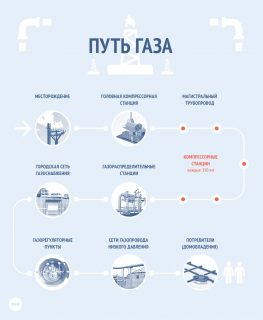
Gas enters apartments and private houses through a complex and extended pipe system. The mixture produced at the field is cleaned, injected under pressure into the main pipeline and sent through it to the gas distribution stations. Here the gas is once again purified and transported to the gas pipelines of cities and villages, and then follows through the network to the consumer. Along the way, the pressure of natural gas gradually changes.
General pressure information

A-priory pressure - physical quantity, equal to the force that acts on a unit area at 90 ° to the surface. Since blue fuel is transmitted through pipelines, here the cross-sectional area of the pipe acts as a conditional surface, and the pressure determines the speed of movement of the substance.
Pressure at different sections of the gas pipeline from the field to the nozzle in the gas boiler is maintained different.
Types of pressure
The pressure in the pipes is strictly standardized... If the value in the main pipe is too small, it will simply not be possible to move the gas to another station. If the pressure in the house network is too high, at the final point - the burner, the gas mixture cannot be mixed with oxygen in the right proportion to maintain combustion, and not provoke an explosion.
Gas pipelines are classified according to the pressure. And since it is constantly maintained, the gas is "associated" with this value.
Distinguish main and distribution gas pipelines.
Trunk - through such a pipeline, the gas mixture is transmitted over long distances. With a certain frequency, gas compressor stations are installed here, which maintain the required level. The termination point for the highway is the local distribution station. By the level of pressure, 2 types are distinguished:
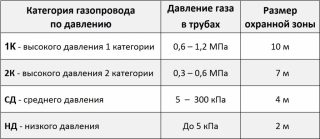
- backbone networks 1st class - with working pressure from 2.5 to 11.8 MPa inclusive;
- 2 class - supported by the standard 1.2-2.5 MPa.
Distribution - through the pipeline, gas is delivered from the stations to the end consumer - in-house networks. Distinguish:
- Category 1 - household gas is transferred under pressure from 0.6 to 1.2 MPa;
- category 1a – more than 1.2 MPa;
- Category 2 - 0.3-0.6 MPa.
Residential buildings are traditionally equipped with the lowest pressure networks. However, with the advent of gas boilers, the situation has changed somewhat. To satisfy the need for gas, a gas pipeline with average rates is supplied to residential multi-storey buildings.
Units
- 1 mm. rt. st - this unit is very descriptive, especially when a liquid pressure gauge is used for measurement.
- 1 atm - the unit of measurement is more traditional. The first quantity that could be compared with something was atmospheric pressure. A value calculated from absolute zero is called absolute. Hence, the overpressure is equal to the difference between the absolute and atmospheric values. When the vacuum changes, it is determined how much the level in a certain limited volume - the pipeline - is less than the atmospheric one. This value is called vacuum pressure.When repairing or inspecting indoor networks, the vacuum gauge is measured in the smoke removal system, and the excess pressure is measured in the gas pipeline.
- 1 bar - a unit more common in Europe. 1 bar equals 100,000 Pa.
- 1 Pa - the unit of measurement adopted in the SI system. It is inconvenient because it is too small - only 1 newton per 1 m². When inspecting gas pipelines, a large unit is used - 1 MPa, equal to 1,000,000 Pa(pascals).
Units can be easily converted to each other using an online calculator.
What affects the gas pressure in the pipes

For normal operation of gas equipment, gas must be supplied under the pressure for which it is designed. If it is a distribution station in a workshop, the head in the pipes must be high. However, an ordinary user - a resident of an apartment or a private house - has to deal only with a low or conditionally average value in distribution networks.
In practice, there are 3 situations.
- Average gas pressure - blue fuel is supplied to the nozzles and burners at normal pressure. At the same time, the gas in the correct proportion is mixed with oxygen from the air and burns, providing heat.
- Above normal - some of the gas does not burn. Either accumulates, or oxidizes only to carbon monoxide. This can lead to poisoning, fire, or even an explosion.
- Low gas pressure - burns out completely, but is supplied in insufficient quantity, as a result, the fire on the burner cannot be made intense. The heating boiler does not generate enough heat.
If the pressure is too low, the gas equipment is turned off.
Pressure measuring instruments
The head in the main or house pipeline is measured using pressure gauges. The devices differ in measurement accuracy, principle of operation, cost, level of security.
By type of pressure
You can measure both gauge and vacuum pressure. According to this parameter, manometers are divided into 3 types.
- Absolute pressure - measure the absolute value, from absolute zero.
- Pressure gauges for measurement excess pressure - the difference between absolute and atmospheric. Most of the models fall into this category.
- Vacuum meters - determine the level of vacuum of the gas mixture.
There are also expensive options that are more commonly used in production: pressure gaugesmeasuring the slightest changes in excess pressure, thrust-pressure gauges that determine the level of rarefaction with the same accuracy.
By the principle of work
According to the mechanism of action, the following types are distinguished.
- Deformation - a tubular spring device acts as a sensitive element of the device. The gas pressure in the gas pipeline affects the inner surface of the tube. It is deformed, and the magnitude of the pressure is calculated from the magnitude of the deformation.
- Mechanical - direct conversion device. The pressure displaces the measuring element - the free end of the spring in this case, the leash transfers the displacement to the gear selector and the arrow on the scale moves along the marks.
- Electrocontact - an improved version of the mechanical one. If the arrow reaches the maximum allowable value during measurement, the circuit is closed and the sensor triggers an alarm. The accuracy class of such devices does not exceed 1.5.
Deformation Mechanical Wiring - Self-recording models - pressure gauge with disc diagram. It is designed to track the dynamics of indicators in a boiler room, for example, and is not used in everyday life.
- Deadweight - consists of a device for creating pressure - a piston, a measuring system and calibration weights. These models can operate over a very wide range depending on the setting and are often used to adjust other gauges.
- Liquid - "classic" U-manometer, consisting of communicating vessels.The value is determined by the liquid level.
Deadweight Liquid Self-recording
Other devices are also produced - with a higher accuracy class, but there is no need for them in everyday life.
Varieties of pressure gauges
Flowmeters are distinguished by other features. Meters are needed in different areas where very different values are determined. In this case, the measurement accuracy will also be different.
Accuracy class
This is understood as permissible error tolerance measurements from measurements on the scale of the device. The indicator is indicated on the dial. When buying a device, you need to pay attention to this.
Pressure gauges with an accuracy class are supplied to the Russian market: 4, 2.5, 1.5, 1, 0.6, 0.4, 0.25, 0.15. In foreign countries, there is also a variant with a class of 1.6.

By appointment
The classification is as follows.
- General technical - manometers for the determination of excess and vacuum pressure in any gaseous medium that is not corrosive to the material of the device. They are used to estimate gas consumption in a network with low compressible gas and to determine the flow rate of LPG in a cylinder.
- Special - designed for measurement in a specific part of an aggressive gas environment.
- Reference - designed for checking and calibrating other pressure gauges.
Gas cylinder pressure gauges used in private homes should be checked at least once a year. This procedure is performed using a reference pressure gauge.
What should be the gas pressure in the pipes
- Main gas - in the mains of the 1st class it is supported from 2.5 to 11.8 MPa, in the pipeline of the 2nd class - from 1 to 2.5 MPa.
- Autonomous system - the gas pressure in the gas pipeline of a private house must be in the range from 3 to 6 bar. The pressure gauge is installed on the gas tank and evaluates the flow rate. If the reading falls below 1.5 bar, call the LNG carrier for refueling. After the gearbox, another analyzer is often installed. The standard reading at this point is 37–39 mbar. Attention must be paid to the constancy of the figure. The pressure gauge at the basement inlet - the third control point of the system, should show the same value as the gauge near the gearbox - 37–38 mbar.
- In an apartment and a private house - the standard is 0.3–0.6 MPa. Recently, medium pressure networks are sometimes brought to buildings - from 0.6 to 1.2 MPa. This is due to the widespread installation of gas boilers for heating.
The pressure gauge allows you to control the pressure in the intra-house network and take timely measures in case of equipment breakdown or leakage.
Low blood pressure reasons
Low pressure in the gas pipeline, as a rule, is associated with some kind of current work on the line, connection of a new consumer, reinstallation of pipes, replacement of equipment. The gas pipeline is an extremely reliable system, it rarely needs to be repaired. However, during repair work, individual fragments are turned off and this can also cause a decrease in the indicator. The tenant of the apartment or the owner of the house cannot influence the situation.
If it is installed in a private dwelling autonomous gas supply, pressure reduction may be due to several reasons. The most commonplace - emptying the gas tank... If less than 20% of the gas remains in it, the latter is supplied at a very low head. The same picture is observed at clogged pipes, overflow of the condensate trap, freezing of the gearbox... In the first case, you should look at what the level gauge indicates. If the scale shows 20-25% fullness, you need to call the gas carrier and fill the gas tank.
In all other cases, you must contact specialists, only they have the right to check and repair the system.