The main parameter by which climatic equipment is selected is the power of the air conditioner. The parameter shows the performance of climatic technology in terms of cold and heating. A competent calculation of the power of the split system takes into account the area of the room and all sources of thermal radiation. A properly selected air conditioner will provide a comfortable microclimate without overpaying for electricity.
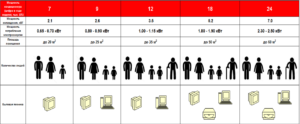
What is the power of the split system (kW per 1 sq. M of area)
Air conditioners are used to cool the room, less often to raise the temperature. Modern models simultaneously humidify and purify the air, but these are additional functions. When choosing the best option, they are guided by the refrigerating capacity of the model.
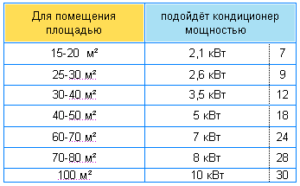
It is customary to make an approximate calculation of the split system according to the formula - 1 kW per 10 sq. m area. It is correct for rooms in an apartment or a private house with a ceiling height of 2.7-3 m.
Selecting the power of the air conditioner for a specific room
The power of split systems is measured in kW or BTU (BTU). The British marking for the measurement of thermal energy can be found in the characteristics of the climatic technology. The ratio between kilowatts and BTUs:
- 1 kW = 3412 BTU / h;
- 1 BTU / h = 0.2931 kW.
Cooling capacity is indicated with round numbers: 5000 BTU, 7000 BTU, 9000 BTU up to 30000 BTU. In the marking of the models, the number 5 "five", 7 "seven", 9 "nine" are indicated. For a preliminary calculation of the split system by the area of the room, the power in BTU is multiplied by 3.
Air conditioners for 5000 BTU / h (1.6 kW) are designed for a room of 15-16 sq.m. More efficient systems of 7000 BTU / Hr (2.1 kW) are suitable for a room of 21-22 sq. m. This is a popular option among buyers, the appliances correspond to the average area of the living room or hall.
When choosing climatic equipment for a particular room, not only dimensions are taken into account, but also related factors. The approximate power calculation is inaccurate. Lack of capacity will push the compressor to its limit. The engine will burn out quickly and replacement is expensive. A significant supply is also harmful. This is a waste of money and electricity. During operation, a high-performance air conditioner quickly cools the room, but due to the increase in temperature, it turns on again. Frequent starting and stopping of machinery accelerates wear.
Power consumption of the device
Comparing the values of power consumption and generation, it is easy to see that less energy is consumed than is obtained. For example, a 700 W air conditioner produces 2000 W (2 kW) cold. The efficiency of the installation turns out to be 300%.
The peculiarity of the work of climatic technology is the transfer of heat with the help of a refrigerant. Electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy. Climate control units do not produce cold, but remove excess heat from the room.
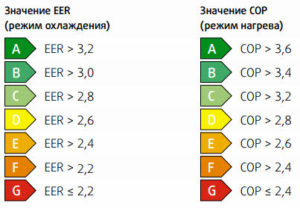
The ratio of power consumption to cooling capacity is the main indicator of the energy efficiency of climate technology. It is denoted by the EER ratio. In household appliances, its value is 2.5-4. For heating, a similar formula and COP are derived. Its parameters are in the range of 2.8-5.
Equipment performance also has two parameters: cooling and heating. The temperature lowering mode is used more often, therefore, they are guided by it. The heating capacity of the split is 3.6-5.5 kW per 1 kW of consumed electricity. The indicator is higher than in the cold. The difference is explained by the absence of heat loss on the line.
Most models are not designed for outdoor temperatures below -5 °. In the off-season, heating a room with an air conditioner will cost less than an electric heater.
Detailed calculation of air conditioner performance
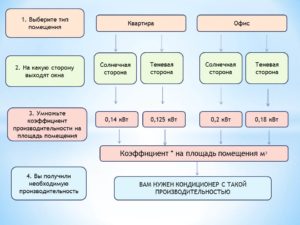
To pre-calculate the power of the split system, information about the area of the room is enough. It is correct to use the volume data, but it is difficult to multiply the parameters right away. When calculating performance correctly, additional factors are taken into account:
- location on the cardinal points (south, north);
- glazing area;
- the number of people gathering in the room at the same time;
- heat inflow from household appliances, electrical appliances;
- exposure to solar radiation, the presence of protection on the window;
- location of the room, on the top floor in summer it is hotter from the heated roof.
The premises are more than 70 sq. m calculating the power by area is not suitable. The split system is selected according to the total heat input.
Calculation formulas
The exact power indicator of the split system, depending on the area and height, is calculated by the formula:
Q = S * h * q, where
- S is the area of the room, sq. m;
- h - ceiling height, m;
- q - coefficient of lighting activity, W / cu. m. Intensive (south side) - 40, middle (east and west direction of windows) - 35, low (north side, shade of trees) - 30.
The total cold performance is calculated using the formula:
Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3, where
Q1 - heat input from the enclosing structures. The parameter formula is presented above Q1 = S * h * q.
Q2 - release of human energy. The value depends on age and degree of physical activity:
- an adult in a calm state - 100 W;
- light load - 125 W;
- hard physical work or intense sports - 200 W.
For children aged 5-12 years, the coefficient is 50 W. When calculating the total heat gain when installing an air conditioner in a house, an average of 110 W is taken, which is multiplied by the number of family members.
Q3 - heat inflows from household appliances. The calculated coefficient of lighting and other devices is 30% of the power consumption.
- TV set - 200 W;
- computer - 300 W
It is not necessary to purchase a model 100% corresponding to the design capacity. Variations of 5% below or 15% above the calculated cooling capacity are allowed.
Calculation example
- room area 25 sq. m;
- ceiling 2.5 m;
- number of people - 3 adults with light workload;
- east side, medium light intensity;
- appliances - TV and computer.
Q1 = 25 * 2.5 * 35 = 2188 W (2.2 kW)
Q2 = 3 * 125 = 375 W (0.38 kW)
Q3 = 300 + 200 = 500 W (0.5 kW)
Full air conditioner capacity for cooling
Q = 2.2 + 0.38 + 0.5 = 3.08 kW
Considering a small percentage of the stock, split systems with a performance of 2.93-3.38 kW are suitable.
Additional criteria for choosing climatic equipment are: manufacturer, type of air conditioner, functionality, design of the indoor unit. In domestic conditions, in terms of the ratio of price and comfort provided, split systems are in the lead.