When building a summer house or a private house, it is important not to forget to install a drainage system. Correct calculation and installation ensures safe and quick removal of rain or melt water from the roof. If mistakes are made at the design stage, the drainage system will not be able to perform its functions: water will get on the cladding, walls, windows, etc.
Rules and requirements for the calculation of gutters
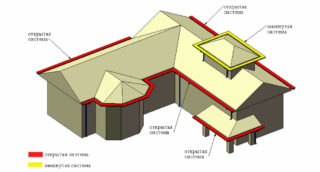
In construction, all drainage mains are divided into two large groups:
- organized;
- unorganized.
The latter received this name due to the fact that water flows down the slopes of the roof directly onto the blind area of the building. With an organized system, rain or melt runoff flows down to a specific place.
Unorganized structures can only be installed on flat roofs. The advantage of this type is one - there is no need to spend money on details. The list of disadvantages is very extensive: water has a destructive effect on the blind areas, basement and walls, spoils the appearance of the entire structure.
To correctly calculate the roof drainage system, you must first familiarize yourself with a number of requirements and rules:
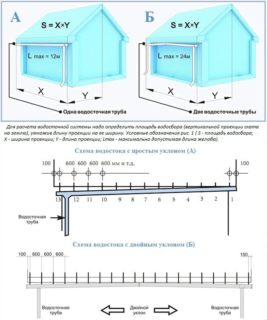
- The maximum spacing between downpipes can be 24 meters.
- A suspended and / or wall gutter can be installed provided that the angle between the wall and the roof slope is at least 15 degrees.
- Calculation of the diameter of the drainpipe by the area of the roof is carried out as follows: 1 sq. M of the roof * 1.5 sq. Cm. section.
- The level of the longitudinal slope of the gutters must be at least 2%.
- The permissible height of the sides is 12 cm.
These rules and requirements are relevant in regions with a minimum probability of water freezing. The option of installing a universal system in the form of an internal drain, which is equipped with an external water outlet, is also being considered. The design is extremely simple yet effective. It consists of a branch pipe, riser, funnel and outlet. If necessary, the standard kit can be supplemented with auxiliary components or accessories. In hardware stores, a large assortment of tools and materials for creating a drainage system.
It is impossible to accurately determine the amount of material by eye. The calculations take into account the average annual rainfall, the configuration of the rafter system, as well as the correctness of the slopes. The first indicator plays an important role, since in regions with an average amount of precipitation, it is enough to install even the simplest system, it will be able to cope with the task.
- The bracket must not be attached to the eaves of the roof, the latter may crack under the weight of rain or melt water.
- You should familiarize yourself with the specific features of the system, determine the number and location of points where it is attached to the building. Drainpipes must not be fixed at the corner of the building, as gusts of wind can damage it or tear it out along with a piece of the "house".
The rules and norms of SNiP require the following data when calculating the drainage system:
- Roof area.
- Average rainfall throughout the year.
- Temperature minimum recorded in the region where the drainage system is being installed.
Also, when designing, you need to think about carrying out rainwater drainage. It is necessary to divert the flow of water.
Where to begin
The main characteristic feature of the system is its throughput, i.e. the volume of water that the structure can drain from the roof. Before proceeding with the calculations, you need to take into account the type of roof and its configuration, the frequency and amount of precipitation.
To calculate the amount of precipitation for a certain area of drainage, use the following mathematical formula: Q = S * q / 10,000, where:
- S is the total roof area from which water will be drained.
- q is the maximum possible intensity of precipitation.
- Q is the amount of precipitation that falls on the drainage area.
Based on the data obtained, a drainage system is selected, the throughput of which will correspond to the available parameters.
Sequence of calculations
- The calculation of the number of gutters depends on the number of gutters and the height of the building.
- To calculate the number of gutters required, divide the length of the eaves by the length of the gutter.
- The number of couplings for connecting gutters depends on the number of joints.
- The number of clamps also depends on the number of connections. A minimum of 1 clamp is required for each connection.
- The number of brackets that are needed to fix the gutters. For this, the length of the gutter is divided by the distance between the brackets. The maximum spacing between plastic products is 60 cm, and 70 cm between metal ones.
- When installing an open-loop system, the number of required plugs for the ends is also calculated. For example, a gable gable roof consists of two gutter threads, therefore, you need 4 plugs, 2 on each side.
- The number of roof outlets will depend on the number of pipes used.
- The number of corner pieces is determined by the number of outside and inside corners of the building. Corner counting is done to minimize waste.
Strict adherence to the sequence of calculations will allow you to find out how many drainpipes on the roof and other details are needed. When calculating, you need to remember that each drainage system is designed for a roof area of no more than 100 sq.m. It is recommended to install gutters on each slope.
To calculate the installation of an external drain, the following number of conditions are taken into account:
- If the length of the gutter is 10 meters or less, and there are no obstacles that block the linear expansion, only one funnel will be enough.
- If the length is more than 10 meters, or the structure has obstacles, an additional compensating funnel will be necessary. It is installed at the end of the slope.
- If the gutter completely encircles the house around the entire perimeter, it is necessary to install a joint funnel and expansion joints.
The counting of the number of gutters is carried out on the basis of passport data, which contains information about the throughput and the fastening methods used. If the roof is flat, the number of funnels is counted as follows: one funnel is needed at least for every 75 sq. Cm. To calculate the pitch between them, divide the length of the roof by the number of funnels.
If there is no time or opportunity to make calculations on your own, you can use a special technical calculator on the Internet. It is enough to enter several parameters and the system will automatically calculate the amount of required material.