The drainage system is a necessary element of the sewerage system. For its arrangement, it is necessary to select the material from which the gutters will be made, then lay underground highways to drain water from the site. If you do not take care of this, every year tons of melt and rainwater will soak the soil under the foundation, as a result of which it can sink, the walls crack or collapse - at best, decorative plaster will fall. A high-quality drainage system is especially important for a newly built house, where the soil has not yet subsided enough and there is a risk of structural destruction.
Why do you need a drainage system

Puddles on the sidewalk, faded paint on the walls and dirty stains are all the result of savings on the construction of a drainage system. If the site is located in a lowland, then water from neighboring territories will accumulate under the house. If the soil picks up a lot of liquid, ornamental crops will not be able to grow on it, since without a sufficient amount of air in the soil, they will die. The same goes for the vegetable garden. In addition to gutters and downpipes, it is necessary to provide for a system of channels through which the liquid will drain into a septic tank or outside into a common ditch.
In addition to its practical value, the storm drain has an aesthetic function. In accordance with the style in which the house is built, a system of suspension devices is selected to collect the liquid, transport it to the gutters. The storm drain can be purchased ready-made or assembled on your own. For this, there are several types of materials that are most often used for installing gutters.
Classification of drainage systems by installation and materials
Drainage systems are distinguished by the method of installation, shape and materials. There are two types of gutters. One of them is designed for a sloping roof and is called open - all elements are located outside the house. Another type, closed, is designed for a flat roof. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The disadvantage of an open system is its vulnerability to mechanical damage, ultraviolet light, frost. For the arrangement, you need to choose durable materials. In winter, additional heating of the structure may be needed so that water does not freeze in the gutters and icicles do not form. To avoid liquid stagnation, builders maintain a slight slope so that it moves faster towards the pipe and flows down.
In internal systems, funnels are used for drainage, which, in the required amount, are evenly distributed over the entire roof surface. The outlet elements are connected into one common pipe through which the liquid flows into the storage.
There are rectangular and circular systems. Round ones are more practical, since the water speed in them is higher. It is easier to build a round drain with your own hands, since ready-made plastic pipes are used for this. For gutters, they are simply cut in half and the edges are trimmed.
Of the materials that are most often used in the production of drainage systems, one can single out:
- galvanized steel;
- aluminum;
- plastic;
- copper.
Galvanized steel and aluminum are cheap gutter options. They are lightweight, easy to install, and do not overload the roof mounts.Steel corrodes over time, but when it comes to cost, this is the best option.
High-strength plastic can be matched to color. It is UV protected and lightweight. Ready-made structures can be ordered from the manufacturer, and assembled independently. It does not take much time. A plastic gutter system kit will cost more than a homemade design, but this option looks much more aesthetically pleasing. The plastic will serve for more than 50 years in the absence of external damage.
Prices for copper drainage systems are the highest, as the material is durable. According to theoretical data, copper does not lose its qualities for about 300 years. Products made of copper with the addition of other metals are able to withstand heat and frost, and withstand the blows of large hail. At the same time, the material is lightweight and does not create stress on walls and roof elements.
Elements of the drainage system
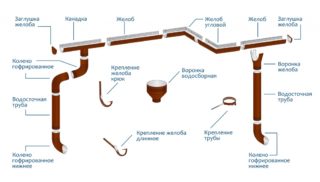
The main structural element is the gutter. It takes water from the roof and directs it into a pipe. Mounted on brackets that follow the shape of the gutter - round or rectangular. If the building has corners, there are corner elements - they can be internal and external in shape. Plugs are installed on the gutters at the edges so that the liquid does not pour out. In the places of risers, funnels are attached to them, through which water flows into the pipe.
Thanks to straight and corrugated pipes, it is possible to build gutters of any configuration - according to the shape of the roof. For convenience, manufacturers produce tees for connecting several gutters located at different heights to one riser. The riser ends with a knee, so that it is convenient to drain the liquid at an angle.
The stand is attached with clamps that are screwed to the wall. This additionally fixes the structure, protecting it from wind and shock.
Trays for collecting liquid are mounted on the ground, through which it is transported to sedimentation tanks or removed from the site. The trays are covered with removable grilles on top. If necessary, they can be opened and cleaned of debris.
Requirements for the drainage project
The materials used in the manufacture must comply with the requirements of GOST for drainage systems. Taking into account the peculiarities of the region, it is necessary to select a metal or plastic that can withstand the maximum and minimum temperatures.
Much attention is paid to small details such as brackets, which bear the entire load. Brackets are often made of durable metal, which will surely hold the structure in strong winds.
The coefficient of thermal expansion is an indicator that is taken into account when selecting materials. When heated, they expand, at low temperatures they contract. In regions with a harsh climate, it is necessary to take into account the resistance of drains to a sharp change in temperature, since the declared service life can change significantly - due to changes, products deteriorate faster.
Before installation, calculations of the mass of the entire structure and the ratio of fastening materials are carried out. You can do it yourself according to the instructions or entrust the planning to professionals.
Necessary calculations
First of all, the number of consumables is calculated - pipes, gutters, brackets, funnels, plugs, corner elements - internal and external. For this, the perimeter of the building and the height are measured. You need to buy materials with a margin of 20% in case of a shortage of gutters or the length of the risers.
When calculating the number of brackets, it should be borne in mind that for plastic systems they are screwed every 60 cm, for metal - every 110 cm.
The number of drainage funnels corresponds to the number of risers. When calculating fastening clamps for vertical pipes, they are guided by the height of the building. For one-story houses, two clamps are enough for one riser.
The number of screws for fasteners is bought with a margin.
Step-by-step guide to installing gutters
After mounting the fasteners, proceed to the assembly of the gutters. For convenience, this is done on the ground, and then lifted and placed in brackets. When the horizontal structure is ready, proceed to the installation of vertical risers. Here it is important to properly fasten the clamps and pipes so that they move freely inside the holders. This is necessary so that the clamp does not damage the riser due to thermal deformation of the pipes.
Prices for finished gutters vary depending on the quantity of consumables and its quality. Plastic is cheaper than copper. The cost of a rectangular drainage system practically does not differ from similar round ones, although in many ways it is more practical.









