The task of the drainage system is to collect excess water in a certain area and drain it from the site. Modern drainage products are efficient, reliable and easy to install. One of the types of pipes used for the construction of drainage systems are corrugated drainage products with perforation.
Scope of corrugated drainage pipe with geotextile

Shallow drainage systems are used to drain storm and melt water from the site. If it is required to lower the groundwater level, deep structures are used.
Perforated corrugated drainage pipe with geotextile is used for:
- protection of foundations, basements and basements of buildings and structures from flooding;
- improvement of sites;
- drainage systems in agriculture and forestry;
- drainage system in the construction of highways.
The drainage system is provided for the construction of any buildings and structures.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Corrugated Drainage Pipe

A corrugated perforated element has holes located between the pleats. This design helps to effectively cope with the problem of removing excess water from the ground surface. Fitting the pipe with geotextiles prevents soil and debris from getting inside.
The use of perforated corrugated drainage products has many advantages:
- The corrugated outer jacket has strength and ring stiffness.
- Geotextile protects the drainage system from soil clogging, serves as a filter for wastewater treatment.
- Depending on the stiffness class, pipes can be laid at different depths.
- Corrugated pipes have good indicators of flexibility - during storage and transportation, they are rolled into coils.
- The materials from which the products are made are not susceptible to corrosion and decay.
- Corrugated pipes are lightweight.
- Installation of corrugated plastic elements is quite simple.
- A large number of fittings are not required, since corrugated products are flexible enough.
- The service life of most products is at least 50 years.
- Low cost of pipes and fittings.
- They are used in areas of any area.
A relative disadvantage of corrugated plastic pipes is the loss of strength at high temperatures.
Using geofabric as a filter also has its advantages:
- not damaged by insects and rodents;
- does not give in to decay;
- resistant to various chemicals;
- elasticity allows you to withstand large mechanical loads;
- service life is at least 25 years.
The use of geotextiles protects the reclamation system from contamination inside the structure.
Types of pipes
Corrugated products are made in a single or multi-layer version. The single-wall perforated pipe is optimal for laying at a shallow depth. The two-layer constructions combine the high strength of the outer shell with a completely smooth inner layer.
Corrugated drainage parts are made of the following materials:
- HDPE (low pressure polyethylene) - the most common in individual construction. Corrugated polyethylene drainage pipes are excellent for laying to a depth of 4 meters. They have good technical characteristics: strength, chemical resistance, flexibility.
- PVC (polyvinyl chloride) - manufactured in standard lengths, used for the installation of systems at a depth of 4-10 meters. They have greater rigidity than polyethylene. But at the same time, they are more fragile.
- PP (polypropylene).
Double-walled products are combined from various plastics. In addition, the parts are produced with different rigidity.
- For deepening up to 1 meter, single-layer products with a stiffness mark SN2 are used.
- Pipes of stiffness class SN4 are laid in trenches up to 2 meters deep.
- When constructing a structure to a depth of 4 meters, it is worth using two-layer SN6 stiffness elements.
Such options are sold both in bays and in lengths. When laying the drainage system below 4 meters, sections of stiffness SN6, SN8 and higher are used.
Drainage pipe filters are made from coconut fiber or geotextile. The price for natural material is higher. The geotextile filter will last a long time if sprinkled with rubble around the drainage system.
Double-layer structures, due to the presence of a smooth inner layer, are often used without an additional filter. They are less prone to siltation and blockages.
A distinction is also made between products with partial or full perforation. Holes in the pipe are made only from the top, or along the entire diameter. They are made round or in the form of slits.
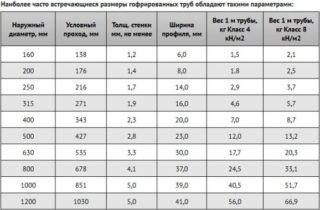
Product dimensions
The size of the drainage pipes is selected depending on the amount of water that needs to be collected and discharged.
- For a drainage device in a small area, pipes with a diameter of 110 mm are often used.
- If the perimeter of the territory is large enough, products with a size of 160 mm are used.
- The large volume of collected water, the individual characteristics of the drainage site may require the use of models of much larger diameter.
Small-format products, for example, drainage corrugated pipes 63 mm or 50 mm, are often used for forced moistening of the soil. This can be the removal of moisture from the stormwater system or treated drains.
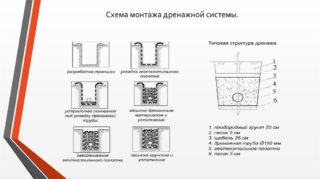
Installation and laying rules
- A well is installed to receive the removed moisture at the lowest point of the area to be drained. This element can often be dispensed with if there is a possibility of draining water into a regular sewer, ravine or stream. Moisture is removed from the well by gravity or using a pump.
- Trenches for the structure are dug manually or with the help of special equipment. The ditch width is calculated as the sum of the pipe diameter plus 20-30 cm.
- The system is given a certain slope towards the catchment well. It is 1-2 cm per lm.
- The drainage corrugated structure is laid on a sand base with a thickness of at least 5 cm. It needs to be leveled and tamped.
- Geofabric is laid on the sandy layer.
- Next, a layer of crushed stone is poured. Fractions from 20 mm to 40 mm are selected.
- All system parts are laid and connected.
- From above, crushed stone is again covered with a layer of 10-15 cm.
- The overlapping geotextile is used to cover the entire structure.
- Sand or fine gravel is poured on top.
- Backfill the soil.
Each layer is rammed, sand is spilled with water.
Individual elements are connected to each other using couplings, bends, tees. Fittings designed for ordinary sewerage are suitable for products with a diameter of 110 mm, 160 mm and 200 mm.But it is better to use special fittings for corrugated drainage. They have latches for quick assembly of the structure.
A method of joining parts without the use of couplings is also used. In this case, the end of one part is cut and put on another element. At the junction, it is required to additionally apply geotextile and fix it. Special tightness of connections in drainage systems is not required.
The angle of inclination of the structure is chosen depending on the level of groundwater, the type of soil on the site and the features of the relief.
Methods for laying drainage elements:
- Parallel to each other with water outlet to the central pipe.
- "Herringbone" - the main outlet element is located in the center.
- Along garden paths, slopes, retaining structures towards the catchment well.
There are some points to consider:
- The deep drainage system is laid below the foundation of the building.
- The design is arranged along the perimeter of the structure or in several directions on the site.
- The drainage system starts at the highest point of the drained area.
- It is advisable to attach all elements to the central pipe at an angle of 45 degrees.
- A distance of 6-10 meters should be provided between the lines.
- Inspection wells are made to monitor the state of the system in places of complex connections. The distance between them should be approximately 50 meters.
After putting the drainage system into operation, it is required to be periodically checked. It is worth inspecting the structure through control wells at least once a year. The water level in the sump is also checked.
The ineffective operation of the drainage system has several reasons:
- clogging of elements with silt;
- clogged drainage holes;
- mechanical damage to elements;
- subsidence of the structure under the weight of the soil.
Compliance with the technology of the device of the drainage system will allow it to be operated for a long time and trouble-free.
Drainage corrugated pipes prices
The cost of drainage products depends on materials, sizes and manufacturer. The price for single-layer PVC corrugated drainage pipes without filter is the lowest. Double-walled models with geotextile will cost significantly more.
Corrugated drainage pipes with geotextile are the best option for use in private construction, or in the construction of public or industrial buildings and structures. Due to their excellent technical characteristics, such systems are operated for a long time and reliably.