Rainwater and melt water can seriously swamp the soil and thereby cause irreparable damage to buildings and soil. To avoid damage caused by moisture, a good drainage system should be provided. The depth of the storm sewer of a closed or open type must comply with the established norms of SNiP. Otherwise, communication will be useless.
The importance of correct calculations when designing a storm sewer system

It is extremely important to adhere to the recommended SNiP standards for the depth and slope of stormwater. If we neglect accurate calculations, this threatens the following problems:
- poor outflow of rain / snow water and, as a result, waterlogging of the site;
- the formation of stagnant moisture and debris in the form of silt, sand, earth in specific sections of the sewage system;
- pushing out the laid pipes due to the tendency of the soil to heave;
- the need for complex repair work to clean the drainage line;
- freezing of pipes or sewer trays in frosts, and hence the possible rupture of drains;
- the risk of dismantling the entire system and re-laying it.
At the time of drawing up the design scheme of the storm sewer, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with SNiP 2.04.03-85 or with an updated version of the SP 32.13330.2012 print.
Determination of the depth of the storm sewer
In order for the mounted communication to work properly for more than a dozen years, it is important to correctly determine the depth of laying stormwater in a private house. SNiP 2.04.03-85 regulates the following minimum standards:
- for gutters / pipes of the drainage system with a cross section of up to 500 mm, the recess is from 30 cm;
- for trays / pipes with a diameter of 500 mm, the depth of the storm drain starts from 70 cm.
For a closed, laid drainage system, drainage pipes should be located 20 cm below the groundwater level. This will allow moisture to freely sink and leave through the pipes during the spring thaw.
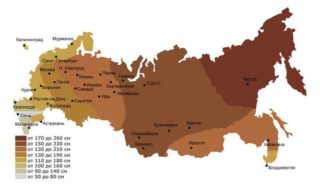
It is important to take into account the level of soil freezing in winter. The more porous the soil on the site, the smaller the thickness of the ice in the ground at sub-zero temperatures. In addition, pay attention to the thickness of the snow in the winter. If it is 10 cm or more, then it is a kind of pillow that reduces the thickness of the freezing of the earth. Thus, knowing the level of soil freezing and taking into account the thickness of the snow, it is possible to deduce the minimum indicators for laying drainage pipes at the site: from the existing level of ice in the soil in winter, approximately 30 cm (with pipes with a cross-section of up to 50 cm) and 50 cm (with a cross-section drain from 50 cm).
Example: the level of soil freezing in the area is 1200 mm. The thickness of the snow layer in the region is 10 cm.The diameter of the pipe is 50 cm.This means that we subtract 30 cm of the permitted ones from 120 cm and we get the minimum depth of occurrence - 90 cm.It is important to remember that 90 cm is the depth along the upper edge of the already laid pipe with all sand and gravel bedding.
If you lay a closed system at or above the freezing level of the soil, the ice in the pipes will melt slowly during the spring flood season. During this time, melt water will flood buildings and garden / horticultural crops.
If for any reason it is not possible to lay the drainage pipes at the recommended depth, they will have to be insulated with high quality.It is necessary to provide for the level of dynamic and static load on the system with a decrease in the depth of the drains.
The value of the minimum slope of the storm sewer according to SNiP
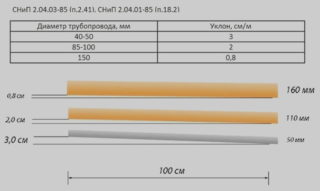
- For a drainage system with pipes / gutters with a diameter of 20 cm and more, the permissible slope for each running meter of stormwater is 7 mm.
- If trays / drains of a smaller diameter are used for the installation of sewers, the slope increases from 8 mm to 1.5 cm. Since the smaller diameter of the pipes forms a greater resistance to the free outflow of liquid.
In SNiP 2.04.03-85, the maximum level of the incline of the stormwater is also prescribed - it is 1.5 cm / m. With an arbitrary increase in the slope, the system will be clogged with sand and earth, which, due to the greater specific gravity, will not be able to move along with the water flow at the same speed.
The slope of open drainage systems depends on the level of roughness of the internal walls of the communication. The regulations set the following indicators:
- drainage ditches and trays on asphalt concrete roads - 0.003;
- crushed stone and cobbled road surfaces - 0.004;
- cobblestone surfaces - 0.005.
As a rule, in the private sector, open ditches are made, covered with broken bricks and cobblestones.
Calculation of the minimum slope of stormwater
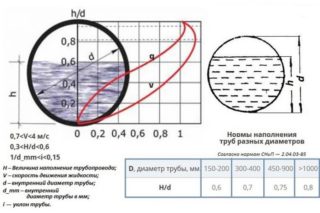
To calculate the minimum slope of the drainage system, you need to take into account the following stormwater parameters:
- type of drainage system (open / closed);
- diameter of pipes / gutters used;
- the material from which the drains are made (water slides on plastic faster than on concrete);
- storm drain slopes by 1 meter according to SNiP, depending on the section of the drains.
Here it is important to choose the correct diameter of the pipes for the volume of water to be discharged at the site. It is calculated using the following formula:
- Q = q20 × F × Ψ
All values in the formula are interpreted as follows:
- Q is the total volume of rainwater that will go through the drains.
- q20 - coefficient of intensity of annual precipitation (calculated in liters per second per 1 ha of land area). The coefficient is taken from the local environmental organization in the region.
- F is the total area of the site, taking into account the roof, from which water will be discharged (calculated in hectares).
- Ψ is a correction factor that takes into account the absorbency of the soil.
Coefficient Ψ is equal to the following indicators:
- open soil - 0.35;
- crushed stone - 0.4;
- concrete - 0.85;
- asphalt - 0.95;
- roof covering - 1.
According to the derived value, the cross-section of pipes for the drainage system or stormwater is selected. According to practical experience, the diameter of pipes for drainage in private ownership is often 110-150 mm.
If, due to the relief of the construction site or for other objective reasons, it is impossible to comply with the recommended SNiP slope norms, it is allowed to reduce it to 5 mm for pipes with a cross section of 20 cm and up to 7 mm for pipes with a cross section of 15 cm or less.
It is important to consider: the larger the diameter of the pipes of the system, the less the slope can be; the rougher the surface of the inner walls of the drain, the more you need to tilt the collector for free outflow of water from the site.
When installing a closed drainage system, it is necessary to observe the security zone. It implies indents from each pipe wall by 3-5 meters. It is forbidden to build, plant trees, organize landfills in this place. It is also undesirable to block the approaches and entrances to the revision / drop wells.