Domestic and industrial wastewater sooner or later gets into rivers and lakes, which causes the death of living organisms, as well as bacteria that utilize organic residues. This problem is relevant on the scale of the Earth. The infamous Pacific Garbage Patch contains more than 350 million tons of waste - plastic, resin, glass - that got there along with currents from inhabited shores. It is constantly growing and poses a threat to the life of all marine life.
The urgency of the problem
The level of wastewater treatment depends on the quality of equipment that massively filters and disinfects liquid, returning it to water bodies or back to the city's water supply system.
Industrial waste is also hazardous. These include:
- waste water from enterprises, saturated with toxins;
- runoff from agricultural work containing phosphates, nitrates and other minerals;
- waste water with inorganic waste - sand, soil particles, heavy metal salts.
Industrial fluid is conventionally divided:
- by the degree of toxic effects;
- concentration of hazardous substances;
- acidity;
- composition.
Substances are divided into conservative and non-conservative. The former do not react with other components, do not form new chemical bonds. They are difficult to remove - these are heavy metal salts, radioactive elements, phenols and pesticides. These substances practically do not decompose. Non-conservative components of dirty water can, over time, be processed by a biological method - anaerobic bacteria - these are organic residues.
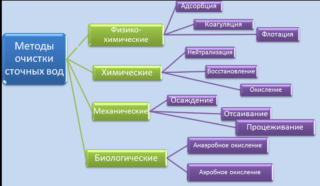
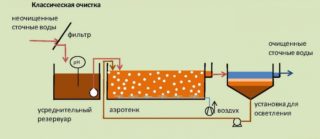
There are many ways to treat wastewater. Depending on what needs to be removed from the water, certain technologies are used. For example, to purify a domestic sewage system, it is enough to build a two-chamber tank and start anaerobic microorganisms. In this case, the water is cleaned by 70% and goes into the ground, where the process of sedimentation of suspended particles and organic matter continues.
Cleaning steps
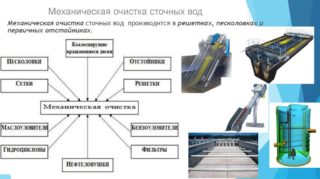
- Mechanical. At this stage, the separation of insoluble residues and solid particles occurs. Various grids, sieves, filters, sand traps, grease traps are used. The width of the holes in the grate is maximum 1.5 cm. Mechanical wastewater treatment also has several stages. After the grate, the effluent enters the sand trap, where fine solid particles, mainly sand, are deposited. The next stage is the grease trap. Fat is lighter than water, therefore it collects on the surface, from where it enters a special reservoir and is removed.
- The biological type of cleaning involves the use of various microorganisms, earthworms. They are able to dispose of soluble organic matter and turn it into a harmless substance. Aerobic and anaerobic bacteria are used.Some work in the presence of oxygen, while others do not need it. During anaerobic fermentation, methane is released - a combustible gas, which, after being obtained in a bioreactor, is purified and used for domestic or industrial needs.
- Physicochemical stage. Here, suspended particles are removed, mainly by gluing them into larger ones - coagulation. There are many methods - flotation, centrifuge, evaporation, sorbents, aeration (oxidation) and others. Physicochemical methods of wastewater treatment allow removing all soluble finely dispersed substances from the liquid. As a result, industrial water is obtained, ready to be sent to reservoirs. Drinking this liquid is not recommended.
- Disinfection is the final step. The most common methods are ultraviolet irradiation, ozonation, chlorination.
In Russia, the main disinfection method is a 30-minute exposure to chlorine. In Europe, this method has long been banned. After purification, the water can theoretically be drunk, but it is better to apply additional processing: filtration at home or boiling.
Waste water disposal
Wastewater is disposed of by a chemical method, achieving precipitation, after which other chemicals are used and the precipitate is broken down to simple components. This method is used to purify water in the production of synthetic polymers.
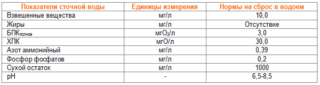
Standards for water purification
Taken into account:
- burden on the environment;
- permissible pollution parameters;
- the amount of wastewater;
- frequency of emissions into water bodies.
The capacity of the treatment plant must correspond to the volume of wastewater produced.
Basic methods
The wastewater treatment system must work in a comprehensive manner in order to completely remove all harmful and toxic substances. The use of any one method does not give one hundred percent result.
Anaerobic bioremediation
The most effective system is in domestic sewage installations, where fecal matter is discharged. Anaerobic microorganisms are added from concentrates that can be purchased at the store. At the same time, it is possible to equip the reception of methane gas, which is released during the processing of organic matter. The bioreactor is an additional plus of the method. To obtain a clean gas capable of burning, it must be purified from moisture and carbon dioxide.
Such complex installations are used in households where animals and birds are raised. With large volumes of raw materials, the bioreactor pays for itself within a year, given that the owners use gas and sell organic fertilizer.
The storage where the primary effluents fall is called the digester. At the bottom there is activated sludge, which is granules - bacterial communities. Microorganisms multiply slowly, so it is important to maintain optimal conditions for their survival. The temperature should be within 30 degrees. In the process of work, it becomes necessary to pump out some of the microorganisms. This is done manually or using a sewer machine. The substance is safe - it can be used for feeding livestock or as fertilizer on the site, since it contains a large amount of minerals.
The disadvantage of anaerobic purification is the low speed of the processes and the need for additional measures to remove organic components. Equipment is expensive, bacteria require constant monitoring of the temperature of the environment.
Aerobic wastewater treatment
It is desirable that anaerobic and aerobic methods be used together as aerobes complete the biological treatment process.
The equipment is represented by open containers - most often reinforced concrete rectangular structures, where liquid, previously purified from solid organic matter, gets into. To increase the bacterial population, it is necessary to increase the oxygen concentration, which requires the installation of additional equipment.
There are certain requirements for the quantitative composition of bacteria. For example, the simplest organisms eat bacteria, eliminating old cells and highly overgrown certain populations.
The disadvantage of the installation is the high price. You also need to find a suitable place to install both tanks.
Chemical and physicochemical methods
If the effluents are saturated with acidic components, alkaline substances are added to them - lime, hydroxides, soda. If alkaline waste liquids are supplied, then acids are used - sulfuric or hydrochloric. As a result, precipitates are obtained in the form of salts. A pH meter is used to control acidity.
Ozonation is a chemical method of purification, the essence of which is the oxidation of organic matter. The process is fast - large masses of water can be purified in a short period of time.
The disadvantage of the method is that before ozonation, it is necessary to purify from solid large impurities, which is usually done in digesters and aeration tanks. Also, energy costs are high for this technology and reagents that are designed for certain ions, for example, iron or manganese.
Physicochemical methods are used when not only soluble, but also suspended particles are present in a pre-purified liquid. The main ones are:
- Flotation - pneumatic, pressure, mechanical, electrical. As a result of the interaction of air bubbles and suspended particles, flotation complexes arise, which float to the surface in the form of foam and are removed at the next stage.
- The ion exchange method is based on the replacement of some particles with others. Cleaning is carried out with ion exchangers - substances like synthetic resins.
The resin must be regenerated after several cycles of application in order to remove the contaminated layer. Various cleaning schemes are used, which depend on the type of pollution and the concentration of harmful substances.
Mechanical methods
For a high-quality separation, it is necessary to correctly adjust the flow rate of the liquid through the sand trap so that the particles have time to settle to the bottom.
Placement of treatment facilities
For treatment plants, level areas with a low groundwater table are suitable so that the liquid can undergo final cleaning in the ground. In private houses, this is a plot hidden from prying eyes. It is desirable that the smells that sometimes appear during the decomposition of organic matter do not reach the neighbors.
Usually, the equipment is selected based on the characteristics of the site and the type of soil. For example, on loams, technical wastewater is poorly absorbed, and stagnation may occur.Therefore, drainage communications are installed, which remove liquid from the site through pipes.
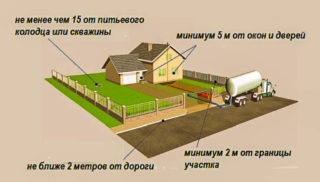
According to sanitary requirements, the sewer tank must be at least 50 meters away from the drinking well. There are filtration fields around the filtration well, within the radius of which wells intended for drinking water are not laid.
It is necessary to keep the distance from the edge of the road - at least 3 meters. If there is a laid electrical cable, the sewer is removed from it by 1 meter. From the gas pipeline - 1.5 meters.