The installation of a sewer network is a complex engineering project and process that can threaten an environmental catastrophe or disaster if it is incorrectly implemented or errors in design calculations.
The most innocuous problems associated with a sewage system can be the outflow of sewage drains to the outside during ground shifts, groundwater movements and its freezing when cold weather sets in. And the larger consequences include additional destruction of pipes (with their inept laying) and huge material costs for construction work associated with its repair.
What SNiP 2.04.03-85 says
Despite a detailed description of such issues as the neutralization of effluents, deep and biological treatment facilities, wastewater disinfection, calculations and technological parameters of treatment mechanisms, filters, sedimentation tanks, pumping, blowing and ventilation stations used in the wastewater treatment system, highlighting the design features of treatment systems and networks and much more, SNiP does not impose significant restrictions on the depth of the sewer pipes and systems for cleaning it.
SNiP in this matter recommends using common sense and experience in operating pipeline networks for a given region, as well as using engineering calculations, taking into account the material and diameter of pipes, terrain, soil and climatic conditions, and the specifics of the work. In other words, you need special specialists who are well versed in this topic.
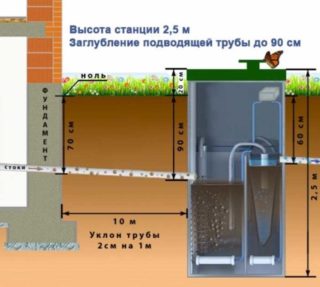
But in clause 4.8 of this SNiP, there are still indications of the minimum depths of laying collectors and pipelines in the ground, laid by the shield penetration method from 3 meters and deeper, depending on the pipe materials.
What affects the depth of the placement and how it can be changed
We see that SNiP 2.04.03-85 does not help much for calculating the depth of pipe laying in the design of sewerage systems, and for clarification it makes sense for us to turn to the practice of designing and creating these networks.
Thus, a large-scale project is required, drawn up by a specialist or a design organization in relation to the required region, and experience in concluding an agreement with a contractor for the implementation of this project is also required, since in addition to checking the work, it will be necessary to monitor compliance with environmental and sanitary standards.
Usually, in practice, the depth of laying sewer pipes should depend on the following circumstances and conditions:
- method of laying pipe connections (laying of sewer pipes can be external, and maybe with the use of reinforced concrete trays, and not only);
- on the climate, that is, on the temperature of the soil, the conditions of freezing of the soil in the area of laying and on its chemical composition;
- on the principle of operation of the sewer network (gravity, pressure, high pressure, ...).
Practice shows that when laying pipes in the ground, it makes sense to use clause 4.8 of SNiP 2.04.03-85 under certain conditions, since developers may consider that its knowledge and application will remove responsibility in case of problems, and dig deeper, thereby increasing the financial cost of laying pipes is impractical for economic reasons.
Also, experts take into account the dynamic loads on the sewerage system when it is laid. A good example is a motorway or just a road that puts more stress on the pipe underneath. Thus, pipes are laid deep - 9 meters and deeper. To take these circumstances into account, you need to create an engineering project.
Minimum and maximum depth, its calculation
- there is a terrain relief (on flat terrain, the depth of the pipes will be the same, and on a more complex one it will depend on the landscape), there are also features of an existing pipeline, features of the connections of collectors with a septic tank and sewage pipes, taking into account the depth;
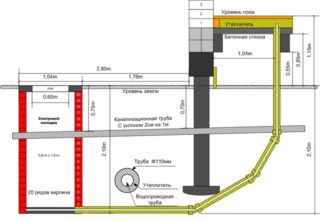
- there are features of laying sewer pipes in private houses operating on a gravity basis, taking into account the slope of the pipeline;
- the most important circumstance is the depth of soil freezing in a given area, since there are marks of freezing, which are given in SNiP 2.01.01.82 and with which the meteorological service is also familiar. When installing sewerage connections (in contrast to the water supply system), the pipe laying depths are calculated by subtracting a certain distance from the freezing points, because the pipes are flowing with a positive temperature (+18 degrees Celsius even in cold weather, which avoids freezing). Therefore, in some cases, it is even appropriate to lay pipes at a shallower depth with small distances between collectors and pipe exits from the house;
- the technological properties and features of materials for pipes are taken into account, in particular, high-strength steel and cast-iron pipes are laid to a great depth. For polymer pipes, laying to a great depth is unacceptable, since this affects not only their technological properties, but also the entire system. And when purchasing pipes, their price, and reliability, and ease of assembly, and delivery, and their other features are taken into account;
- during the design, special pipe cleaning devices are being introduced into the system to protect against freezing (often pumping equipment). The working pump saves not only from stagnation, but also increases the temperature in the pipes, saving from ice particles;
- additional insulation of pipes is used, sometimes the pipes are placed in dry insulation (often fiberglass, rolled thermal insulation material wrapping pipes from all sides by more than 10 cm with an additional layer of waterproofing), additional soil filling or other conditions depending on the situation (one of the examples this is a heating cable).
What about the maximum sewerage pipe laying depths? This is a very important indicator for the operation of pipes. Since, on the one hand, the heat will be stored longer at a greater depth, on the other hand, it is important to take into account the comfort of the environment, the weight of the earth and its pressure on the pipes to assess the likelihood of their damage and the complexity of the work performed along the entire length of the pipeline drain.
For certain types of soil (saturated with moisture or with a rocky base or rocky particles) SNiP recommends using pipe depths not exceeding 4 meters. And lay pipes to a depth of 5-8 meters in the case of dry lands.
From the point of view of these standards, when certain depths of pipes are exceeded, it is necessary and logical to use pallets or trays made of reinforced concrete for reliable protection of pipes with increased operating loads and their greater safety.
In certain cases, with increased loads (such as laying pipes under an actively used roadway) or non-standard service life, corrugated rigid pipes on a polyethylene basis can be used.
In the wording of SNiP, the nature of these standards for non-specialists is not entirely clear. Therefore, it is important to contact experienced specialists in the design of these systems. So the issue with the optimal depths of the sewer pipes must be resolved with the designers of these systems. SNiP 2.04.03-85, which was mentioned all the time in this article, in many ways gives only recommendations, leaving the question of the depths of laying sewer pipes under the responsibility of specialists.
Since this issue is very important and, in addition to climate and soil geology, it is necessary to take into account sanitary and epidemic standards and environmental standards, no general instruction can give an answer to all decisions on the design of this system. The main thing is that the sewer system does not freeze in the cold, so that it requires supervision and maintenance with immediate repair in case of emergency.