Incorrectly calculated depth of laying of sewer pipes leads to unpleasant consequences. At the most unexpected moment, drains from sinks, toilets and bathtubs stop draining. Often such a nuisance occurs in winter, when repair and excavation work is more difficult to carry out.
Why is the depth of placement important and why mistakes are dangerous
The pipe is buried too shallow
Incorrectly calculated slope
With a slight slope of the pipe towards the septic tank, the water stagnates, it comes off badly even in summer. In winter, this stagnant water can also freeze and shut off the drain altogether.
The pipe is buried too deep
Its end enters the lower part of the septic tank, and this worsens the discharge by gravity. The level of effluent in the septic tank will always be above the pipe. In this case, the drains will leave the house, but weakly, according to the law of communicating vessels, and not by an active one-time discharge. And this can lead to stagnation of drains in the pipe, the deposition of solid organic matter, clogging the drain. In winter, drains in such a system can also freeze.
The pipe is laid in an arc, humped up or down
In both cases, the flow will be difficult, water stagnates, muddy deposits accumulate, and in winter the system may freeze. Unpleasant odors can enter the house from all siphons.
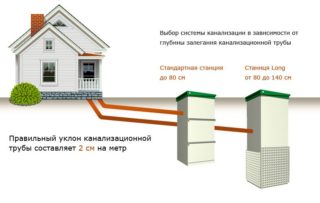
Laying depth according to SNiP
The depth of laying the sewer pipes at the exit from the building should be 30 cm higher than the average annual freezing point.
But in any climate, no less than 70 cm.
In reality, the depth of freezing cannot be taken into account. In most climatic zones north of Voronezh, it reaches 2 m.Therefore, according to SNiP, the pipe at the exit from the house should be at a depth of 200 cm - 30 m = 170 cm.
A depth of 1 m 70 cm is not justified and unnecessary even in the northern regions. In addition, it should be taken into account that at the other end, due to the slope, the pipe will be even lower.
Optimal depth
- The pipe goes under the road, then it is buried as deep as possible.
- The building has a shallow foundation. During construction, a hole was not provided for the output of the pipe. Then the pipe is laid below the foundation so as not to hammer a hole in the concrete.
- The site has uneven relief with steep elevation changes. It may turn out that the depth of placement in different places will be very different. The incline of the pipe will have to be steep.
- For some reason, the capacity of the septic tank is installed shallowly, then they try to lay the pipe as high as possible.
The depth of the septic tank is determined individually for each site, taking into account local conditions. The factor of freezing of effluents in the tank itself is not taken into account. the following reasons:
- Factory septic tanks, as a rule, are about 2 m high. The earth at such a depth retains heat throughout the cold season (for this reason, it is warm in the cellars and basements in winter).
- Warm drains are regularly supplied to the septic tank.
- Biodegradation reactions of organic matter in the effluent generate additional heat.
In severe frosts in the northern regions, a septic tank buried in the ground can be insulated from above with snow or any insulation used in construction.
Depth calculation
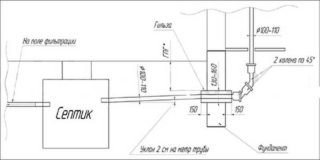
The basic standard can be adjusted depending on the pipe diameter. The larger the pipe diameter, the smaller the slope can be. Conversely, for a thin pipe, a greater slope is needed.
Specific indicators:
- Pipe D50 - 1 m slope 3 cm long.
- D100-110 - slope 2 cm.
- D160 - slope 1 cm.
- D200 - 0.7 cm slope.
Using this simple scheme, it is easy to calculate a sufficient slope for an average house in which a family of 3-7 people lives. For buildings with a large number of plumbing fixtures (several baths, toilets, etc.), you will need to calculate the diameter of the pipes and the slope using the formula V = H / d ≥ K, where:
- V is the flow rate;
- H - occupancy;
- d - pipe diameter;
- K is the coefficient adopted for each type of pipe.
In such cases, the sewage system is made according to projects prepared by specialists. Installation of sewage systems in such buildings is carried out by qualified workers under the supervision of a foreman or site manager. A level is used to determine the slope when digging a trench.
When installing the sewage system on your own, the slope is controlled in one of the following ways:
- According to the level marks.
- Along the cord stretched without sagging.
It is pulled strictly along the horizon, controlled by an ordinary building level or a hydro level. The distance from the cord to the bottom of the trench is measured with a tape measure every meter, achieving the desired height difference for each meter.
Instead of a cord, you can use metal profiles (corner, square) 4-6 m long. The profile is placed on the bottom of the trench. They put a level on the profile, align it horizontally, and measure the distance to the bottom of the trench.
Calculation example
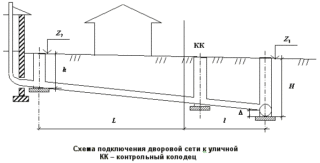
Then the profile is transferred further, and according to the same scheme, they continue to level the slope up to the septic tank itself.
It is advisable to sprinkle the bottom of the trench under the pipe with sand along its entire length. Then the pipe will fit tightly, without sagging. The pressure from the upper layers of the soil will be evenly distributed. The pipe will not burst from pressure from above, which can happen if there is a void under it, and the load from above is significant. For example, a truck or a sewage truck will come to the site.
Sometimes, for various reasons, it is not possible to bury a sewer pipe even by 30-50 cm.This can be:
- on rocky soils,
- in areas with steep slopes, when the pipe comes out in places
- when crossing a pipe with communications (gas pipes, high-voltage cable).
Then the pipe is buried as far as possible, and two methods of protection are used against freezing (one of them or two together):
- The pipe is insulated from above with a material with good thermal insulation properties that are not lost from soil moisture (slag wool, mineral slab, expanded clay, polystyrene).
- The heating cable is pulled in parallel with the pipe.If in cold weather there is a suspicion of freezing of the pipe, the cable is turned on and the ice melts.
In addition to the depth of laying and insulation, the material from which the pipes are made also affects the resistance to freezing. Metal and ceramics hold heat poorly and freeze faster than plastic pipes made of PPN, HDPE and PVC.
The thicker the wall of the plastic pipe, the less chance of freezing. The possibility of freezing is also reduced if, in severe frosts, the pipe is covered from above with a thick layer of snow.
The best option for sewage is a one-piece plastic pipe without joints. It does not rust, does not require unnecessary work to seal the joints, is smooth along its entire length and is less prone to blockages, and is designed for a long service life. Such pipes are sold both in coils and in sections of the required length.