Domestic and industrial wastewater can contain hazardous contaminants. The removal of waste fluids must be strictly supervised. Control is exercised by both authorities and organizations involved in wastewater disposal.
Norms and prohibitions for discharged wastewater
- containing impurities for which standards of permissible content have not been developed;
- recyclable, for example in return water supply;
- posing a danger of exceeding the epidemiological threshold;
- which are the end products of industrial and household waste disposal;
- forming explosive mixtures, poisonous gases, as well as harmful impurities that impede biological treatment.
- containing components containing oil and construction waste.
In the effluents permitted for discharge, the maximum permissible concentration of impurities (MPC) must be taken into account. According to GOST - no more than 500 mg / l of suspensions and floating substances. The temperature is not higher than 40 degrees, and the pH is 6.5-9.
It is also necessary to take into account the salvo waste discharges. This concept means the release of sewage into the treatment plant from all plumbing devices at the same time. It is important to correctly calculate the volume of VOCs to prevent liquid filled with pollutants from entering the sewer or, worse, into the body of water.
Volley discharges are subdivided into emergency and forced discharges due to poor pipe flow. All of them violate the rules of wastewater disposal, because due to the impossibility of controlling the MPC and the speed of wastewater movement, they can pollute not only the reservoir itself, but also the area adjacent to it.
Discharge control
The main document containing the rules for wastewater discharge is SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00. According to him, before draining, the composition is checked for the content of contaminants and the presence of pathogenic bacteria. A verification is carried out with the indicators of the declaration provided by each enterprise on hazardous substances in wastewater.
Scheduled activities for the collection of samples and their laboratory research are carried out no more than once within three months, but at least once a year. Sometimes unscheduled checks are carried out when:
- dumping violations, including without the use of treatment systems;
- inconsistencies with the data entered in the declaration on the composition and content, as well as the identification of prohibited impurities;
- problems not resolved by prescription.
Checks are carried out on the fact of emergency situations, the occurrence of infections and poisoning.
Obtaining permission to discharge effluents
Sanctions for the discharge of sewage into natural water bodies are issued with the consent of the authorities for the protection of natural resources and the protection of the environment.
To obtain a permit for wastewater discharge from the relevant organizations, you must provide:
- Documents that confirm the work performed on the installation of sewer pipes, drainage wells, insulation, foundation, soil compaction.
- Technical data sheets for equipment and materials.
- A certificate confirming the application of an anti-corrosion coating to welded seams and joints, as well as their diagnostics.
- Information indicating any deviations from the original design of the structure.
- Operational acts for external and external sewerage systems.
- Help on assigning an address and number to an object in the registry.
In addition, design drawings of the drainage main, the dilution of the sewerage pipeline and sanitary equipment are attached.
Relief relief scheme
According to the laws of the Russian Federation, dumping of clarified wastewater from the sewer onto the relief and burying it in the ground is not allowed. This is allowed only in rare cases, when the liquid is pre-purified to 95 percent. In this case, it is required to obtain permission with the provision of a document on decontamination. The location of the discharge is coordinated with local authorities and Rospotrebnadzor.
Discharge scheme into water bodies
- checking the distance from the treatment plant to the reservoir and the economic component of laying the pipeline;
- obtaining an extract from the water register, based on which information is generated on the state of the water body and the actual purpose of its use;
- hydrological characteristics;
- investigation of the state of the shore and the basin for the construction of a water-discharging installation;
- obtaining fishery characteristics;
- establishment of a nearby sanitary zone and a source of drinking water supply;
- analysis of the likely impact on the environment.
Coordination of the discharge point is necessary when creating a project and erecting septic tanks, treatment plants with filtration fields and other VOCs, storm drains and industrial wastewater. It is one of the necessary steps in obtaining permission to discharge the clarified liquid into a water body. The time for approval is no more than three months from the date of submission of all the necessary documentation.
It is necessary to obtain a permit, take samples to control the quality of water, as well as drained volumes. The requirements that are presented depend directly on the reservoir itself and its application.
Any release on the territory of household water supply farms, as well as water protection zones, is prohibited.
Varieties of drainage
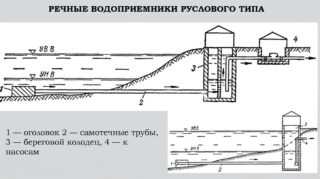
For dumping treated wastewater into water bodies, coastal, channel and deep outlets are used. The former are divided into two categories: non-flooded and submerged. The latter are wells installed on the shore with the drainage of sewage water under the level of a river or lake. Non-flooded ones combine streams at a certain angle. Deep outlets provide high volume ejection. They allow you to move the discharge point further from the coast.
Channel outlets, as a rule, are located at some distance from the coastal zone. They are of three types:
- Lumped outlets are needed to dilute the main water flow using the pressure method or to supply liquid to a certain point where the level of contamination will be acceptable.
- The scattering ones are located on the horizontal section of the pipe line, along the entire length of which several heads are placed or slots are made. With their help, wastewater is poured into rivers.
- Ejectors are equipped with nozzles of different sizes. Thanks to this, it is possible to effectively drain fluids in water bodies with different currents.
A suitable structure is chosen depending on sanitary standards, the need to dilute wastewater, the "mirror" of the well and the water body.
The standards for wastewater treatment must be observed not only because of the possible fine, which is provided for by article 8.14 of the Administrative Code. On the conscience of the offender will be the death of aquatic inhabitants and harm to human health.