Used water from the sink, toilet bowl, bathtub, household appliances goes into the sewer pipe. All human waste in a volume of approximately 100-200 liters per day. The effluent goes through several stages of cleaning and is discharged into the reservoir.
What happens to wastewater after it enters the sewer

The first receiver of household wastewater from each apartment is a sewer pipe. Further, the water flows through the common building riser into the city sewer. The diameter of the pipeline here is large enough to accommodate an average of 2 million m3 of sewage per day. The city highway often has a diameter of 70 cm or more.
In the course of the route, domestic polluted water is combined in the city sewer with storm waste. They are transported either by gravity with a favorable terrain and a created slope, or they continue to go along the collector with the help of powerful pumps.
All collected wastewater is drained into the sewerage basins of the districts and then sent to a treatment plant. She, as a rule, is arranged outside the village. The point here is not in sharp specific smells, but in the scale of the enterprise. The station covers an area of up to several km2.
The length of the urban collector depends on the size of the settlement and can be more than 5,000 km in total (for cities with a population of over one million).
The municipal wastewater treatment system does not accept wastewater from industrial plants. These contaminated waters have their own treatment systems.
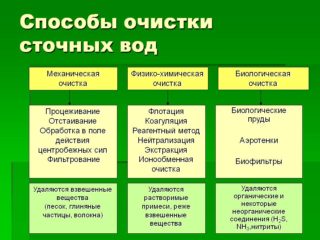
Wastewater treatment methods
Sewerage maintenance in cities and further wastewater treatment is carried out by two main methods - mechanical and biological. And in strict sequence.
Methods of disinfection of clarified liquids before their discharge into open water bodies are considered additional.
Mechanical cleaning
The next stage of mechanical cleaning is grease traps. They remove all oily impurities, since bacteria cannot cope with such contaminants. Water continues to flow through them in a continuous stream.
The sewage flows at high speed through the sand trap basin. The bottom of such a tank is tapered. Heavy particles of sand, earth in water settle into it. They enter the drains along with storm water or from the household sewer after cleaning the floors.
Biological treatment
Organic impurities in effluents are good food for a certain kind of bacteria. Microorganisms process fecal matter, converting them into organic sludge and, at the same time, reducing in volume.
Aerobic and anaerobic bacteria are used for biological wastewater treatment. The first ones work on condition that oxygen is supplied to the sewage tank. The second - actively operate without oxygen at the very bottom of the aeration tank. The same process takes place in the soil, resulting in fertilizer compost.
During biological treatment, wastewater enters an aeration tank (sealed tank). It is loaded with bacteria in the form of activated sludge and constantly maintain a certain temperature and oxygen supply. If you observe the process from the side, you can clearly see a moderately powerful seething. This is the process of decomposition of sewage into carbon dioxide and water. Due to the continuous supply of oxygen, organic sludge does not settle to the bottom of the aeration tank, but is constantly in contact with organic matter (fecal matter). The entire clarification process takes 8 to 10 hours.
The resulting sediment in the form of organic sludge is squeezed out through a centrifuge and sent to production for composting. Clarified water goes to the next tank for additional treatment.
During the work of anaerobic bacteria, methane gas is released. It is used to generate heat energy.
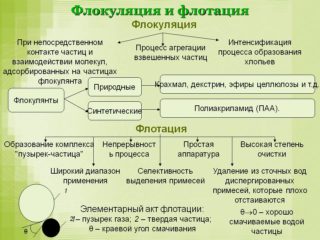
- flotation;
- coagulation;
- adsorption;
- extraction;
- reverse osmosis;
- dialysis;
- electrocoagulation, etc.
Each of them is selected depending on the composition of the effluents purified by the bacterial method.
Where treated waste water is discharged
Last but not least, the water goes through the post-treatment process. Here, the clarified wastewater is passed through a fine sieve cloth to trap the remaining debris particles. Then the entire volume of water is sent towards the outlet channel of the treatment plant. In this place, a block is installed for disinfection of effluents using ultraviolet radiation.
A preliminary idea was put forward for the final chlorination of water before discharge. But this method of post-treatment was abandoned, since chlorine causes irreparable harm to the environment. All living things in reservoirs after the discharge of clarified water would simply die.
Wastewater completely purified and disinfected by ultraviolet light is discharged into a nearby reservoir. In most cases, these are local rivers. In resort towns - the sea. Water is supplied to natural reservoirs through deep pipes so as not to disturb the microclimate in the source.
The discharge level of treated effluents is at a depth of 4-17 meters. Such water does not harm the underwater world. Its sanitary indicators are several times higher than the river / marine environment. This water can be used for domestic purposes. It is better to boil it for eating.