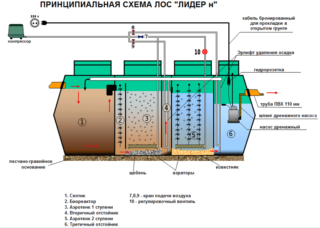
Contaminated domestic, household and industrial wastewater is treated before being discharged into natural water bodies. At the first stage, mechanical cleaning of debris is carried out using grids and nets. Then the liquid fraction is sent to the settling tanks, where solid organic waste is separated, which makes up 35% of the pollution. Waste with dissolved organic matter is sent to aeration tanks - tanks with a rectangular horizontal section filled with activated sludge, where further biochemical water purification takes place.
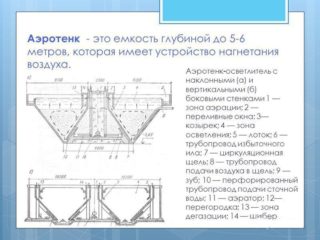
Types and principle of operation of aeration tanks
At the outlet of the aerotank, water containing a minimum amount of dissolved organic matter, together with the sediment that forms during the life of microorganisms and bacteria, passes through a system of sedimentation tanks. The sediment from the secondary sedimentation tanks is sent to the digester, and then replenishes the amount of activated sludge. After the final sedimentation tank, clean water is discharged into the reservoir.
The technological scheme with a clarifier - a rotator with natural aeration - retains pollution more efficiently and withstands peak loads than the use of conventional vertical clarifiers.
The principle of operation of mechanical aerators is to capture air from the surface while mixing the liquid, pneumatic - in the supply of air from the compressor. Combined aerators allow mechanical devices to crush air currents in water.
The main factors affecting the cleaning system:
temperature regime;
- the continuity of the supply of source water;
- oxygen saturation;
- toxic substances;
- acidity level of the environment.
To eliminate ammonium nitrogen from industrial or household wastewater, a nitrification process is used with the help of aphtotrophic bacteria that feed on inorganic carbon. As a result, nitrites and nitrates are formed in the water, which are removed with the help of bacteria - denitrifiers, heterotrophic bacteria decomposing harmful compounds to free nitrogen and using bound oxygen for their vital activity.
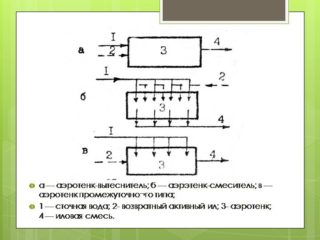
Depending on the method of supplying wastewater and activated sludge, and removing purified water, several types of aeration tanks are distinguished.
Mixing aeration tanks
Designed for the treatment of industrial effluents with a high concentration of contamination - up to 1000 mg / l. They allow for cleaning with an uneven flow of wastewater and a change in their composition, the principle of operation of aeration tanks for wastewater treatment is to supply water and sludge through holes along the entire length of the tank. The purified water is evenly discharged. This achieves better mixing of sludge with source water, which accelerates biochemical treatment.
Aeration tanks-displacers
The main disadvantage is a decrease in the quality of cleaning with a sharp change in the content of organic matter and toxic substances. With a uniform flow of wastewater, the use of displacement aeration tanks is preferable due to their small volumes and simplicity of design. They are subdivided into sectioned and corridor.
The first ones are used in aerotanks over 60 m long. At regular intervals, the corridors are separated by partitions to prevent a change in the direction of movement of the source water.
Aeration tanks-displacers are called corridor tanks when the ratio of the width of the tank to its length is 1:50. If the width is 6 m, then the length is respectively 300 m, with a width of 9 m, a length of at least 450 m. For compactness, two-corridor aeration tanks are made if the tank occupies more than half of the volume of treatment facilities. The use of three-corridor structures allows working without sludge regeneration.
Aeration tank displacer with regenerator
For a more intensive process of organic matter oxidation, displacer aeration tanks with built-in regenerators are used, where the dosage of activated sludge is increased by two to three times, which makes it possible to increase the quality of cleaning.
Aeration tank in the septic tank
Owners of private buildings make an active septic tank for effective wastewater treatment. It requires a large volume, has a simple design and high purification of domestic wastewater - up to 99%. The productivity of aerobic microorganisms is higher than that of anaerobic bacteria present in cesspools. To increase the number of aerobes, an aeration system is connected to the septic tank and a compressor is installed.
The quality of wastewater clarification in aerotanks must comply with SNIP 2.04.03-85.
Installation and start-up of the cleaning system
The installation begins with digging a pit for an aeration tank. To create a pillow, a layer of sand up to 20 cm high is poured onto the bottom. After that, a reservoir is installed. At the same time, the tank is filled with water and the tank is backfilled, and the water level should be 15 cm above the ground level to prevent the tank from deforming under the pressure of the bulk soil.
At the next stage, communications are laid, a compressor is installed and connected to the aeration system. The entire structure is covered with earth. After checking the operation of all systems and the control start-up, the aerotank is put into operation.
Advantages and disadvantages
- high quality wastewater treatment at high speed;
- compactness combined with simplicity of design;
- full load of equipment;
- it is not necessary to insulate the object, since redox reactions go with the release of a large amount of heat;
- there is no unpleasant smell.
Minuses:
- high price;
- electricity costs for the aeration system;
- the need for operating personnel for maintenance.
For the normal functioning of aeration tanks, a continuous supply of wastewater with dissolved organic substances is required to feed microorganisms. When the system stops in the absence of oxygen, decay processes begin, aerobic microorganisms die.
If the air supply is reduced, deposits may form.The minimum oxygen concentration to maintain the vital activity of microorganisms should be above 0.2 mg / dm3, for effective biochemical purification - 0.5 mg / dm3.
The aeration system is selected at the design stage. The calculation of the volume of aeration tanks is determined on a calculator from the product of the maximum flow rate in peak hours by the time the waste water is in the tank. The speed and quality of cleaning is influenced by the size of air bubbles supplied from the compressor. The smaller their size, the better the oxidation process is. There is an active increase in biomass, microorganisms better tolerate the effects of toxic substances. On the other hand, the fine-bubble fraction does not allow sufficient mixing of the activated sludge, which leads to the appearance of deposits in the "dead zones".
To increase the intensity of mixing, incentive nozzles are installed on the walls of the aeration tank, creating a turbulent circulation of flows. They increase the rate of rise of small bubbles and reduce the interaction time between effluent and activated sludge. Aeration tanks with a wall aeration system work more efficiently than models with an aeration unit at the bottom of the tank.