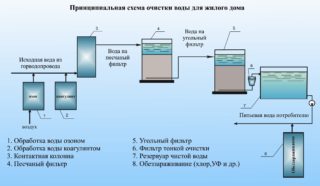
High-quality preparation of liquids for drinking or household needs is a guarantee of good health. There are various methods of water purification. The simplest of these is filtering. However, special coagulating reagents are often used for water treatment and water purification. Chemicals should be used strictly as directed in precise dosages.
Purpose and scope of coagulants for water purification

Coagulation is a chemical process that results in an enlargement of dispersed colloidal impurities in the treated medium. They turn into flakes visible to the human eye, which are formed in the process of adhesion of small particles. Later, the flakes precipitate and are removed using mechanical filters.
Coagulation as a method of water purification is used in the following areas:
- VOC (for effluent clarification);
- industrial dirty water treatment;
- pool cleaning;
- preparation of drinking water.
The processing of a liquid medium with coagulants for its further use requires a preliminary analysis of the most accurate possible. And also a scrupulous calculation of the dose of coagulant when treating water.
Types and principle of action of drugs
All coagulants are made on the basis of chlorides, sulfates or polyoxysulfates of metals such as magnesium, iron, titanium or aluminum.
There are two types of chemical reagents for water treatment:
- inorganic;
- organic.
- Titanium dioxide. The most expensive of all types of coagulants. At the same time, it maximally cleans the liquid to a drinking state. Titanium dioxide removes dirt and bacteria from water. Doses of the drug are used less than when working with other drugs. At the same time, the settling time of the medium treated with titanium dioxide is reduced by several times, in contrast to working with other inorganic reagents.
- Aluminum sulfate. The drug is easy to use, does not require long settling after dilution. But the reagent is sensitive to the pH level of the water. It is desirable that the indicators do not go beyond 6.5-7.5. Otherwise, aluminum sulfate will be ineffective. In addition, this coagulant seriously affects the level of acid-base balance of the liquid. After processing, it must be brought back to normal.
- Ferrous sulfate. Helps to purify water from oily impurities, hydrogen sulfide, to cut the concentration of heavy metals in it.
Iron sulfate does not completely dissolve in the treated medium.
All organic reagents are produced exclusively on the basis of hydrochloride (it is also called aluminum polyoxychloride). Such coagulants for wastewater treatment have a number of advantages over inorganic drugs:
- fast process of dissolving the product in water;
- high quality liquid purification;
- economical consumption of drugs;
- high coagulation rate;
- reduced settling period;
- low residual percentage of aluminum and salts in the treated medium after the chemical process;
- the ability to use hydrochlorides even at low outdoor temperatures, in cold liquid environments.
If an organic preparation gets into the soil, it does not change the acid-base balance of the soil, does not form an ecological disaster in the region.
Criterias of choice
Coagulants are chosen according to the following parameters:
- Form of the drug (liquid or powder). The first option is more convenient, since the reagent is already ready for use. But solutions, as a rule, are more expensive than dry preparations.
- Product type (organic / inorganic). It is selected depending on the problem with which the fight is being waged. For drinking water treatment, it is better to take organic matter. Sometimes the user prefers the more expensive electronic Aquaflow unit. With its help, it is possible to form impurities in the processed liquid into flakes without adding reagents to the water.
When buying a drug, you should pay attention to the integrity of the packaging and the timing of the preparation of the product. If the coagulant is expired, it will most likely not give the expected effect. It will also be useful to pay attention to the GOST marking and the composition of the product. If they are absent, it is better to refuse to purchase.
Application features
Otherwise, when using the coagulation method, you need to adhere to the following rules:
- Before pouring the drug into a liquid medium, it is worth turning off the filter system. Otherwise, the flakes will simply clog the installation.
- It is necessary to calculate the displacement of the reservoir in order to determine the exact dose of the drug. The volume is calculated from the width, length and depth of the pool. All measurements are made in meters. If the bowl is round, measure the depth and diameter. The finished value is already converted to liters.
- In case of severe contamination of the liquid, you can use 1.3 of the recommended dose of the drug in the instructions. That is, to slightly increase the effect.
- The dry reagent must first be diluted in water in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations.
- For temporary reservoirs, it is better to build special hinged skimmer fences. They will pick up the flakes that have formed. You can also use a dedicated vacuum cleaner.
- As a rule, after 9-12 hours, all the flakes precipitate. You can also remove them from the bottom with a water vacuum cleaner.
Correctly purified liquid is suitable for further use without the need to replace it. This is extremely important for large artificial reservoirs (swimming pools, aquariums, fish ponds), therefore, coagulants are popular as a method of liquid purification.