The Sanitary Protection Zone (SPZ) is a section of the territory where local treatment facilities (LOS) are built. Their area is calculated according to the possible degree of dispersion (dispersion) of harmful substances in the sewage. The larger the emissions, the wider the area. The sanitary protection zone of sewage treatment plants according to the SanPiN standards is also determined from the calculation of the type of VOC - open or closed. Additionally, the type of installed equipment is taken into account.
Basic rules for industrial SPZ
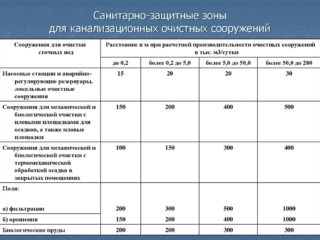
The SanPiN indicates the dependence of the size of the sanitary protection zone on two parameters: the technical equipment of local sewage systems and the treatment capacity, measured in thousand m³ / day. If the VOC is equipped with pumps, sedimentation tanks and emergency tanks, the relationship is as follows:
| Productivity, thousand m³ / day. | up to 0.2 | 0,2-5 | 5-50 | 50-280 |
| SPZ size, m | 15 | 20 | 20 | 30 |
If the VOC package includes structures for a certain purpose - for mechanical and biological treatment, - as well as sludge pads where sewage sludge fermentation occurs, the size of the buffer zone must be increased:
| Productivity, thousand m³ / day. | up to 0.2 | 0,2-5 | 5-50 | 50-280 |
| SPZ size, m | 150 | 200 | 400 | 500 |
If thermomechanical treatment of sewage sludge is added to mechanical and biological treatment, and all this takes place in closed rooms, the parameters of the SPZ are as follows:
| Productivity, thousand m³ / day. | up to 0.2 | 0,2-5 | 5-50 | 50-280 |
| SPZ size, m | 100 | 150 | 300 | 400 |
In addition to active wastewater treatment, local treatment networks use facilities that belong to the post-treatment category. These are filtration or irrigation fields, the so-called biological ponds. For them, there are also norms that are defined by SanPiN. Here, the dependence is the same on the power of the VOC.
| Productivity, thousand m³ / day. | up to 0.2 | 0,2-5 | 5-50 | 50-280 |
| SPZ size, m filter fields irrigation fields biological ponds | 200 150 200 | 300 200 200 | 500 400 300 | 1000 1000 300 |
The newest sewage treatment technologies and equipment, which is being introduced into the sewage network, increase the degree of treatment. At the same time, the areas on which it is installed are reduced. Therefore, amendments and additions are made to legislative documents. If the efficiency of filtration and irrigation fields, mechanical and biological treatment facilities increases, then the size of the SPZ can be reduced to 100 m, provided:
- filtration fields are located on an area of up to 0.5 hectares;
- irrigation fields up to 1 ha;
- the productivity of cleaning systems does not exceed 50 m³ / day.
If filtration fields of an underground type are being constructed, and their productivity does not exceed 15 m³ / day, the size of VOC can be taken within 50 m. If the surface flow of treatment facilities has an open design, the size of the sanitary protection zone can be 100 m, with a closed type of execution, the size is reduced to 50 m.If the VOC includes drainage stations, the zone parameter increases to 300 m.
If industrial treatment facilities are located outside the territory of the production facility, and domestic sewage is connected to them, the SPZ parameters are determined according to the values indicated in the above tables.
- build residential buildings;
- carry out landscape work;
- organize recreation areas, sanatoriums, resorts, health institutions;
- build cottage settlements and form garden partnerships;
- build sports and playgrounds.
In the sanitary protection zone of an industrial type, it is impossible to organize food and pharmaceutical production, to build warehouses where food and medicinal products, raw materials and semi-finished products are stored. It is impossible to build water supply systems where water is purified and stored.
A few more requirements for the sanitary zones of sewer systems:
- The SPZ should be located on the leeward side of an industrial facility and residential buildings located nearby;
- when designing, it must be taken into account that in the future, local treatment facilities will expand;
- VOCs are being built, taking into account the gravity movement of sewage wastewater, as well as surface wastewater - the entire territory is located at a slight slope;
- when determining the size of the SPZ, the type and class of the enterprise are taken into account.
The design of the sanitary protection zone determines the approximate size. Normative calculations are formulated in SanPiN. But over time, during operation, the dimensions of the SPZ can change up or down. Based on observations and various measurements of the air condition, the final (established) size of the SPZ is approved.
The criterion by which the final parameter of the zone is determined is the permissible (maximum) concentration of pollutants. This parameter is measured at the border of the zone.
The size of the SPZ can be reduced if new treatment technologies are introduced in the VOC and new highly efficient equipment is installed, or the enterprise itself is redesigned - its capacity, composition or hazard class is reduced.
The road that runs inside the sanitary protection zone is not taken into account when calculating the size of the SPZ. Car exhaust emissions are taken into account without fail.
Household sanitary protection zones
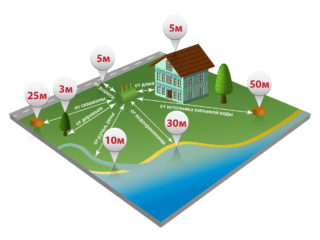
The rapid development of suburban construction has led to the emergence of a large number of local sewerage systems located right on the suburban area. They are small in size, many are completed with fields or filtration wells.
Manufacturers offer septic devices with a high degree of purification of sewage and sewage, which is brought up to 99%. But regardless of what type of VOC is used in a suburban area, what is its degree of purification, the standards and requirements for all types are the same:
- the distance to the foundation of the house is at least 5 m;
- to a well or a well, on the basis of which an autonomous water supply system of a house is formed, - at least 50 m;
- to open reservoirs - 30 m;
- to the neighboring site - 3 m;
- to vegetation - 3 m;
- to the road passing by the site - 5 m.
In SanPiN there are standards that determine the size of the filtration fields. The latter are classified as VOCs and form the SPZ. The calculation of the area occupied by the filtration fields is established by the ratio of the daily volume produced by the septic tank and the absorbing capacity of the soil.










It is not clear how at the end of the article they returned to the norm at 5 meters from a residential building? When did the whole article appear 50m?