When household waste water gets into water bodies or into the ground without treatment, the environment suffers greatly. In order to prevent an environmental catastrophe, various methods of cleaning polluted wastewater are used.
Basic cleansing techniques
Most often, the following methods are used to clean drain liquids:
- biological;
- mechanical;
- physical and chemical.
Due to the simplicity and efficiency, the first two cleaning methods are usually used to clarify household and domestic wastewater.
Mechanical methods
- defend;
- filter;
- filtered.
The process takes place through the use of coarse filters or in sedimentation facilities by settling heavy components under the influence of gravitational forces. Mechanical treatment removes approximately 60–70 percent of contaminants from domestic wastewater.
Sludge facilities are used to clean sewage fluids, which are sent to them not only from residential, but also from industrial complexes.
In the course of settling, it turns out to eliminate most of the oil-containing impurities that emerge with industrial effluents. Mechanical cleaning is used by car wash owners and oil refineries.
They are mechanically cleaned and storm drains. For this, sand trapping structures are attached to the highways. The composition of sediments that are collected from the surface of the earth contains:
- soil impurities;
- branches;
- foliage;
- pebble inclusions.
Trash boxes trap large debris, preventing it from clogging storm drains.
Biological treatment methods
The technological process consists in the use of aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms capable of processing complex organic components found in sewage. In this case, they decompose into gas and water.
Aerobic microorganisms need oxygen to live. To increase the efficiency of cleansing, you will need to create suitable conditions by installing an aeration system.
Anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen, so they can live in sealed containers. Methane is a by-product of their life. Installations in which purification is carried out with the help of such microorganisms are equipped with a ventilation system.
Cleaning standards
Structures and devices for clarifying wastewater must provide the required level of purification - this is controlled by legislation. The most stringent rules regulate the work of sewage from industrial facilities. The norms provide for the possible concentration of each substance in the clarified liquid separately.
For domestic waste water, the requirements are not so severe. However, the regulations still do not allow wastewater discharge into open water bodies or soil without purification. Homeowners can be held accountable for this.
There are no strict requirements for wastewater that is discharged into the ground after being treated. It is also important for the homeowner himself that a relatively clean liquid gets into the soil. Otherwise, he can bring his territory to such a state that living in the house will become impossible.
Types and principle of operation of VOCs
VOCs used for bioremediation:
- Septic tanks are sealed chambers into which sewage drains are discharged. Anaerobic microorganisms live there, processing sludge and contributing to water purification. The liquid after the septic tank requires additional purification, for example, in a filtration well, before it is discharged into a reservoir or soil.
- Septic devices with biological filters. The principle of operation of the biofilter is to seep water through the thickness of coarse-grained material (crushed stone or sand), which is covered with a film of special bacteria. Filtration fields and well installations operate according to this scheme. When sewage passes through a biological filter, microorganisms activate the oxidation and decomposition of organic components.
- Bioponds are artificial water bodies with a depth not exceeding a meter. In them, the contaminated liquid after undergoing mechanical cleaning is processed due to the action of bacteria. To accelerate the activity of microorganisms, it is necessary to warm water bodies with the sun's rays: in the Central Russian winter, these ponds have low productivity and are almost never used. Strengthening the activity of aerobic bacteria is also carried out through forced aeration.
- Aeration tanks are hermetically sealed installations in which forced aeration is used. To process the liquid faster and more efficiently, activated sludge containing the necessary microorganisms is used.
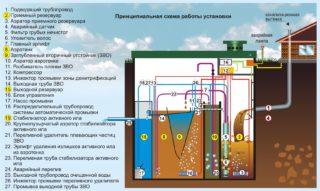
- Deep cleaning stations. The structures are used for complex wastewater clarification with maximum effect. After passing through them, the liquid becomes purified up to 98%. The water is pumped through several different filters and purifiers.
Any biological treatment methods are used exclusively after mechanical wastewater treatment, for example, their settling.
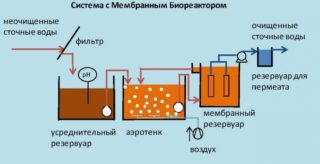
A membrane bioreactor is increasingly being used to clarify wastewater at enterprises and in residential complexes. It combines activated sludge biotreatment and mechanical membrane filtration. The membrane module is used to separate the sludge mass and is an alternative to the sedimentation of this substance in classical biological treatment plants.
Advantages of bioreactors:
- compact dimensions with high productivity;
- use of old cleaning complexes when updating equipment;
- the ability to work with a significant accumulation of activated sludge.
There are two types of biological reactors: with internal and external membrane placement. In the second version, the filter is isolated from the process chambers, and it is necessary to install intermediate pumping equipment.
Among all local systems, only membrane biological reactors and deep purification stations allow obtaining such clarified water that it can be discharged into natural reservoirs or used in an irrigation system for irrigation. Despite the fact that these installations are not cheap, the absence of additional stages of work for pumping out or treating wastewater makes them worth purchasing.