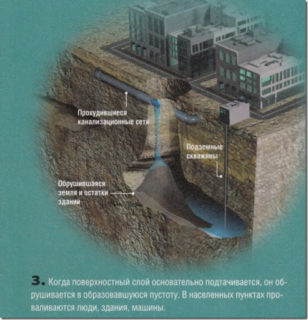
Most of the territory of Russia is dominated by soils characterized by looseness and a high level of groundwater occurrence. During the construction of foundation pits, such phenomena as crumbling of their walls and flooding are observed. To create a cut-off barrier and prevent the displacement of soil layers, cut-off piles are used. The finished structure is a monolithic wall with high strength and tightness.
Construction of bored piles
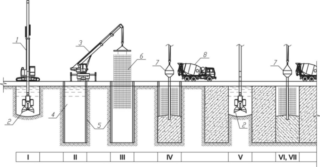
The foreshaft for bored piles is a closed system of supports submerged below the groundwater level (wall in the ground). The structure consists of piles connected at the edges, the manufacture of which is carried out directly at the construction site. The walls of the wells are reinforced with bentonite mortar, and a reinforced concrete screed is installed on the top of the pillars. Thanks to this engineering solution, the structure gains integrity and solidity.
A feature of the installation is the complete absence of vibration, which is typical for piling technology. The underground wall consists of a continuous series of concrete pillars, the edges of which intersect by an amount equal to 5-7% of their diameter. Every second pile is reinforced with a steel frame that runs along the entire length of the support and closes on the external reinforcement like a monolithic grillage.
In construction, foreshafts with a diameter of bearing elements in the range of 36-150 cm are used, the most common are supports with a section of 62-82 cm.
Application area

BSS piles, with all their inherent features, pros and cons, are widespread in construction, especially when it is carried out on unstable and highly moistened soils. The design device is so well thought out that it allows you to solve the most complex installation tasks when there is simply no other solution or it is fraught with a lot of undesirable effects.
Boring piles are used to create such objects:
- tape recessed foundation;
- walls of underground structures of industrial and commercial type - parking lots, shopping centers, warehouses, pedestrian crossings;
- shallow tunnels, subway lines and stations, highways;
- reinforcing structures for walls of buildings in emergency condition, including objects of cultural and historical value;
- underground collectors for collecting waste water;
- hydrotechnical facilities (ponds, lakes, pools);
- sedimentation tanks for the development of chemical, energy and processing enterprises;
- emergency tanks near high-risk facilities;
- strengthening systems on unstable slopes;
- fences for underground utilities;
- anti-seepage curtains on dams;
- containers for storing garbage, industrial waste, compost;
- closed cattle cemeteries.
It is contraindicated to install foreshafts in the following conditions:
- powerful underground currents;
- high percentage of coarse-grained rocks;
- the presence of old masonry, pipes, reinforced concrete foundations, steel structures underground;
- the presence under the surface of voids and cavities of natural or artificial origin;
- high concentration of chemical reagents aggressive to concrete in the soil.
Foreshafts can be installed as an enclosing structure, and when installed in hydraulic structures - in their body and base.
Design features of the frame for bored piles
Concrete has high compressive strength, but does not tolerate bending and twisting well. Lateral pressure is a major critical factor for deep buried structures. Only reinforced concrete products, in which strength is combined with flexibility, can withstand such loads without the risk of breakage.
Such a function in bored piles is performed by a volumetric steel frame. The most effective is a square section, where solid-bent frames are installed between the longitudinal rods. The size of the frame is made as close as possible to the diameter of the hole, but with the expectation that the metal does not protrude from the concrete after it has solidified. This solution allows the frame to capture part of the previously installed concrete supports without reinforcement.
An important task of imparting strength to the wall in the ground is performed by the upper belt made of reinforcement. This structure is made in the form of a rectangular beam with strong fastening to the frame of each underground column. After installation, the armopoyas is poured with concrete. The finished structure becomes completely monolithic. From below it is held by a dense layer of soil, and from above by a reinforced concrete closed belt.
Foreshaft purposes

The foreshakhta performs several functions at once, which makes it a unique invention that has significantly advanced the technology of private and industrial construction.
Underground structures are multifunctional and can be used for the following purposes:
- protection from external pressure on underground structures;
- creation of the basis for laying the basement and floor slab;
- blocking of groundwater during digging of foundation pits;
- strengthening of slopes, embankments, dumps and other irregularities, where there is a high probability of landslides;
- isolation of toxic substances in a confined space, provided that the bottom is strengthened.
Self-creation of a wall in the ground is impossible. The construction of this structure is carried out on the basis of professionally designed drawings, preliminary soil studies and with the help of powerful, high-tech equipment.
Construction technology

The technology for installing bored piles has been worked out to the smallest detail and consists of the following stages:
- Geological studies, based on the results of which a scheme of groundwater occurrence is drawn up.
- Drilling wells at a distance of 90% of their diameter. Casing pipes are used.
- Pouring concrete, sealing the mortar with a vibrator.
- Removing the casing from the hole.
- Maturation of concrete. This takes 24-28 days.
- Drilling holes between previously drilled holes with excision of their edges.
- Installation of the frame and filling the shaft with concrete.
The final phase is the creation of the formwork, the installation of the reinforcing belt and the filling of the form with concrete.
The main differences between bored piles and bored piles

The technological process for creating both structures is almost the same, but their purpose is different.
Bored piles are installed at a distance from each other, reinforced and perform an exclusively bearing function in the arrangement of the foundation.
Boring piles are connected to the grab of adjacent fragments, performing the tasks of waterproofing, retaining earth layers and strengthening emergency support systems.
Benefits of bored piles
The use of bored piles has the following advantages:
- applicability to almost any type of soil;
- lack of construction waste and consumables;
- noiselessness and absence of vibration;
- compactness of drilling equipment;
- safety for the infrastructure facilities surrounding the site.
All this makes this technology indispensable for construction and restoration work in the conditions of dense development of settlements and industrial facilities.








