A practical and accurate gas pressure gauge is essential for measuring fuel pressure in cylinders and other containers, as well as in gas pipelines. To choose the right device, you need to familiarize yourself in advance with its structure, principle of operation, classification, installation and operation rules.
- The device of pressure gauges for measuring gas pressure
- Pressure gauge requirements
- Classification of pressure gauges by type of measured pressure
- Functional classification
- Aquatic
- Electrical
- Digital
- Others
- Functional classification
- General technical
- Reference
- Special
- Instrument selection criteria
- Manometer installation
The device of pressure gauges for measuring gas pressure

The gas pressure gauge helps you know differential, gauge or full pressure values for general technical purposes. Such devices are divided into several categories according to the characteristics of work, purpose and type of measured data. The mechanism of the standard type includes a case with a protective glass, a Bourdon tube, a lever-gear train and a scale with an arrow.
In the process of measuring indicators, the pressure inside the device acts on the tube from the inside and displaces its loose end. After that, an arrow comes into motion, stopping at the desired mark. Good regulators for gaseous media have a higher level of resistance to vibrations with a frequency that cannot exceed 10-55 Hz, an amplitude with an offset of up to 0.15 mm, and accuracy classes ranging from 1 to 2.5.
Pressure gauge requirements

The exact indicators, in accordance with which the device takes measurements, directly depends on the correctness of its selection and installation in combination with operating conditions. The selection must take into account the physical and chemical properties of the measuring medium and the expected pressure data. For example, for conditions with a high content of corrosive gases, it is better to purchase special devices made of durable materials. The diameter of the pressure gauge glass must be at least 10 or 16 cm if it is placed at a distance of 2 to 3 meters.
Devices used in gas environments have different body shades, for example, blue indicates operation with oxygen, yellow with ammonia, red and black are suitable for combustible and non-combustible gases, respectively. According to safety rules, it is not recommended to use pressure gauges with an expired verification period, as well as in the absence of a seal or a mark about this procedure. If the arrow of the device does not return to zero after turning off, it is also considered inoperative.
Any damage, such as deformation of the case or broken glass, indicates that the regulator needs to be replaced, as it directly affects the accuracy of the meter.
Classification of pressure gauges by type of measured pressure
Classification of regulators based on the type of pressure:
- vacuum meters and manovacuum meters;
- barometers;
- pressure gauges;
- differential pressure gauges;
- traction meters.
The principle of operation of any of them depends on the structure, in addition, it must be borne in mind that the meters are divided into categories within a single class, taking into account the level of accuracy.
Devices using the vacuum principle are designed for rarefied gases. Pressure gauges are able to determine the parameters of the limiting pressure with indicators up to 40 kPa, traction meters up to -40 kPa.Other differential devices help to find out the difference in readings at any two points.
Barometers are most often used to clarify only the atmospheric pressure in a particular environment.
Functional classification
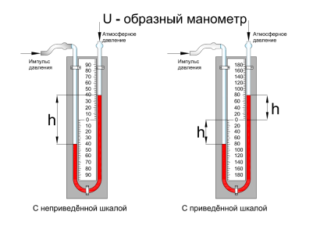
Aquatic
Water devices operate on the principle of balancing a gaseous substance with pressure, which forms a column of liquid. Thanks to them, it is possible to refine the sparsity level, difference, redundant and atmospheric data. This group includes U-type regulators, the design of which resembles communicating vessels, and the pressure in them is determined taking into account the water level. Compensation, cup, float, bell and ring gas meters are also classified as water ones, the working fluid inside them is similar to the sensitive element.
Electrical

This domestic gas pressure measuring instrument converts it into electrical data. This category includes strain gages and capacitive pressure gauges. The first ones change the readings of the conductive resistance after deformation and measure indicators up to 60-10 Pa with minor errors. They are used in systems with fast processes. Capacitive gas meters affect the moving electrode in the form of a membrane, the deflection of which can be determined by the electrical circuit, they are suitable for systems with accelerated pressure drops.
Digital
Digital or electronic devices are high precision devices and are most often used for installation in air or hydraulic environments. Of the advantages of such regulators, they note the convenience and compact size, the longest possible service life and the ability to calibrate at any time. They are mainly used to monitor the condition of vehicle components. In addition, digital gas meters are included in the fuel lines.
Others
In addition to regulators with standard characteristics and settings, other types of instruments are used to obtain accurate data. This list includes deadweight gas meters, which are original samples for checking similar devices. Their main working part is a measuring column, from the state and accuracy of the readings of which the magnitude of the error changes. During operation, the cylinder is held inside the piston at the desired level, at the same time, on the one hand, it is affected by the calibration weights, on the other, only the pressure.
Functional classification

According to its purpose, a pressure gauge for high or low pressure gas can be general technical, reference or special.
General technical
Such devices help to measure indicators of maximum and vacuum pressure and are used most often in production, including in the process of technological work. They are suitable for measurements in gaseous media, and they must be non-aggressive for copper alloys at temperatures up to 150 degrees. These devices can withstand vibration vibrations ranging from 10 to 55 Hz, amplitude up to 0.15 mm, their accuracy class varies from 1 to 2.5.
Reference
Instruments of this type are designed for the purpose of testing, adjusting and calibrating other devices to provide the most accurate measurements. Such pressure gauges for measuring gas pressure are divided into three categories, their list includes control and exemplary regulators, as well as their counterparts intended for ordinary and composite cylinders. Gas meters of the first type are used most often and help to control the reliability of these devices at the installation sites, their operating limit ranges from 0.06 to 1600 bar.
Special
Special regulators create for a specific type of gas, as well as the environment formed by it.The bodies of such devices are painted in a variety of colors, taking into account the type of substance for which they are intended. Pressure gauges for this purpose are made of durable materials that can withstand exposure to gaseous media. They are considered the most common and have a simple design.
Instrument selection criteria

When selecting a device, you need to take into account all the requirements for pressure gauges used in the gas industry. The main criterion is the measuring range; during the selection process, it must be remembered that the standard pressure should be within the range from 1/3 to 2/3 on the measurement scale. An ideal option would be a regulator with a scale of up to 0-10 atm. In second place in terms of importance is the indicator of the accuracy class, which shows the normal error of the measurement results during the operation of the device.
If desired, this indicator can be calculated individually, for example, if the device is designed for 10 atm, and its class is 1.5, the error indicator of such a gas meter is 1.5% of the total scale. According to the type of fitting of the nozzle, the pressure gauges are radial or end, in addition, the regulators are supplemented with metric or pipe threads. When choosing a device, you need to take into account its calibration interval, it will be better if it is two years.
Appliances for household use may not go through the calibration procedure, but it is mandatory for devices used in factories, gas pipelines, heat or furnace type points, as well as similar facilities.
Manometer installation

In order for the gas meter to measure and regulate the pressure correctly, it is placed in areas where it will be as easy as possible to take readings, carry out maintenance and repair of the device. There are maximum intervals between the regulator and the walls that must be observed during installation. If the device is placed at a height of up to 2-3 meters, the diameter of its body must be at least 160 mm.
In addition to the mounting structure of the pressure gauge, a three-way valve is installed between the pipe and the regulator itself. If the unit is operated in conditions due to which its functionality can be affected by high temperature, precipitation or other external factors, it is additionally protected with siphons, buffer elements or other protection, as well as thermal insulation, if necessary.