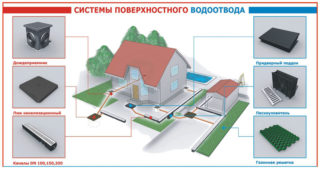
A dry foundation and building structure is the key to the strength and durability of any structure. Most private houses are built of timber, they especially need protection from any moisture. For this reason, it is important to build a water drainage system on the site.
Types of drainage systems
There are two main principles of drainage at the site: closures (deep drainage) and surface drainage.
Closed drainage is characterized by the fact that all systems by which water is removed from the site are not located on the surface, but are laid under the top layer of the soil. This method of drainage is suitable for areas that are located in an area where groundwater is close to the surface.
The second type of drainage system for a suburban area is surface. It performs the function of getting rid of water that gets outside: rain, snow, flooding, puddles from another area, if it is higher. In turn, surface drainage can be of two types: linear and point.
The linear type of water drainage works on the principle of its accumulation with the help of elongated gutters that are installed throughout the site. They are placed in such a way that the water under the action of gravity flows into the drainage funnels.
Point type surface drainage helps to get rid of water from roofs of houses or other surfaces located above ground level. The structure consists of a system of vertical and horizontal pipes with storm water inlets.
System selection criteria
An open or surface drainage system must be installed in places where there is a high average annual precipitation level, so that the water after regular heavy rains has somewhere to go. The same applies to climatic zones where a lot of snow falls in winter: melt water in spring can fill the soil with excess moisture and flood basements.
A closed type of drainage system is needed on a site that stands on groundwater close to the surface. Drainage is needed 1–2 m thicker than the ground so that the soil is not too loose, otherwise all buildings and structures will be under the threat of subsidence or even collapse.
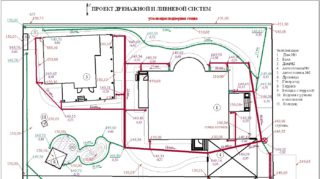
Drainage design rules
Consider how the overall system designs should look to be appropriate for the project. You need to take into account the following factors:
- Dimensions and total surface area from which excess water needs to be removed.
- What kind of waters is mainly used to flood the site in this region. If the terrain is characterized by the proximity of groundwater to the surface, and rains and snowfalls do not cause great inconvenience, closed drainage should be prioritized. And under the condition of frequent torrential rains, you need to take care of the emergency drainage of water from the site by a surface route.
- The depth of underground pipes for closed drainage depends on the quality of the earth. The looser the soil, the deeper the highway is laid.
- Determine the boundaries of the drainage system within the site.
- Calculate how far the water will need to travel from the receiving to the outlet parts of the structure.
An artificial or natural reservoir will help to solve two problems at once: to get rid of the erosion of buildings with liquid and to give a suburban area a beautiful look.
Self-installation of the drainage system
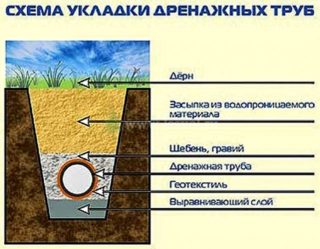
First you need to dig trenches to install drainage pipes. Next, it is necessary to evenly pour a layer of sand and crushed stone on the bottom so that the communications do not sag or deform. Run the entire length of the pipes and connect them with sockets. For better tightness, it is worth covering the joints with an adhesive solution.
The piping system must be connected to the place where the water will be discharged. If this is an artificial pond, dig a pit in advance and fill it with concrete, not forgetting to first bring the pipes into it. The effluent can be discharged into any container, from where the liquid will be periodically pumped out. Even an old canister with a volume of 200 - 300 liters will do.
When the entire system is closed, the trenches can be buried. To do this, sprinkle the pipes with gravel or crushed stone, then with sand, and finally with the same soil that covers the entire area. Tamp each layer tightly.
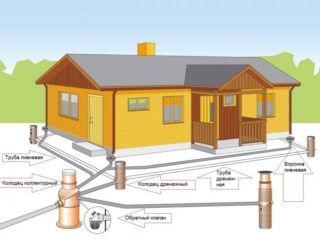
For surface drainage, screw the drain pipes along the entire length from the roof to the base of the house. Along the perimeter of the roof, install gutters on the rafters that will not allow water to drain in arbitrary places. They should have a slight slope so that all sediment falls into the water intake funnel.
The general drainage system combines surface and closed drainage. To do this, you need to lay the drain pipes underground and attach them to the drainage pipes.
It is advisable that the drain goes directly under the grate, and not be located above it. This will allow to avoid icing up the space near the walls and pipes in winter.
How to avoid installation errors
Do not install roof gutters horizontally, otherwise the water will not drain, but stagnate. In winter, this is especially dangerous, as it freezes and blocks the drainage. The pipe must not be in contact with the wall. It should be at a distance of several centimeters from the facade so that it does not get saturated with water and does not lead to dampness in the interior.
The number of funnels is also important. Consider the region's average annual rainfall. If there are not enough water collectors, the system will not handle the load and will leak through the edges of the gutters.
Choose the right time to start work. Outdoor temperature is important when installing some materials. For PVC, it is considered optimal when outside the window is not lower than +5 ° C. Avoid bad weather, start working when it's dry and sunny.