The purpose of the drainage system is to drain water from the roofs of buildings and structures. It consists of two parts: horizontal and vertical. The first is the gutters laid under the edge of the roofing material at a certain angle. The second is vertically installed pipes. Both parts are connected to each other by receiving funnels. The main characteristic of the system is the angle of inclination of the gutter.
What is the bias for?

The inclined plane causes the fluid to move. In the vertical pipes of the east, it will move without problems. In order for it to flow down the gutters of the first part of the drainage system, they must be laid at an angle. If this is not done, water will collect in the gutters, stagnate there, and when it accumulates, it will overflow over the edges of the trays, flooding the walls and foundation of the building.
There is also the opposite side of the situation. If the angle of inclination of the drain is large, this will primarily ruin the facade of the house. The drainage system from the roofs will not stand out in the best way.
In this case, water drainage will be as efficient as possible. But at the junction of the gutters with vertical pipes, a large volume of water will accumulate, which the pipes may not completely accept, the same overflow may occur. The problem can be solved by installing larger hoppers. But this will also affect the appearance of the facade.
Optimal tilt angle
The movement of water can occur already at an angle of inclination of 1 ° - this is 1 mm of vertical displacement of one of the edges of the gutter relative to the opposite side, taking into account the length of the tray of 1 m.But for the drainage system, this parameter is critical, especially when it is raining. Nobody forbids using this indicator in the process of designing or installing a drain, but the horizontal part of the drain with a large flow of liquid in this case cannot be handled.
There are recommended standards:
- the minimum slope of the gutters of the drainage system is 3 mm;
- maximum - 5 mm.
The angle of inclination is chosen depending on the diameter of the gutters to be installed. The relationship is as follows: the larger the diameter, the less the slope of the horizontal part of the drainage system.
The slope is also increased if the drain is a prefabricated structure: the system has a complex structure, consisting of separate sections, butted together. Typically, such gutters are installed on multilevel roof structures.
Rules for installing gutters
- roof area within 50-70 m² - gutters 90 mm wide;
- area of slopes from 70 to 140 m² - gutters 125-130 mm wide.
There is one more parameter that determines the length of the horizontal part of the drainage system of the house: the distance between the vertical pipe gutters. The maximum size is 12 m. The slope of the gutters will be set exactly on this part of the roof structure.
Calculate the slopes of the downpipe by 1 m in millimeters. For example, if the length of the horizontal part of the drain is 10 m, the angle of inclination is calculated as follows: for each meter of the structure, one of the ends of the tray is lowered, for example, by a maximum of 5 mm; this means that a ten-meter length will be lowered by 50 mm or 5 cm.
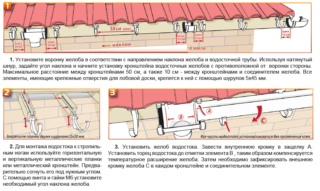
At the first stage of the installation of the drainage system, the marks of the two ends of the grooved structure are set.They do it like this:
- A mark is made from one of the edges of the horizontal part, which is located on the opposite side of the vertical part. Its vertical position is determined by the dimensions of the selected brackets on which the gutters will be laid.
- A self-tapping screw is screwed into it.
- Screw in a self-tapping screw on the opposite side of the roofing structure. It should be level with the first fastener.
- From the second screw, they lower 5 cm down, where the third self-tapping screw is screwed in. The second can be unscrewed.
- The first screw and the third are connected together, for which they use a strong thread or fishing line. This is the contour of the location of the grooved structure.
- In the locations of the screws, they are installed along the bracket. They are attached to the frontal board, to the first element of the sheathing or to the roof rafters.
- Intermediate brackets are installed every 50-100 cm strictly along the outlined contour.
- The thread is removed and proceeds to the installation of the eastern gutters.
Installation of horizontal gutters is the installation of trays on brackets using socket connection technology. The subsequent element fits under the previous one. The overlap is 10 cm. It is recommended to additionally seal this area, using, for example, silicone sealant. Optimal - if the joint of two trays falls on the bracket.
As soon as the horizontal part is mounted, go to the vertical. This is a common installation of pipes in a socket way, which are fixed to the wall with special clamps using self-tapping screws and plastic dowels. Further, receiving funnels are installed, which are a transitional element between the horizontal part of the drain and the vertical one. Here, the main task is tightness between the funnel and the gutter, as well as between the first and vertically installed pipe.
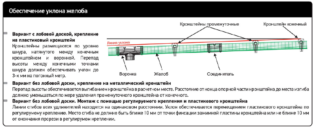
Often there are situations when the horizontal part of the drainage system, installed on one roof slope, consists of two parts, which are located with an inclination to one point. A vertical pipe stand is mounted in it. In this case, the slope and dimensions of the drainage elements are calculated taking into account half of the slope area, if one vertical riser is installed on the latter. For example, if the length of the cornice is 12 m, the risers are mounted in the middle - 6 m from the edges of the roof.
It is not always possible to do this for purely aesthetic requirements. Therefore, the pipes can be placed at different distances. For example, 4 m from one edge, 8 m from the other. This is the norm. But the calculation of the permeability of the gutters will have to be calculated taking into account the part of the area of the slope, under which there are two parts of the grooved structure that are different in length.
The correct choice of the angle of inclination of the horizontal part of the drainage system will ensure the most efficient operation of the drainage circuit. A slight deviation from the norms in one direction or another can lead to a decrease in the quality of work.









1 degree is 17 mm / m, not 1 mm / m.
And below, I suppose, should be: minimum - 30 mm / m (not 3 mm / m), maximum - 50 mm / m.