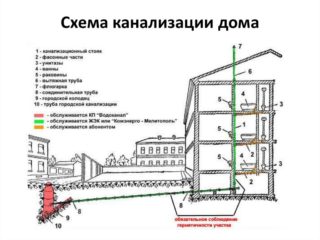
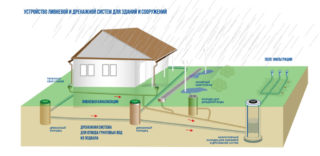
Drainage is called an engineering structure, through which contaminated used water, fecal matter, excess sediment, groundwater are removed from the facility. Thanks to this system, it is possible to maintain optimal sanitary conditions for living or production according to SanPin. Downstream communication allows you to remove wastewater into a common receiver for the purpose of their further treatment before being discharged into a nearby reservoir or reused for technical needs.
Types and device
- Storm sewage. Promotes superficial removal of excess moisture from the foundation of the house and from its pitched roof with a large amount of precipitation in the region. The stormwater drain includes a drainage system from the roof and linear channels for further transporting water to the nearest ravine, ditch, reservoir, septic tank or central sewage system.
- Drainage. Closed communication removes excess groundwater from the site. It looks like pipes connected to each other, laid underground at a depth of up to 1.5 m. The liquid is discharged into reservoirs or wells. No cleaning required.
- Household. The structure through which all used water is removed from the apartment / house to the central sewer receiver. The difference with previous systems is that the pipes remove fecal matter, waste from washing, washing dishes, etc.
Water disposal is divided into internal and external. The first option is its entire part located in the building. The second is everything outside of it. In turn, the outer part of the drainage system can be general-fusion (both rain and domestic water are utilized through it), semi-separate (drains go through different pipes, but merge into one receiver), separate (polluted domestic water, industrial and storm waste move along different channels to individual VOCs).
Unorganized removal of rain / melt water from the site leads to waterlogging.
Manufacturing materials
For laying an open linear storm drain in private construction, it is better to purchase trays made of composite, polymers or asbestos cement. They are easy to transport and stack, are not afraid of temperature extremes, and do not react to aggressive impurities in drains. It is only important that the gutters are selected in accordance with the required throughput and have protective grids.
For the drainage system of household waste, you can choose pipes from the following materials:
- Cast iron. The metal is durable (lasts up to 70 years), strong, not afraid of temperature extremes. Due to the insufficiently smooth inner wall, sludge deposits quickly form inside. The weight and price of cast iron pipes are quite high.
- Plastic. For the internal part of the communication, preference is given to PVC or polypropylene. It is better to lay the external network from HDPE pipes. Low-pressure polyethylene is plastic, inert to temperature extremes, and has a perfectly smooth surface. PVC pipes, but brown in color, have the same characteristics. They are intended for the outer part of the drainage system. Inside the building, gray tubes are used.
- Ceramics. Such pipes are used outside.The ceramic collector withstands temperature extremes, has a smooth wall surface, and is inert to chemical inclusions. Such material is worth impressive. It is not easy to work with it due to its large mass.
For large public collectors, reinforced concrete pipes are used.
Installation steps
- Roofing. The trays are fixed along the entire perimeter of the roof with a slope towards the drain pipe.
- Linear storm drain. Trenches are prepared, the bottom of which is compacted. Then a layer of sand is poured and rammed. A 5-7 cm thick concrete mixture is poured over the sand cushion. After it dries, trays are laid. On the sides, they are also poured with a solution. Protective grilles are laid on top.
- Drainage drainage system. Canals are prepared for drains below the groundwater level. Sand is poured at the bottom of the trenches, and then a layer of fine crushed stone. Perforated pipes in geotextiles are laid on it. From above, everything is again sprinkled with rubble and canals are buried.
- The household drainage system is mounted sequentially. First, the inner part, then the outer. The minimum diameter of pipes for drainage in an apartment is 50 mm. From the toilet - 110 mm. The central riser has a cross section of 110-150 mm. The pipes of the outer part are taken with a section of 160-220 mm. All drainage elements are connected to each other using fittings, adapters, tees.
Any of the systems should have a slope towards a common house riser or a private septic tank. The calculation is done depending on the cross-section of the pipes. The larger it is, the smaller the slope can be.
Wastewater disposal in utility bills
In the receipts for utilities, housing and communal services there is a column "drainage". It involves the removal of all consumed water to the city VOCs through the sewer system from the apartment / house. The tariff includes not only the transportation of wastewater, but also their subsequent treatment, and then proper disposal. Users of hot and cold water pay for the entire technological process to which the effluent from the apartment / house at the local treatment plant is subjected, including its maintenance. The exception is private homeowners in suburban settlements that are not connected to the central city highway and discharge their drains into a personal septic tank. They only pay for the water supply.
How to calculate the cost of the service
- The amount of payment for water disposal = (cold water supply m3 + hot water supply m3) x tariff
For example, the meters show that the user has consumed 3 m3 of cold water and 5 m3 of hot water. As a result, we have 8 m3. We multiply 16 rubles by a single tariff. and we receive 128 rubles for payment.
If the meters show that the total water consumption for the month was 8 m3, and the water disposal column indicates 10 m3, this is a gross violation. The user physically cannot dispose of more wastewater than the amount of cubic meters of consumed water. In this case, it is worth filing a complaint with the management company, and, if necessary, with the court.
If there are no water meters in the apartment, the amount for the sewerage service is calculated based on the norms of water consumption per person established for a specific period. By law, they are different for each region and are published in local media.
In apartment buildings, the bill for the wastewater service is calculated according to the general house meter and is divided by all apartments. In this case, the bills are marked with DPU (house metering devices) or ODN (general house needs).
Some users want to install a personal meter in the apartment not only for water supply, but also for water disposal. To do this, you need to submit an application for the installation of the device and its sealing. In the future, you can calculate the sewage service regardless of the general house meter with markings in the KPU receipt (apartment metering devices).