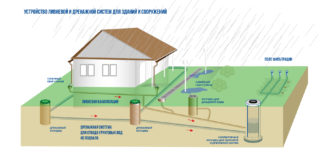
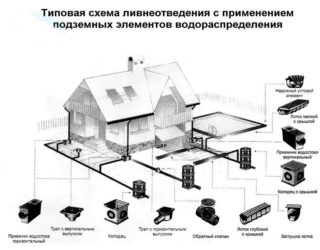
Storm drainage is necessary to protect the roof and foundations of the house, road surface and home ownership. If you know the basic rules for installing a drainage system, you can independently make a storm drain on the site. Conventionally, it includes three stages: catchment, drainage and disposal.
Current requirements for the installation of a storm sewer in a private house
The principle of operation of the rain shower is based on gravity, therefore all its elements - gutters, gutters, pipelines - are installed with a slope towards the sewer wells.
SNiP take into account the slope and depth of pipes, the material for their manufacture, the nature of the soil and the depth of freezing. For the middle strip, laying pipes with a diameter of 50 mm is allowed at a depth of 0.3 m; with a large section - 0.7 m.
If there is evidence of severe freezing of the soil, the depth of the pipeline is increased in order to prevent the formation of ice plugs, which will inevitably lead to damage to the stormwater system.
For pipes of different diameters, SNiP provide for appropriate slopes.
Types and arrangement of storm sewers

According to the device, storm sewage is divided into three types:
- Separate system, in which storm water and reinforced concrete wastewater have a different disposal system.
- Semi-divided network - the drainage system is separate, but the sewer wells are common.
- The system of common fusion of storm water and ZhWO has a common waste water pipeline.
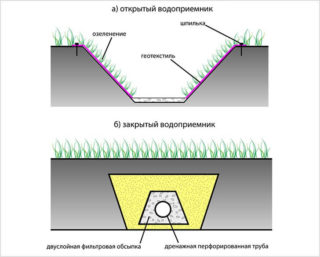
A point rainwater collection system consists of storm water inlets through which water enters the pipes. To avoid clogging the downpour, the grooves and trays are covered from above with gratings that retain tree branches and debris. Sometimes, before entering the drainage system, sand traps are installed.
The urban network has an extensive system that includes pipelines and wells, through which water is directed to the city sewers. The final stage is treatment facilities, after which the clarified water is discharged into reservoirs or soil. The pipes are located at different depths with a slope towards sewer wells with a diameter of at least 1 m. Such a drainage system is called linear. If the terrain does not allow it to be performed on a slope, transfer pumps are installed.
The linear rainfall scheme is more complicated than the point one, it serves to collect water from the roof of the building, door pallets and canal systems in the adjacent area. The external storm sewer, which is located along the paths, consists of rain trays with grates. Its advantages include:
- easy cleaning from blockages;
- simple repairs to replace storm water inlets;
- simplicity of design.
The internal system requires a thorough approach with the calculation of the required volume of the pipeline to collect any amount of precipitation.It involves digging trenches, laying pipes, arranging inspection wells.
Designing and carrying out the necessary calculations
- at the weather station;
- in SNiP;
- in the building company.
Stages of designing the laying of storm sewers:
- The type of soil and the corresponding throughput are determined.
- A storm storm scheme is drawn up, taking into account the relief of the site and the availability of communications in the area.
- The depth of the soil water is taken into account.
- The place of reception is indicated on the plan.
- The drainage area is determined. It is the sum of the moisture-proof surfaces in the selected area, including the roof of the building, asphalt and concrete paths.
The theoretical volume for collecting rainwater is calculated taking into account correction factors and data on the amount of precipitation. If the calculation is wrong, this can lead in one case to an overload of the system, and in the other - to an increase in the cost of the project. Experts advise to make a fivefold reserve in the throughput of rainstorms (based on the average amount of precipitation). For better drainage, pipes are installed at an angle of 4-5 degrees, although with a slope of 1.5 cm, a clean drainage system works quite well.
Choice of materials

The material for pipes, gutters and gutters is selected taking into account the operating conditions and design load. The task of the storm drain is to ensure the integrity and durability of the structure.
Criterias of choice:
- strength - when laying underground, pipes will experience pressure not only from the inside, but also from the outside;
- elasticity to withstand shock loads;
- UV resistance;
- the ability to withstand temperature changes;
- resistance to aggressive compounds.
For the device of external sewerage, cast iron and polymer pipes are used, for inspection wells - reinforced concrete products with a large section. Cast iron pipes are strong and durable, but do not tolerate shock loads. Difficulties arise during their installation and the search for fittings of suitable configurations.
Polymer pipes have a number of advantages:
- strength;
- light weight;
- a wide range of fittings;
- affordable price;
- smooth inner surface with water-repellent properties.
Large-sized reinforced concrete pipes are very strong and durable, but have limited use.
Installation steps
For laying downpours, choose a secluded place on the site. According to the drawn up scheme, three routes are planned with their own pipes and observation wells:
- collection of water from the roof of the structure;
- diversion from the site;
- removal from the road surface.
Installation of routes is carried out sequentially according to the algorithm:
- A trench is dug with a slope of 2-3 cm per linear meter.
- A 20 cm sand or gravel pad is poured under the pipeline.
- Pipes are laid under the established slope up to the inspection well.
- Revisions are arranged every 10 m and at every turn of the storm.
- Bypass pipes are installed in open places.
- Tests are carried out for the operability and tightness of the storm sewer system.
Turns, connections are made using fittings of the correct configuration. The pipeline is backfilled in two steps: first, the soil is sprinkled and tamped in order to make a uniform load, then backfill is continued to the soil surface.
For each branch, the amount of discharged water is calculated based on the diameter of the section, on which the throughput depends, and the served area. This approach will allow you to properly balance the rainfall system.
Installation cost
To determine the approximate cost of installation work, the number of storm water inlets and the length of the tracks are calculated.Without taking into account earthworks and a length of at least 50 m, the price for work on installing stormwater runs will be from 1190 rubles. per running meter. This cost includes the construction of 4 viewing wells, materials and work.
Installation of 1 stormwater tray will cost 1000 rubles, the same installation for cement mortar will cost 1500 rubles. For the installation of a stormwater pipeline with sprinkling, they require 200 rubles. per running meter.
The cost of installing the drainage system will be influenced by the depth of the pipeline, the layer of granite crushed stone for backing, the use of pipes with geotextile winding, the material of the pipes. Laying at a depth of 1 m to 2.5 m varies from 2,000 to 4,500 rubles. per running meter.
The cost of a viewing sewer well made of a plastic pipe with a diameter of 315 mm and a depth of 3 m will cost 9,000 rubles, with a depth of 1 m - 6,500 rubles.