Not all private developers get land plots with ideal soil in all respects. Quite often, it is necessary to build houses and dachas on clay and sandy loam, which is fraught with many difficulties associated with the instability and heaving of the soil. In such cases, a strip pile foundation is an excellent solution. This is a design that combines simplicity, economy and high reliability. There are several ways of arranging a strip foundation on piles, each of which has its own characteristics, pros and cons, construction and operation rules.
Pile-strip foundation design
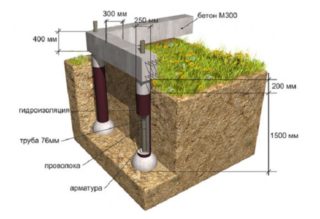
The pile-flooded foundation is a monolithic structure consisting of the following elements:
- Support. They are immersed in the ground to a depth where dense layers are located. A prerequisite is lowering below the freezing point of the soil. Piles are hollow and solid, round and square. Immersion in the ground can be carried out manually or using mechanization.
- Tape (grillage). It is a continuous reinforced concrete block that runs under the outer and inner walls of the building. The fragment is made of reinforcing cage and concrete.
- Insulating layer. Depending on the type of tape deepening, certain types of insulation and waterproofing are used.
- External finishing. Designed to give the structure a complete and presentable look, as well as to protect it from external factors.
The underground and above-ground parts of the structure are rigidly interconnected, which ensures its strength, stability and uniform transfer of the structure's mass to the ground.
Varieties of bases

Pile-strip foundations are divided into several categories based on the type of supports used and the location of the grillage relative to the ground.
Depending on the type of piles used, there are such bases:
- Screw. They are steel pipes sharpened on one side with blades on the tip. They are screwed into the ground manually or using a mechanical device. The diameter of the products varies within 57-133 mm, and the length is 165-350 cm. After installation, the pipe is poured with concrete, which, in combination with the blades, gives the tape-screw foundation strength and stability.
- Bored. The installation consists of several stages, the first of which is the production of a well with a manual or mechanical drill. After that, the formwork, the reinforcing cage are inserted into the hole, and then the cement mortar is poured. Steel, asbestos-cement, plastic pipes, waterproof cardboard, plastic and roofing felt are used as formwork.
- Submersible. Supports are monolithic reinforced concrete pillars. They are lowered into the ground with the help of an impact driver or by indentation. In all cases, the involvement of specialists and expensive equipment is required.
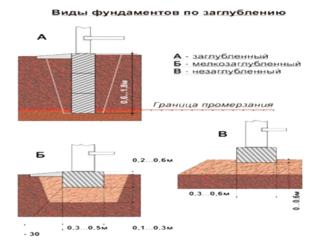
- Recessed. They are used in the construction of heavy buildings and on stable ground. The tape is lowered to 70% of the freezing depth of the earth.This method is rarely used, because it is costly and does not differ in efficiency, since there is no possibility of arranging a basement. In addition, there is always a risk that the supports will be pushed out by back ground pressure.
- Shallow. They are the most common option on almost all types of soil. The tape is immersed in the ground up to 30 cm, and a plinth up to 50 cm is made above the surface. At low cost, the optimal distribution of the building's weight on the tape is ensured, and the supports act as anchors.
- Shallow. They are used on highly heaving soils or areas where there is a risk of flooding the building with flood waters. The belt rises above the zero level to a height that is dictated by the operating conditions of the building. In such cases, the entire load falls on the supports.
To choose the right construction technology, you need to analyze all the factors, and even better contact specialists who, based on the available data, will draw up a competent project.
Application area
Construction can be carried out on the following types of soil:
- layered;
- loose;
- heterogeneous;
- heaving;
- complex in composition;
- with a high level of groundwater;
- frozen.
Scope of application of structures:
- private low-rise buildings;
- summer cottages;
- cottages;
- sheds;
- baths;
- garages, subject to a gentle ramp;
- moorings and piers;
- buildings on slopes and over depressions where leveling is not economically viable.
High-rise and heavy houses are installed on thick and powerful piles, where the role of the tape as a supporting element in such structures is practically absent. It is used to create a level support for the floor to prevent deformation under the weight of the structures on top.
DIY technology

If you have data on the properties of the soil, the weight of the building and the skills of working with household tools, you can make a pile foundation with your own hands. The first step is drawing up a diagram of the pile field. On its basis, a calculation of the necessary materials and equipment is drawn up, a construction estimate is prepared.
For work you will need:
- hand or motor drill;
- welding machine, grinder;
- pliers;
- hacksaw, shovel, hammer, ax,
- putty knife;
- level, tape measure;
- brick;
- cement, sand, crushed stone;
- formwork material;
- wire;
- fittings;
- roofing material.
The type of piles is determined by the selected technology. These can be screw-type products, hollow pipes or reinforced concrete pillars.

Step-by-step instructions for the construction of a strip-pile foundation:
- Site preparation. The removal of trees and bushes is carried out, the fertile soil layer is removed. Grass is mowed around the working site, a place for storage and disposal of waste is being set up.
- The markup is in progress. The compliance of the horizontal and diagonal lines with the design data is checked.
- Excerpt from the trench. If the installation of the formwork is not planned, it is done along the width of the finished strip. This option is only possible in stable and stable soil, which does not crumble during the excavation process.
- Making holes for bored piles. Reinforced concrete and screw products are submerged to the planned depth, which is controlled by a tape measure and level.
- Backfilling the trench with a cushion. First, a layer of crushed stone is laid, and then sand. The pillow is wetted, leveled and compacted.
- Formwork manufacturing. With the submerged method, it is brought out over the ground level or slightly above the design level of the basement. Non-immersed formwork is installed on brick supports to avoid sagging under the weight of the mortar.
- Reinforcement. The strapping of the metal structures of the piles and the frame of the tape is being carried out.This is a prerequisite for the structure to be strong, solid and stable.
- Filling the molds with concrete. It is better to pour the foundation under the house on piles all at once, starting from the supports and gradually moving to the tape. The solution should be fed continuously, small gaps are allowed for the preparation of the next batch of concrete. As the piles and formwork are filled, air bubbles are removed from the solution. The surface of the belt is leveled so that the base plate lies flat and without distortion on it.
- After pouring the pile foundation, you need to wait 3-4 hours and cover it with dense polyethylene on top to protect it from precipitation and intensive evaporation of moisture. After that, the structure must be moistened every 6-8 hours for 28 days.
After the final hardening of the concrete, waterproofing, insulation and finishing works are carried out. 2-3 layers of roofing material are laid on top of the tape.
Advantages and disadvantages of the design
Pile-belt structures are popular due to the following advantages:
- the ability to conduct construction on problem soils, including swampy areas and permafrost;
- profitability, since a small amount of materials is required to create the base;
- simplicity of technology, the ability to do it yourself without involving equipment;
- stability and reliability of the structure;
- applicability for the installation of surface structures when fastened to the bottom of the reservoir;
- bored piles are made from scrap materials, which eliminates the cost of purchasing factory products and their transportation.
The main disadvantage is the waste of time and money on conducting a geological survey of the construction site. It is advisable to start it only if you have all the data regarding the type, moisture and composition of the soil. There is no possibility of arranging a basement, the owner of a finished property needs to carefully consider the issues of insulation and waterproofing of the lower level of load-bearing structures. Without proper protection from moisture, the supports will quickly become unusable, and this is an expensive and time-consuming overhaul.