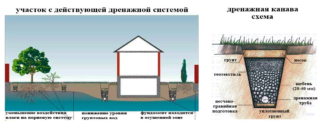
Drainage pipes, also called drains, are designed to drain excess moisture from the soil. Pipe-based drainage is the most practical. All elements are buried in the ground, they take water from the ground, while not spoiling the landscape.
Principle of operation
Products for diversion are devoid of perforations. They have a different working principle. They are needed to empty the drainage reservoirs. The water goes into the collector devices or specially equipped ditches. A characteristic feature of such highways is that they can be buried more than 10 m into the ground.
Pipes are also often laid in storm ditches near the road, connecting them to a common drainage system. This will provide a comfortable passage for vehicles.
A variant of moisture-collecting products are models with a filtering effect due to winding with coconut fiber or geotextile. The filters keep suspended solids out, preventing the formation of plaque, which increases the life of the entire system. This is especially important in clayey areas where groundwater contains many impurities.
Types and design features of drainage pipes

Drainage products are classified by price and design characteristics. But first of all, you need to pay attention to the material of production.
- Asbestos cement. Most often, pipes are made with cuts on top to get moisture inside. These holes are staggered.
- Ceramics. Clay pipes come with perforations, slots and grooves on the outside for better moisture absorption.
- Expanded clay glass and plastic concrete. These are porous building materials that absorb moisture well. The products do not need punching.
- Plastic. Pipes are made of high or low pressure polyethylene compounds (LDPE or HDPE), as well as PVC.
The lowest price of asbestos-cement products. They pick up moisture well, but are not popular, since it is believed that the material is harmful. In the west, it is prohibited for use. Chrysotile cement products are a variety of asbestos structures. This type of white asbestos is environmentally friendly and does not harm health. In such models, cuts are not made, since the material is porous.
The most popular are PVC and polyethylene pipes. The former are usually not perforated, they are used to drain moisture. They look like sewer pipes. They are quite cheap. The latter are more often corrugated and equipped with moisture-absorbing holes. Such products are flexible, but durable, they can be laid in an area with any landscape. Outwardly, they look like large irrigation hoses.
Pipes made of polymeric materials are made of two types: single-layer or double-layer. The number of layers is chosen depending on the density of the soil.
The most resistant products to external influences are the Softrock systems. Pipe sections are first covered with expanded polystyrene filler, and wrapped on top with geotextile mesh. Such a design prevents the ingress of suspended solids into its pipeline and its freezing, increases the drainage efficiency by 40 percent. Due to the complete readiness of the systems for laying, the labor intensity of the work when arranging the drainage system is reduced.
Flat drainage pipes are gaining market share. They are also referred to as "panel". They are somewhat similar to fire hoses. Similar products are produced with perforation and in a geotextile filter casing. Rectangular products have increased compressive strength, so drainage can be arranged almost at the very surface. This contributes to savings in earthmoving work. Thanks to their compact folding, flat models take up minimal space during transport. Such a drainage pipe works no worse than a round analogue.
For drainage work, simple sewer pipes are sometimes used. They are perforated with their own hands and installed as moisture-collecting drains.
Size range
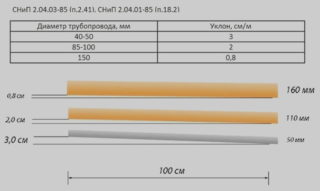
According to GOST, drainage pipelines are produced in lengths of 6 or 12 meters. Flexible options can be longer, they are rolled into coils. Products are also distinguished by diameter - 110, 160, 200 mm.
For systems with a high load, pipes are produced with a large cross-section - up to 300 mm.
In a small area with low groundwater, products with a minimum diameter can be installed. But if the drainage consists of many branches, even in a small area, both large and small sections of the pipeline will have to be used.
Criterias of choice
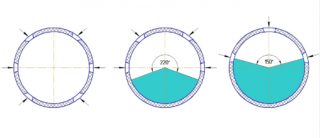
The main criteria for the selection of drainage system elements are the rigidity and location of the perforations.
The first characteristic depends on the depth to which the pipes are laid. They should not deform under a heavy layer of soil. When purchasing pipe sections, they look at the marking, which indicates the stiffness class:
- SN 2–4 are installed to a depth of 3 m;
- SN 6 - up to 4 m;
- SN 8 - up to 10 m.
The depth of the groundwater, the amount of precipitation and the method of installing the drainage main are important. These data are taken into account when selecting a perforation pattern. If holes are made along the entire circumference of the pipe, it is suitable for reducing the level of subsurface sources, drainage of drains after rains and snowfalls.
For "stormwater" choose pipe sections with holes in 1/3 or 2/3 of the circle. Half-circle perforated pipes are used for universal sewerage systems.
The choice of pipeline elements also determines their cost. For a running meter of a perforated pipe with a cross section of 110 mm in a geofabric filter, on average, you will have to pay 55 rubles, 160 mm - 110 rubles and 200 mm - 185 rubles. For panel models, the cost per running meter starts from 75 rubles.
The price of smooth non-perforated drainage pipes for groundwater drainage is lower - it starts at 12 rubles per meter. The highest cost is for a large-diameter drainage pipe (over 200 mm) in a coconut bark filter - from 1000 rubles per meter.
Among Russian manufacturers the greatest demand is for the brands Ruvinil, Naskhorn, Politek, and KamaPolymer. From foreign brands, Polieco, Wavin, Uponor, Rehau are popular.
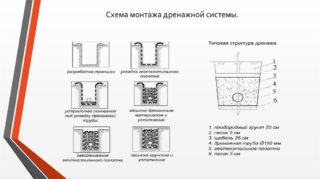
Laying rules
The distance between the drainage lines during their installation is determined by the amount of water on the territory: the more there is, the closer the pipelines are.
Also decide on the location of the inspection hatches needed to check and remove possible blockages. They should be installed in the places where the highway turns.
Before installation, be sure to create a project with a drawing to scale. This allows you to calculate how many and what section and stiffness of pipes will be required for the device of the drainage network.
Stages of laying the drainage pipeline:
- A trench is dug to a depth of at least half a meter and a width exceeding the cross-section of the pipeline by 50 cm.
- A sand cushion 10 cm thick is poured at the bottom.
- Gravel is poured over the sand with a layer of 10–20 cm.
- Pipe sections are laid, connecting with each other and with revision wells.
Burying occurs in the reverse order: a layer of crushed stone, a sand cushion, a layer of soil.
At the final stage, the pipeline is taken out of the boundaries of the site and connected to the catchment. If it is necessary to increase the throughput of the drainage line, a system assembled from several pipes of different sections is laid in the trench.
Errors when installing pipe drainage
- Drains are at a great distance from each other. Systems are installed with a distance of no more than 10 m for clayey areas and 50 m for sandy areas.
- Incorrectly selected trench depth. Such a mistake can lead to water imbalance, which will cause stagnation of moisture in the area. Shallow depths cause the formation of ice plugs, which will lead to flooding of the area in early spring. The pipeline may be above the water level, and it will not be able to enter the drainage system.
- Failure to comply with the slope. If the line is installed strictly horizontally and there is no slope towards the header, moisture will stagnate in the pipeline.
- A large number of revisions. The distance between the inspection hatches must be more than 50 m, otherwise they will interfere with the normal operation of the system.
A typical mistake is an attempt to save on the use of pipes inappropriate for the project for the pipeline, which leads to malfunctions and a significant decrease in the service life of the system. This applies both to the cross-section of the pipes and to the material of production.
Operation and maintenance rules
The drain piping requires a systematic check for dirt build-up inside and cleaning as needed. For this, revision wells are installed in the system. The inspection must be performed at least once every 12 months. An unscheduled drain check is required after heavy rainfall, flooding and flooding.
The fact that the pipes need to be cleaned can be indicated by stagnation of water in the inspection well. There is also a settling of mud, silt, sand.
Scheduled cleaning of the line is performed every 3 years with the correct arrangement of the system and equipment with the necessary filters. Otherwise, cleaning is carried out as soon as it gets dirty. Drains are cleaned in two ways: mechanical and hydrodynamic.
The first option involves crushing solid impurities and mechanical extraction of dirt using a pneumatic unit. In the second method, the line is flushed with water and air under pressure using a compressor and a pump. This option is more expensive but also more reliable.
There is nothing complicated in the drainage device. If everything is done technologically correctly and according to the project, the independently laid system will last more than half a century.