The main gas pipeline is designed to transport natural gas from production sites to gas distribution pipelines, and then, through building pipes, to end consumers. The system has its own construction rules, operating standards and standards of use.
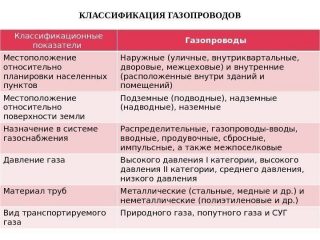
- Gas distribution systems
- General requirements
- Gas reduction and metering points
- Reserve and cylinder LPG plants
- Gas filling stations and LPG points
- Outdoor gas pipelines
- Overground
- Underground
- High and low pressure
- Crossing water barriers and ravines, railways and highways
- Distances to buildings and structures, other engineering routes
- Requirements for gas pipelines in special conditions
- Restoration and repair
- Internal gas pipelines
- Gas distribution
- Equipment
- Crimping
- Safety engineering
Gas distribution systems
The complex is equipped special devices to create and maintain the required pressure inside the pipes, and also:
- instruments for measuring the consumption of blue fuel;
- shut-off valves in case of a leak or an accident on any branch of the gas pipeline;
- communication devices;
- alarm.
The main elements of the system are gas distribution networksthrough which the fuel is directly transported.
General requirements
- The need to deliver fuel to consumers in the right amount and certain parameters.
- Construction and design new facilities of the system, as well as the reconstruction of old ones, should be carried out in accordance with the existing schemes developed as part of regional, interregional and federal gasification programs.
- Inner diameter the pipeline should be calculated based on the peak maximum gas consumption in the region.
- Quality natural gas is determined by the standard GOST 5542 - liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
- Systems must be designed to provide maximum level of protection during the operation of gas distribution networks.
- Pipe laying carried out taking into account hydrogeological conditions.
- Various pipeline deformations, for example, temperature, are unacceptable.
- Special requirements of SNiP provide for construction standards in seismically unstable regions.
- Steel structures must be protected against rust, soil corrosion and stray currents.
- Steel structures located under highways, must be protected by additional technical means to avoid punching or puncture.
- For an underground gas pipeline, steel and polyethylene pipes, for aboveground and ground - only steel.
- There are standards for steel quality, from which pipes for gas transportation are made. They must be taken into account.
- Impact strength steel for regions where the temperature can drop below 40 degrees Celsius, should be at least 30 J per cm².

Gas reduction and metering points
- emergency shutdown of fuel supply;
- gas consumption metering;
- maintaining pressure regardless of the inlet pressure;
- reduction (decrease) of inlet pressure.
Distinguish between industrial and home points for gas reduction. Equipment is also classified:
- by the number of outputs - one or more;
- by the number of reduction lines - only main, main and backup, with two lines configured for different pressure, with two backup, with two main and two backup, with sequential pressure reduction, with one or two outputs.
Gas control points of two or four lines are divided into installations with sequential or parallel regulation. By outlet pressure - the same or different. In addition, the points have different throughput.
Reserve and cylinder LPG plants
Liquefied petroleum gas can serve additional reserve fuel for installations fueled by natural gas. LPG is cheaper than diesel fuel or fuel oil, as well as coal, but this practice is not yet widespread in Russia.
Low running costs... The advantage is that LPG does not need to be heated at low temperatures. The transition to the usual form takes place thanks to mixing systems.
Fuel reserve necessary for the operation of boiler houses in socially significant facilities - schools, hospitals, kindergartens.
LPG can be stored in tanks - aboveground or underground - as well as in cylinders. The tank installation must be equipped with a regulator of pressure, volume and residual gas inside, shut-off valves, pipelines for each phase - liquid and vapor.
Must follow installation rules aboveground and underground tanks to ensure their stable position for the entire service life. It is desirable to have at least two tanks in the installation. If only one works, according to the operating rules, a long break in the consumption of LPG should be allowed - at least a month.
Total capacity an underground standby unit - 300 cubic meters. Overground - from 5 to 20 cubic meters. One underground tank can hold from 50 to 100 cubic meters of LPG, ground - from 5 to 10.
LPG cylinder plants subdivided:
- on complexes individual useconsisting of two cylinders;
- group, consisting of several cylinders - usually up to 10 - 12 pcs.
Different types of steel cylinders - with valves, shells, as well as with various combinations of these elements.
- steel cylinder for LPG;
- shut-off valves - valves, angle valves;
- pressure regulator;
- residual gas pressure gauge inside;
- PSK valve;
- low and high pressure pipelines.
Balloon installations can be located both inside and outside the building. They are connected to each other using rubber hoses or a metal manifold. The volume of one cylinder varies depending on what area needs to be heated: for residential buildings volume up to 1 cubic meter, for industrial facilities - up to 1.5 cubic meters.
Gas filling stations and LPG points
Gas filling stations are designed for storage of liquefied petroleum gas, distributing it among cylinders and supplying it to consumers... There may also be equipment for refueling vehicles.
Stations are usually built away from residential areas, but so that a fire station is located nearby, as well as there are convenient approaches to the facility. The nearest forest belts must be at least 50 meters away. The ground cover is not flammable.
The filling station should be equipped with parking areas for disembarking passengers.
Outdoor gas pipelines
- outdoor - among them are street, yard, intra-quarter, inter-workshop;
- internal;
- underwater;
- surface;
- aboveground.

An external gas pipeline is considered to be laid to the outer edge of the building. For its installation, there are special SNiP rules:
- laying on the walls of buildings is allowed if pipe pressure does not exceed 0.3 MPa;
- pipes high pressure are laid over the windows of the upper floors, and only in non-residential buildings;
- gas pipeline cannot be installed next to the power lineif it is not in a steel pipe;
- if a power line intersects with a gas pipeline, it must be located level above;
- the distance between the gas pipeline and other pipes is from 100 to 300 mm - depends on the diameter;
- must be shut-off valvesto turn off the entire gas pipeline or its section;
- when combined placement of different pipes must be provided Free access to each type of communication.
The construction of gas pipelines in basements, as well as their entry into the elevator, waste bin, transformer station and other utility rooms, is not allowed.
Overground
Accommodation is possible:
- on columns or overpasses;
- in boiler rooms or other industrial buildings for industrial purposes;
- on blank walls or near non-opening windows;
- on bridges made of non-combustible materials - in this case, the pipes must be seamless or electrically welded;
- on the walls of the roof of buildings.
Transit laying a gas pipeline with any pressure on the walls and roof of public buildings is not allowed. Also, you cannot build a gas pipeline. On Bridgemade of combustible materials.
Overhead gas pipelines can cross ravines, rivers, road, rail or tram tracks on their way.

Special requirements for laying a gas pipeline are indicated in SNiP regarding subway lines. In this case, large-scale accidents due to sparks and gas ignition are possible if a leak occurs.
Underground

The choice of the route for the underground gas pipeline should be selected based on heaving of the soil and other geological features, as well as the corrosiveness of soils in the region, the presence of stray currents.
With a close location of aboveground and underground gas communications, it is necessary to use seamless or electrowelded pipes, especially if, according to technical specifications, the distance between them is reduced by 50%.
Underground gas pipelines at the points of exit and entry into the ground are cases... If there is no danger of damage to the pipe, the installation of the case is not necessary.
The joint laying of the gas pipeline and electrical lines for its maintenance is carried out in accordance with the PUE - the rules for the installation of electrical installations.
It is possible to lay underwater crossings of an underground pipeline through rivers. In this case, the installation is carried out in the narrowest but evenest stretch with gentle non-washed slopes. Avoid rocky areas.
Underwater gas pipeline sections are usually laid in 2 branches with the same bandwidth - in case any of them are damaged.
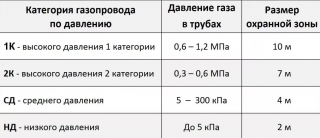
High and low pressure
- gas pipeline low pressure - it is used to supply blue fuel to residential buildings, administrative centers, utilities and household enterprises, the working pressure usually does not exceed 0.005 MPa;
- gas pipelines withmedium pressure - for servicing industrial facilities, gas control facilities, operating pressure from 0.005 to 0.3 MPa;
- high pressure category 2 - from 0.3 to 0.6 MPa to provide gas to large industrial enterprises, as well as gas pipelines with lower pressure;
- high pressure gas pipeline category 1 - from 0.6 to 0.2 MPa - for fast delivery from production sites through gas distribution networks to consumers.
In turn, the main gas pipelines are divided into 2 pressure class:
- 1 includes pipes in which the pressure is from 2.5 to 10 MPa;
- to 2 pipes with pressure from 1.2 to 10 MPa.

Crossing water barriers and ravines, railways and highways
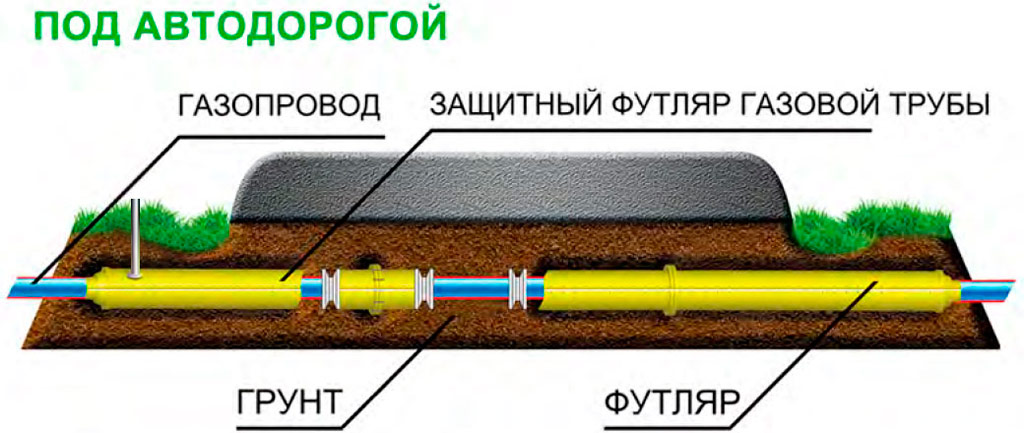
Underground gas pipelines of any pressure level that cross rail, road or tram tracks are required put in a case... The question of the need for arranging the case and its level of strength, as well as the depth of laying, is decided by the design organization in each specific case.
In such places, the wall thickness of the steel pipeline should exceed the calculated by 2 - 3 mm... If polyethylene pipes are used, their safety margin must be at least 3.2 in the city.
Gas pipelines in places of underwater crossings are being laid with deepening into the bottom. When calculating for ascent, sometimes ballasting of the pipe is necessary.
The pipe is laid by the method directional drilling... Laying of pipes - 2 m below the estimated bottom profile.
Pipes used for underwater areas must be with thickened walls - more than the calculated thickness by 2 - 3 mm, but not less than 5 mm. It is possible to use PE pipes with a safety factor of 2.5 if the gas pressure does not exceed 0.6 MPa. Stop valves are installed 10 m from the proposed border of the crossing.
Distances to buildings and structures, other engineering routes
When constructing above-ground or above-ground gas pipelines, they should be taken into account. location relative to residential, industrial facilities, as well as buildings of a special type. Distance is indicated in meters.
| Types of buildings and structures | With pressure up to 0.005 MPa | Pressure from 0.005 to 0.3 MPa | 0.3 to 0.6 MPa | 0.6 to 1.2 for natural gas |
| Buildings of category A and B - boiler rooms, outbuildings | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 |
| Buildings of category B1-B4, D, D | _ | _ | _ | 5 |
| Residential, administrative, public buildings, with fire hazard class C0, C1 | _ | _ | 5 | 10 |
| The same buildings, but with fire hazard class C2, C3 | _ | 5 | 5 | 10 |
| Open ground warehouses with flammable liquids, volume: | ||||
| 1000 to 2000 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| 600 – 1000 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| 300 – 600 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| Less than 300 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Flammable liquids, volume: | ||||
| 5000 to 10000 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| 3000 — 5000 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| 1500 — 3000 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| Less than 1500 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Closed above ground storage facilities for flammable and flammable liquids | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Railway and tram tracks from the bottom of the embankment slope | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Underground communications - sewerage, water supply networks, heating systems, electrical cables | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Highways from a curb or ditch | 1,5 | 1,5 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| Open switchgear fence | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Overhead power lines | In accordance with the PUE | In accordance with the PUE | In accordance with the PUE | In accordance with the PUE |
Requirements for gas pipelines in special conditions

The set of rules "JV Gazosnabzhenie" provides for the construction of pipelines in especially unfavorable conditions:
- on heaving, subsidence, swelling, permafrost, rocky, eluvial soils;
- with possible seismic activity above 6 - 7 points;
- in karst and undermined territories;
- in cities with a population of over 1 million people and seismicity above 6 points;
- with a residence of more than 100 thousand people and seismicity above 7 points.
In such conditions, a negative impact on the gas pipeline is possible. In the case of a large number of people, it is necessary to provide spare gas supply line, located at the other end of the city - in case of damage to the main one. In this case, pipelines of medium and high pressure must be looped back and provide for the disconnection of the segments by locking mechanisms.
Pipe crossings through rivers and ravines up to 80 m wide in seismically active regions should be carried out by air... At the same time, the pipe supports and stoppers must ensure its sufficient mobility in order to avoid dropping from the support during an earthquake.
Allowed to use polyethylene gas pipes with a safety margin of at least 3.2 in a protective shell. In this case, welded joints are checked by physical methods for damage.
For LPG tanks located underground, surface gas pipelines for the liquid and vapor phase are provided.
Before the construction of the pipeline, a hydraulic calculation of the gas pipeline is carried out to correctly select the diameter of the pipes and ensure uninterrupted fuel supply with the specified parameters.
Restoration and repair
Repair of equipment and replacement of a pipe section can be carried out two ways:
- when the technological process is stopped, when the gas supply stops in this area;
- without stopping gas pumping.
Repair workwhich are most often performed:
- replacement of a worn-out section of a pipe;
- bypassing the defective area for repair;
- repair or replacement of the shut-off valve;
- installation of additional pipeline branches;
- installation of remote control devices, alarms, accounting equipment;
- installation of a plug with subsequent dismantling of the pipeline.
Repair technologies allow working without stopping the technological process on the branches of the main pipeline with a pressure of up to 10 MPa and a temperature of up to 370 degrees.
Internal gas pipelines

Internal gas pipelines are a system of pipes and various control devices that transport gas to heating units inside a house or apartment... Internal wiring is connected to domestic low pressure gas pipelines with pressure not more than 3000 Pa.
When connecting intra-apartment wiring to networks with medium or high pressure, the presence of reducing equipment is required, for example, a cabinet-type gas control unit.
Every facility that consumes gas must be equipped with metering devices consumption of blue fuel in accordance with the requirements of regulatory documents of the Russian Federation.
Gas distribution
First compiled project documentation... The place where the pipe enters the house is taken into account - it must be a non-residential premises or a boiler room. It is easiest to conduct further wiring around the house from it. Through a hole drilled in the wall, into which a steel sleeve (case) is inserted, the pipe is introduced into the house.
If the layout of the building does not allow the introduction of the pipeline into the non-residential premises and the pipe passes through the living rooms, this method is called transit... In this case, it is not allowed to install shut-off valves in such areas, as well as make threaded connections.
For safety reasons, the pipe is laid inside in an open way. This degrades the aesthetic characteristics, but opens up access for timely repair or shutdown of the fuel supply.
It is possible to lay pipes in grooves and close them with ventilated screens, which can be easily dismantled upon hearing the smell of gas in the room.
The pipes are connected by electric welding. This is the most reliable way.
Do not install gas distribution in ventilation pipes.

Equipment
- mini boiler room;
- gas consumption meters - meters;
- equipment for the use of liquefied gas;
- control systems, gas leak alarm.
In addition, there are gas boilers, stoves and heating devices that run on blue fuel.
Crimping
Gas pipeline pressure testing is necessary for the further safe use of the system. It is carried out by pumping air into the system under pressure. If after a while the pressure gauge reading drops, there is a leak in the gas line.
Safety engineering
When installing an internal gas pipeline, it is prohibited:
- lay thin-walled gas pipes through door or window openings;
- lay pipes below 2 m from floor level;
- make flexible pipe sections longer than 3 m;
- carry out wiring in hard-to-reach places;
- if the kitchen wiring is made in ventilation, this area cannot be combined with the general ventilation system;
- the ceiling and walls near the gas pipe must be made of non-combustible materials;
- steel brackets and rubber-lined clamps are used as fasteners.