In order for the wetland around the house to turn into a flowering garden, it is necessary to take control of groundwater and rainwater. The drainage system can be created independently or with the assistance of specialists.
How to dig and reinforce a drainage ditch
- Stormwater - removes surface rain or snow water from the site.
- Drainage - prevents groundwater from rising to the surface of the earth.
Do not discharge storm water into the drainage system. Otherwise, during the rainy season, the perforated drainage pipe will quickly overflow, water will penetrate through the holes into the soil. Instead of draining, the drains will saturate the earth with moisture.
If you need to quickly drain the site, the easiest way is to invite specialists. They will plan an effective drainage system of open, closed or mixed type, taking into account the characteristics of the relief and the wishes of the owner. Craftsmen, using special equipment, will carefully dig trenches, lay pipes, restore or re-plan the landscape.
If you have free time, you can independently dig a ditch to drain water along the site, armed with a bayonet shovel. A drainage channel is an easy way to achieve the desired result.
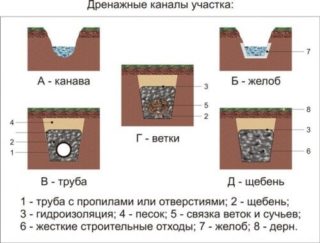
Definition and purpose of the drainage ditch
A drainage ditch is part of an open drainage system constructed to protect the soil from excess moisture. Waste water along the channel bed is discharged outside the territory of the site into catchment wells or reservoirs.
A ditch is a drainage ditch located along the perimeter of the site, or a roadside ditch along the sides of the road to drain water.
Nagornaya - a ditch designed to intercept water coming from the overlying slope.
Regulatory Requirements
Based on construction standards (see SNiP 2.05.07-85) drainage channels:
- are constructed in areas where groundwater is located deeper than 2 meters;
- laid in the direction of the catchment with a slope of 10 m of the channel: 2 cm on clay soils, 3 cm on sandy;
- located on the side of the inflow of water from the overlying area;
- laid in closed trays in the presence of water in the ground throughout the year;
- to prevent silting, the flow rate should be 25-30 cm / s (if the slopes are not landscaped).
It is forbidden to drain groundwater into natural reservoirs with fish, running water or used for recreation.Runoff should not lead to waterlogging of lowlands or further erosion of ravines. The standards define a differentiated approach to the construction of gutters, depending on the terrain, soil characteristics, the degree of watering of the site.
Device and principle of operation
Building codes do not regulate the location, size of drainage channels, their number for a particular site. These parameters depend on the watering of a particular area and are determined for each case individually.
As a rule, the channels have a trapezoidal shape, the depth is about 0.7 m, the width is 0.5 m. The walls of the gutter to prevent shattering are made with a slope of 25-30 degrees, carefully compacted. A thin layer of fine gravel or sand is poured onto the bottom. The lifespan of the ditch can be significantly increased by strengthening the walls in various ways.
First of all, it is necessary to provide for the diversion of water from the places of its accumulation on the site: puddles and streams will show them after rain. The scheme of the drainage system of drainage ditches can be linear or U-shaped, covering the estate from several sides, or, like a tree, have a main trunk with adjacent branches. However, the most efficient drainage is achieved by placing drainage trenches around the perimeter of the site.
A minimum slope of 2% or more is created in the drainage ditch to ensure an even flow rate, avoiding stagnant water and drain clogging. It reaches a maximum of 7% in flat areas.
If the site has weak soil or there is not enough space for a large canal, it is advisable to use drainage trays.
The sequence of work to create a ditch
For self-laying trenches you will need: bayonet and picking shovels, wheelbarrow, building level, pegs, twine, tape measure. Further:
- a place is selected;
- with pegs and, stretched between them, a string marks the laying line;
- earthworks are being carried out, surplus soil is removed in a wheelbarrow.
The slope of the canal bottom is brought out towards the catchment area, it must be constantly monitored using a building level.
Strengthening methods

By design, the drainage ditch is a simple short-lived structure. However, at no extra cost, drains can be turned into a decoration for the landscape of the homestead.
Unformed earthen walls of the drainage system are washed out by water flows, crumbled, which leads to clogging and deterioration of the drainage properties of the canal. This problem is easily solved by strengthening the slopes. The choice of the most optimal method depends on the type of soil and the desired result.
- The channel gutter is lined with natural stone.
- Ornamental shrubs or wild-growing herbs with a developed root system are planted along the edge of the canal, which reliably fix the slopes.
- Strengthening the walls of the drainage system with a three-dimensional geogrid.
- Sodding the upper part of the slope: securing pieces of turf is done with special wooden knitting needles.
- Use of geomats consisting of three-layer plastic gratings.
- The use of gabions.
- On clay soils, a good result is achieved by using geotextiles covered with a thick layer of sand or gravel.
- For a summer cottage, let's say a budget option: strengthening the slopes with old slate sheets or car tires.
In all cases, having strengthened the side walls, it is necessary to strengthen the bottom by creating a 5-10 cm layer of sand, crushed stone, gravel, rock or broken brick.
Advantages and disadvantages
Open drainage protects the soil from waterlogging and helps to avoid problems associated with high humidity.The lifespan of buildings increases, soil fertility increases, and the yield of cultivated plants increases. The advantages of an outdoor drainage device are:
- simplicity of the device, low cost;
- the ability to carry out work on their own;
- quick removal of melt or rainwater outside the home territory.
Among the disadvantages are:
- short service life;
- unattractive appearance;
- the need for frequent repairs due to shedding of slopes and clogging of narrow areas.
The device of open drainage systems is often used in the arrangement of summer cottages or adjoining territories. This is a low-cost but effective way to improve the comfort of living on the ground. Creativity can turn a simple ditch into a unique landscape feature.