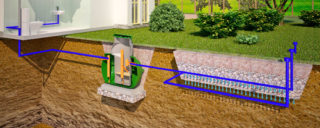
A soil-root system is an environmentally friendly and practical solution for treating water drains, which will look completely organic on the local landscape. Plants will hide all unpleasant odors and become a favorable place for some insects, birds and animals. All cleaning systems using plants are basically very similar in terms of design and operation. Wastewater is preliminarily purified, then enters the filtration layer, where, with the help of various microorganisms, the final decomposition of water discharges occurs. The site for this system is usually planted with plants that can grow in swampy areas, such as common reeds, reed mace, shrub willow, etc.
- penetrating into the filtration layer, oxygen molecules, in turn, oxidize and break down organic compounds (reed is capable of maximum transfer of oxygen to the soil by its roots);
- stable maintenance of the soil layer with the necessary looseness, which allows the filtration layer to remain permeable for a very long time;
- nutrition of plants with necessary substances directly from wastewater;
- rather intensive purification of water waste.
In the eighties of the twentieth century, the first cleansing structures with the help of plants were created, which perfectly cope with their functions today.
How it works and the cleansing process
After the settling tank, the effluent is directed to a cleaning layer in the plant root system. The development of the root system ensures a stable and continuous flow of all effluents. Although oxygen, participating in aerobic decomposition, is supplied by plants deep enough into the filtering layers, still there are places in the neighborhood without it. In areas without oxygen, an anaerobic decomposition reaction occurs. The presence of silt intensifies all reactions. Filtration duration is several days, as a result, a fairly high quality purification is obtained. Plants participate in a maximum of 15% of the processes.
To waterproof the pit of the root cleaning system, a polyethylene (or PVC) film is used, but you can also use clay and water-repellent concrete. In the middle of the distributing and collecting layers, there is a drainage layer made of crushed stone of various fractions.
The distribution of effluents is carried out by perforated pipes, after which the treated effluent is collected by a similar pipe system. The slope of the pipes is about 2%.
The aisles can be vertical, horizontal and mixed. A well is placed under the drainage layer, from which the quality of wastewater can be checked.
The final direction of the effluent can be a pond, river, soil, or irrigation of the garden and vegetable garden.The ideal location for this cleaning system would be a sunny location, sheltered from the wind. The size of the site can be increased as needed, the most important thing is that the size of the septic tank allows it to accommodate daily sewage drains. And the location of the root cleansing system is possible both on a flat area and on an inclined one.
Care and prevention
After the roots have sprouted to a depth of 10 cm, the amount of drains is reduced so that the roots, in search of moisture, sprout in a short time to the very bottom of the pit. This period of up to four weeks is called "dry". After that, the amount of moisture is immediately increased almost to the very surface of the soil, this period is "wet".
Weeds are removed mainly in the first three years: in the spring, by raising the water level above the soil surface by ten centimeters and left in this state for four weeks.
The wastewater level is easily regulated by installing a movable drain pipe in the lower well.
Although after three years the reed grows and does not require special care, it still needs to be monitored and new plants should be planted. Outlets and drainage piping also require regular checks, and flush them every couple of months.
In a septic tank, on average, once every three years, it is necessary to clean it. A properly constructed cleaning system works flawlessly at any time of the year, only in cold weather it is 15% less efficient.