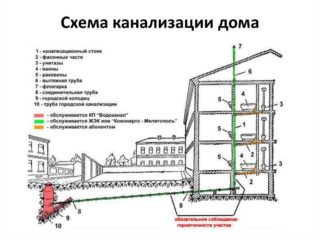
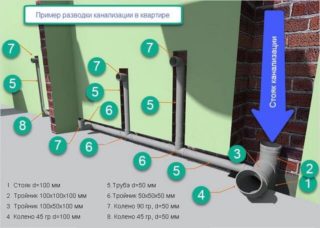
To carry out an autonomous sewage system in private ownership, it is necessary to have an idea of how the sewage system is arranged in a multi-storey building, since the principles of approach and the rules are the same.
Actual requirements for the sewer system in an apartment building
Fittings of appropriate configurations are used to connect pipes of different diameters, make turns and branches. The pipeline, before the discharge of the drain into the first inspection sewer well, constitutes the in-house sewage system. According to the rules, sections of the pipeline are laid in a straight line, the connection is allowed at an oblique angle.
The pipes must be made of durable and corrosion-resistant materials. Risers are installed discreetly in mines, niches or boxes. Doors for access to pipes made of polyvinyl chloride are allowed to be made of "combustible" building materials, for polyethylene pipes from "hardly combustible".
When designing a sewerage scheme for a panel house, the point of insertion of the apartment wiring into the riser is taken into account. It is located in the interfloor overlap. The depth of its location is taken when calculating the slope of pipes for intra-apartment drains, depending on the size of their cross-section.
Outlets from the house to the inspection well are carried out with a slope of 0.02 and an angle of connection to the mains of at least 90 degrees. The slope for pipelines with a diameter of 40-50 mm should be 0.03; the slope norm for a section of 85-100 mm is taken equal to 0.02. A maximum slope of 15% is negotiated. The slope is measured in% or fractions, for example, a slope of 0.02 means 2 cm per linear meter. With a length of 10 meters, the height between the beginning and the end of the pipeline section should be 20 cm.
The inset of the drain from the shower stall, which is 3 meters from the riser, should be located at a height of 9 cm. The inset of sinks and washstands can be designed at any height, and the bathtub must be raised by adjusting its position in space with the legs. Plumbing devices in a high-rise building should be connected to the riser through siphons, which trap unpleasant odors using a water plug.
The inset of toilet bowls and bidets does not require the installation of a siphon, since they have it in their design. Dishwashers and washing machines are equipped with a check valve to prevent odors, therefore they are connected to the riser without an additional locking device. The flat arrangement of the bath and shower siphons allows them to be connected at a low height.
In the basements of residential buildings, open laying of engineering communications is allowed, but only in the absence of office or warehouse premises. The ceilings through which the communications pass must be sealed with a cement mortar. In the place of the tie-in into the horizontal collector, the 8-10 cm riser is also supposed to be sealed with a cement jacket 2-3 cm thick, before that the pipes are covered with a waterproofing material.
The depth of pipe laying outside the house depends on the operating conditions: the pipeline must withstand constant and temporary loads and be protected from freezing.
Sewerage device in a typical MKD
- with a drain pipe diameter of 110 mm for toilets;
- with a diameter of 50 mm for collecting waste water from washbasins and sinks.
Contaminated water from both branches enters the sewer riser, from where it is transported to the prefabricated general house collector, which on the one hand is connected to the collector of the street network, and on the other side has an exhaust pipe for ventilation of the sewage system. The accumulated vapors are removed and dispersed in the atmosphere due to the thrust formed in the riser. The height of the funnel above the roof must be at least 20 cm. The amount of draft is influenced by the wind force.
A vacuum valve is installed on the outlet of the fan riser. It controls the movement of air when a vacuum appears during a salvo discharge into the sewer. When discharged, air enters through the air intake grille of the valve, without breaking the hydraulic locks. As soon as the pressure is equalized, the valve closes and blocks the movement of the stench through the valve grate into the apartment or into the attic of the house.
The entire system, from plumbing fixtures to a common collector, works on the principle of gravity and requires observance of the slopes of the collectors and mains, ensuring the required pipe diameters along the entire branch, the correct configuration of the network, selection of connecting fittings and the presence of inspection hatches.
Features of installation in an apartment building

Typically, one toilet riser is used to collect wastewater from the bathroom, kitchen and toilet. If the kitchen is removed from the bathroom, a second collector is made. The shorter the wiring, the more efficiently the waste will be disposed of into the sewer system.
Risers collect drains from all plumbing fixtures located on different floors under each other and have a continuation on the roof in the form of a chimney - a weather vane. Vertical risers go out into a common building horizontal collector with a slope towards the cesspool to ensure gravity transportation. A street sewage pipeline collects wastewater that has fallen into inspection wells and delivers it to the city's wastewater treatment plant.
To drain the precipitation, a storm sewer is carried out. Its calculation is based on the condition that 1.5 cm2 of communications remove water from 1 m2 of the roof.
Operation and maintenance
Sewer system blockages, when installed in compliance with SNiP, are caused by fatty deposits, which settle in cooled drains along with other waste. In such cases, cleaning by hand or power tools is required. For small blockages, chemical cleaning methods are effective.
Often missed items end up in the sewer and create a blockage, they cling to irregularities, delaying the flow of wastewater, and become overgrown with debris. With the addition of fatty deposits, the passage narrows, the sewer is clogged. We have to remove the obstacle with the help of mechanical cleaning machines. Cleaning is carried out from two sides: through the inspection hatches in the basement and from the side of the sewer well.