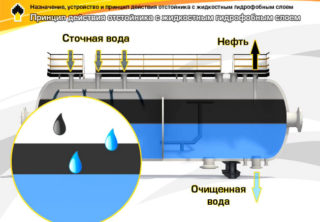
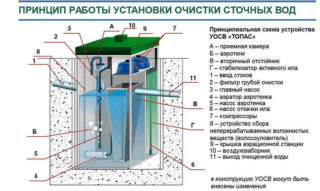
Sediment tanks are artificial reservoirs or natural reservoirs in which suspended impurities contained in them are separated from industrial and domestic wastewater under the influence of gravity or with the use of reagents. The sewerage sump can be used as a filter for preliminary and final treatment of wastewater in the sewerage system.
The primary stage consists in the separation of mechanical impurities or suspended particles and the beginning of biological wastewater treatment. In sedimentation tanks-biocoagulators, the activated sludge is mixed with the source water, colloidal and finely dispersed impurities are separated. Secondary sedimentation tanks of treatment facilities, final treatment devices, are called environmental protection, since after them clarified water is discharged into natural reservoirs.
Scope of use

They are used in water supply and sewerage systems in industry and private households, for the treatment of sewage, waste water in the process of hydromechanization in quarries and mines, at mining and processing plants, for household and drinking water supply.
Purpose:
- protection of surface water bodies and lands from pollution;
- reduction of equipment wear;
- capturing components;
- hydromechanization of earth and mining operations.
During the construction of structures and roads, settling ponds are created to accumulate and clarify surface runoff. Industrial effluents contain fatty substances that negatively affect the operation of treatment systems:
- cause blockages;
- contribute to metal corrosion, leading to the destruction of the pipeline.
To prevent the consequences, grease traps are built into the sewer canals, which are made in the form of a box with a tire. Its functional purpose is to retain and remove oil and fat.
In the spring thaw and rainy season, pollution of a very different nature is washed off into the sewage. Storm wells and chambers, which are made of concrete, allow to reduce pollution. They collect storm flows from a certain area, therefore, the calculation necessarily includes a volume that can accommodate the discharge of water from this area. Gabions are used to trap pollution in runoff from roads.
To remove some suspended compounds, flocculators with a built-in camera are mounted. In devices, with the help of laminar flows or turbulent flows, particles collide with each other and interact with reagents, which contributes to the rapid flocculation and removal of the formed sediment.
In rolling mills, sedimentation tanks are used to capture scale. In ceramic workshops, drains contain a large amount of clay, which leads to sewage blockages if it is not removed in time with the help of sedimentation tanks.
After aeration during biochemical wastewater treatment, water enters the sludge separator, from where the activated sludge returns to the aeration tanks for further continuous water purification.
Wastewater must be separated from liquid household waste - ZhBO or feces pumped out of cesspools. For this, ZhBO settling tanks are used. Polygons or filter fields are used to place them.
Homeowners make do-it-yourself sump for their backyard plots.
Principle of operation
The baffle that creates the overflow edge prevents the ingress of contaminants thrown from the reflective shield.
Classification and arrangement of water sedimentation tanks
Types of sedimentation tanks depending on the operating mode:
- contact (periodic);
- with continuous supply of the initial suspension at a low speed;
- semi-continuous mode.
Batch thickeners look like shallow pools. After filling the tank, time is allowed for the settling of suspended solids and colloidal particles to the bottom of the structure. Clarified water is drained through taps located above the sediment level. Sludge in the form of a viscous liquid mass is scooped out manually or poured into a pipe hole at the bottom of the device.
Sediment tanks for wastewater treatment in the direction of movement of the initial mixture are divided into two types:
- horizontal;
- vertical.
Horizontal sump
The design of the horizontal settler is a tank with several corridors. The conventional division by height distinguishes the working area and the sludge part. In the first, the sedimentation process takes place, in the second, the settled sludge is collected. According to the norms, a distance of 25 cm is provided between the zones. The sediment is collected in a pit at the point of entry of wastewater, from where it is pumped out by pumps or raked up.
Vertical sump
The shape and size of the sedimentation tanks are selected depending on the concentration of the suspension and the size. As the concentration and size of particles increase, the diameter of the thickener decreases. An increase in temperature lowers the viscosity of the liquid, which increases the speed of cleaning.
Semi-continuous action
The principle of operation consists in the continuous supply of the original liquid and the discharge of the clarified water. Lost sludge is removed periodically. To increase the deposition area, structures with inclined partitions are used. They repeatedly change the direction of flow from bottom to top and vice versa. In this case, the residence time of the original liquid in the tank increases, and a better water purification is achieved.
Continuous action
They are used in industrial production. According to their design, settling basins of continuous action are subdivided into one-, two- and multi-tiered.The use of two-tiered and multi-tiered devices is caused by the degree of pollution of the effluent.
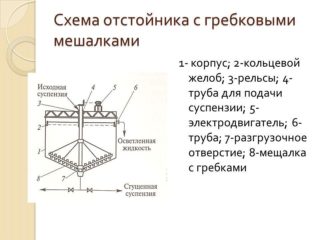
With rowing mixers
The sludge, containing a large amount of water, is sent to another settling tank, where the sludge is washed and settled. When using a settling tank system, the sludge is dewatered to 98%.
The principle of counterflow is applied, in which the movement of the sediment goes in the direction of series-connected tanks, and the flow of the clarified liquid in the opposite direction, to replenish the losses in the previous devices.
Advantages of rowing machines:
- continuity of work;
- high productivity with sediment removal up to 3000 tons per day of work;
- changing the density of the sludge by adjusting the capacity;
- effective dewatering of the removed sludge;
- fully automated process.
The main drawback is the bulkiness of the device. The diameter varies in the range of 1.8-30 m. In industrial installations, the diameter of the sedimentary tank can be 100 m. For compactness, in order to save space in industrial premises, multi-level sedimentation tanks are used. They are a structure consisting of several modules stacked on top of each other.
In turn, multi-tiered devices are divided into two types: closed and balanced.
In settling devices of the first type, the agitators are mounted on one shaft with one drive. Sealing glands are used to eliminate leaks. The process of unloading the sludge, as well as draining the clarified liquid, is carried out separately for each settling tank.
Sequential sludge removal is used in balanced sedimentation tanks. The sediment from the previous one is poured into the glass of each subsequent tier. As it moves down, the sludge thickens and is removed from the lower tier. In this case, no sealing glands are required in the previous tiers, since in them the pressure of the sediment at the bottom is much lower than in the lower sump.
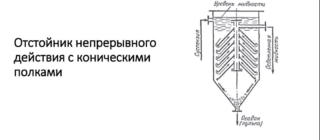
With tapered shelves
- no moving parts;
- simple operation.
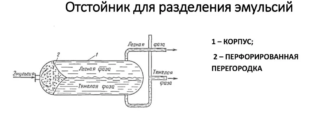
For emulsion separation
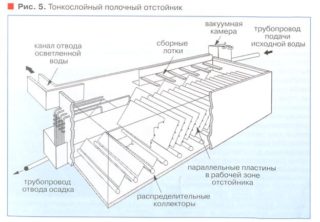
Thin-layer clarifier
Operation and maintenance
The efficiency of the wastewater treatment plant depends on competent operation, which implies control over the volume of effluents and their composition. The limited capacity of sewage treatment systems is most susceptible to malfunctions.
Negative factors affecting the wastewater treatment system:
- overload;
- salvo discharges;
- rise of groundwater;
- non-compliance with the repair schedule;
- violation of operating rules.
For normal operation of primary sedimentation tanks, the following rules should be followed:
it is forbidden to exceed the load permissible for the project;
evenly distribute wastewater in the settling tank system;
remove sediment up to 2 times a day.
The operating personnel must visually observe the level of the sludge, measure its weight and volume in the sludge wells, and measure the moisture content of the sludge twice a month. The norm is 93-95%. Simultaneously monitor the cleanliness of valves, fittings, switchgears. After removing the sediment, empty the sludge tanks from large objects and sand.