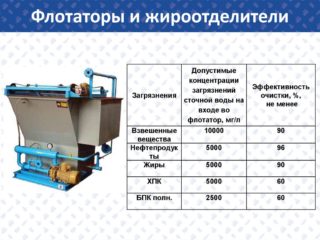
Flotation - removal of finely dispersed impurities not capable of wetting from wastewater using specially created gas bubbles. Dirty foam that forms in this case is on the surface and is eliminated. For work, various types of devices are used - flotation devices. The efficiency of the process is largely determined by their technical characteristics, productivity and automation.
Design and purpose of flotators
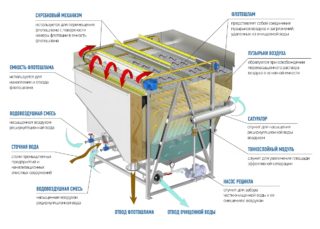
Liquid purification is carried out with the help of block flotation units. The main units of the apparatus are:
- a container with a pump that mixes oxygen with liquid and reagents;
- flotation tank with a valve to eliminate excess air;
- degasser to remove residual oxygen.
Flotation blocks are not used as stand alone cleaning tools. They are used in a complex at treatment plants of industrial enterprises and car washes, since they require preparation - processing of sewage drains mechanically.
Scheme of action
The principle of operation of a flotation plant is quite simple:
- The effluent enters the working tank, where it is enriched with fine air.
- The mixture enters the flotation chamber, where the hydrophobic waste interacts with gas bubbles.
- The layer separating hydrophobic particles and air bubbles gradually decreases and ruptures. This is due to the change in the surface tension of the water.
As a result, dirty foam appears on the surface of the liquid. Its removal takes place using special rake devices.
Flotation in devices is a forced process, when the density of debris is artificially reduced.
Flotation techniques
- mechanical;
- pressure head;
- vacuum;
- biological;
- electrochemical.
Forced flotation is a simple method of wastewater treatment, when reagents are added to the liquid and oxygen is supplied under high pressure using a pump. Bubbles are formed throughout the entire volume of sewage. This method is often used to remove activated sludge from liquids. The technology assumes the presence of a saturation chamber.
This unit is not available in electroflotators. The technique does not require electroflotation and reagents. It involves removing suspended solids from a liquid using an electric current. The electrolysis process is carried out in the electroflotator: hydrogen is released at the cathode, oxygen is released at the anode.
The principle of operation of the vacuum device is to reduce the pressure below atmospheric in the flotation tank. At the same time, air dissolved in water is released.
Biological flotation is the heating of the sludge after primary cleaning with steam and settling it for several days. Bacteria that form give off gas bubbles. Thanks to them, the sludge particles are floated into the foam layer, where they are compacted and dehydrated. Moisture can be reduced by up to 80 percent within five days, allowing for easier post-processing.
Features of mechanical flotation
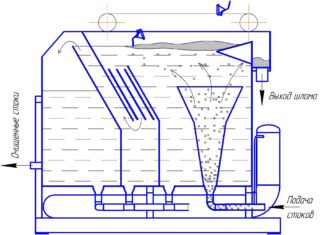
There are several flotation methods for mechanical wastewater treatment:
- The liquid is mixed with a special impeller with blades.This cleansing technique is performed without pressure and is well suited for removing coarse and fibrous impurities from the water - hair, threads, wool.
- Wastewater is discharged into a centrifuge (impeller). There they mix, acquiring a homogeneous structure. When moving, polluted water is enriched with oxygen, small bubbles are formed. They are able to attract even the remains of petroleum products.
- The effluent is enriched with air using special pipes located at the bottom of the receiving chamber. The method is called pneumatic. It is used in the case when it is required to purify drains that are aggressive for their treatment in an impeller or gravity installation.
In pressure treatment, the level of purification depends on the rotation speed of the impellers - the more it is, the better. But you need to calculate the exact acceleration. At a certain stage, streaming turbulence grows, debris flakes can collapse, which reduces the efficiency of the process.
Cleaning of sewage fluids in mechanical flotation units is used when light hydrophobic impurities are present in the fluid - fats, oil residues, oils.
If the effluent contains impurities that require aggregation, a different method should be preferred. Due to significant turbulence, the destruction of pollution molecules occurs, and the quality of cleaning is sharply reduced.
A compromise between the mechanical and pressure method is the saturation of water with oxygen using a porous material. The direction of the air flow here occurs through special plates with slots. The thinner the slit holes in the plate, the less air bubbles and the better the cleaning.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of flotation devices has both advantages and imperfections. The pluses include:
- ease of maintenance of machines;
- budget in most ways;
- high quality and speed of effluent purification.
Using the technique, you can remove most of the fine impurities, but not all. The disadvantages also include the need for additional use of reagents to increase the degree of hydrophobicity of mud particles. In the case of using an electric skimmer, it is necessary to fine-tune the device to create bubbles of the required diameter.
Reagents used
- coagulants - reagents that promote the formation of flakes and are salts of iron and aluminum;
- flocculants (polyacrylamide compounds) - substances that create larger and more stable flocs (floccules);
- acid and alkaline reagents to adjust pH. They are added to water to ensure normal working conditions for the two previous types of reagents.
Pine oil, phenols, and cresol are also used to stabilize foaming. They prevent air bubbles from collapsing, making them elastic. This helps to remove more contaminants from the sewer.
The use of chemical reagents to improve the process requires precise selection of the dosage, which can only be achieved empirically.
What determines the quality of cleansing
The following factors affect the effectiveness of the technique:
- resistance of air bubbles to destruction;
- uniform foam formation;
- the degree of hydrophobicity of particles - the greater this indicator, the more actively they interact with air bubbles.
The size of the bubbles is also important. Large ones float up quickly and do not have time to capture impurity molecules, while small ones are less strong.
The use of the flotation technique is indispensable for purifying wastewater from fats, fibrous inclusions, oil products, and other contaminants that cannot be precipitated. This method is used for cleaning sewers and for mineral processing.