, beams, logs, aerated concrete with a reinforced concrete floor slab;
- 40 cm - two-storey brick houses, cottages with attics, small hotel complexes.
When planning the arrangement of the foundation, one should approach the choice of the thickness of the slab with a perspective for the future. It is quite possible that after a while it will be possible to build an additional floor, and this will require a more powerful foundation.
The arrangement of a monolithic foundation is carried out in the following sequence:
- Marking on the ground. Designation of the boundaries of the building, taking into account the installation of the formwork.
- Excerpt from the foundation pit. Bottom alignment and compaction.
- Geotextile laying. The fabric is laid in strips with an overlay of 15-20 cm. The joints are glued.
- Placement of pipes for sewerage and water supply. Backfilling of the cushion from layers of crushed stone and sand.Leveling and compacting the dump. If provided by the project, insulation is laid.
- Formwork erection. Considering the small height of the slab, it is advisable to use boards with a thickness of 30-50 mm.
- Arrangement of waterproofing. Roofing material based on fiberglass is well suited for this. A margin is made to bring the material to the surface of the plate.
- Reinforcement. Frames and rods are connected with wire, which is tied into a tight knot. The iron is wiped from the grease, cleaned of rust, and then treated with a corrosion agent. Supports and struts are installed.
- Preparation of concrete and pouring it into the formwork. The surface is smoothed with a long-handled mop.
After 2-3 days, the formwork is removed, the slab is covered with polyethylene and watered daily with water. You can continue construction in 28 days.