Almost any floor includes a finish and rough subfloor. The quality of the former depends on the characteristics of the latter. The subfloor must be level, solid, dry and clean. Its design depends on the type of building: wooden, brick, on wooden beams, on concrete.
Sub-floor device

The top deck is always referred to as the finish floor. Lower and intermediate can be considered a draft or treated as separate items.
Most often, roughing means some rigid base that ensures the evenness of all subsequent layers. Its functions are as follows:
- Subsurface - the base absorbs the load from the flooring and distributes it evenly from wall to wall. This role is played by the slab, floor, soil.
- Leveling - the subfloor forms a flat or sloped surface.
- Intermediate - plays the role of an interlayer or binder between the top and bottom layers.
- Insulating - insulation and waterproofing of the base ensure the functionality of the entire structure. The “right” floor does not squeak underfoot, does not amplify the sound of footsteps, does not conduct noise from the lower or upper floors, and keeps the room warm.
A rough floor in a wooden house is made from the most waste material: slab, picket fence, non-planed boards. This layer serves as a kind of buffer and absorbs all loads arising from displacement, temperature and humidity fluctuations, so that the top layer does not undergo deformation.
Varieties of roughing in wooden houses
There are 3 main designs:
- on logs;
- on beams;
- on the ground.
The latter option is carried out if the house does not have a basement or basement.
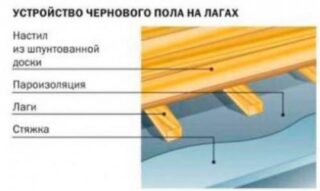
On the lags
Installation is simple, beginners can also handle it.
- The timber is cut to size. They are treated with an antiseptic.
- Lay with a distance of 40-50 cm.
- A gap of 20-30 mm is left between the wall and the edge of the timber. Mineral wool is laid here, which is later hidden by the baseboard. In the cavities obtained between the slats, insulation can be laid.
- When installing, check the horizontal laying using a level.
- Sheets of plywood and boards are attached to the logs as a finishing flooring.
With a low floor height, insulation can be dispensed with.
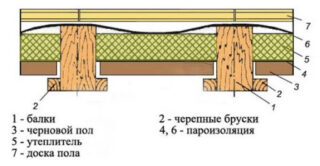
On beams
Beams can be placed directly on the foundation.
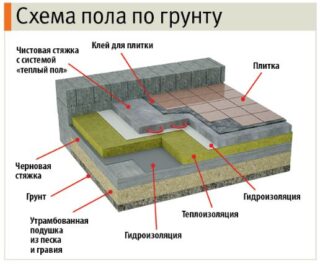
On the ground
- The soil is taken out to the required depth, compacted. At the bottom of the resulting trench, a bedding of river or ravine sand is tamped.
- Then a layer of crushed stone or expanded clay is poured. The addition prevents capillary rise of water and dampness.
- A layer of stone and sand is poured with concrete. For a rough screed, a material of a lower grade is taken.
- Laying waterproofing, better film.
- Install thermal insulation.The choice depends on the area and design of the building itself. Slab material is taken under the final concrete screed: polystyrene, penoplex. For the option on logs, mineral or basalt wool is needed. In some cases, expanded clay is simply poured.
- Cover the "cake" with a vapor barrier and lay the finishing floor.
When laying on the ground, you can equip a "warm floor". When planning the base, an additional height of 10–20 mm is laid. Electric mats or hot water heating are placed in a concrete screed. In this case, the construction of the subfloor will be somewhat different.
To increase the efficiency of heating, a foil layer is placed under the screed to reflect heat into the room.
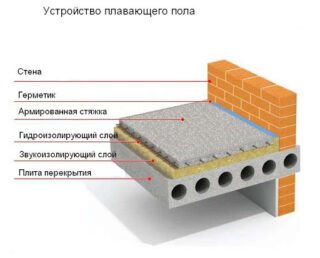
Floating floors
The floating sub-floor guarantees a long service life and stability for any floor covering such as laminate or parquet. They equip it on an old floor on logs, on a concrete slab, on the ground.
Most often, a floating floor is built on the basis of a concrete screed. At the same time, the roughing can be dry or wet. Despite the large weight and long construction period, wet floors are equipped more often.
- Prepare the base. If the floor is laid on the ground, a mixture of sand and gravel is tamped to the bottom of the site. If on a reinforced concrete slab, the latter is cleaned, treated with an antiseptic primer. The cracks and chips found are closed up.
- The subfloor in a wooden or light frame house does not need to be reinforced. In heavy three-story cottages, this is necessary. For reinforcement, take a metal mesh or tie the rods on their own.
- A damper tape is laid along the perimeter of the room to the entire height of the structure. The concrete screed must not be in contact with the walls.
- The structure is poured with concrete of grade B7.5 – B10. The thickness of the layer is 7–10 cm. The reinforcement should be deepened into the layer by at least 3 cm.
- The layer is aligned according to the pre-arranged beacons using a rule or a laser level. After the initial setting of the material, the beacons are removed and the holes are filled with fresh concrete of the same brand.
- After drying, the surface is insulated with a polyurethane film.
Any finishing flooring can be laid on the screed obtained.
If a dry floor is being set up, instead of pouring on the backfill of expanded clay, perlite and sand, dry board materials are laid, like plywood, chipboard, asbestos-cement sheets. This option attracts with the speed of installation: you do not need to wait until the concrete dries to continue working.
Floating floor on dry and wet screed can be additionally insulated.
Material selection

The construction includes several layers. For each of them, a material is chosen that is combined with the rest and meets the general requirements.
- For backfilling, take small and medium-sized crushed stone - 5-10 mm in diameter, sand - river or ravine. Instead of crushed stone, you can use expanded clay: it also prevents the absorption of moisture by the screed, but at the same time it will also allow you to keep warm.
- If the subfloor is a backfill, only river sand and fine crushed stone are taken for it.
- For a wet rough screed, concrete, cement-sand, gypsum and foam concrete mixtures are taken. They also use bulk compositions, where polyurethane or polyester resins act as a binder. Such mixtures harden faster, a thinner layer is required for styling.
- For waterproofing, you can take an ordinary roofing material in 2-3 layers. Concrete is treated with liquid bituminous mastics.
- Insulate the structure with foam or foam plates, mineral or basalt wool. Here the choice depends on the climatic conditions and the depth of the base.The heat-saving coefficient of mineral wool or expanded clay is less than that of a foam board, therefore a thicker layer of thermal insulation is required. This is not always possible.
The material of the finishing flooring also influences the choice of the material of the rough screed.
Required tools and building materials

There are several different technologies for installing subfloors. This requires different materials, but the same tools. The main list includes:
- devices for removing the old floor, if repairs are being made;
- building or laser level, tape measure, corner;
- shovels, trowels, hacksaws for wood, jigsaws;
- screwdriver, drill, grinder;
- beacons and a rule for leveling the screed;
- concrete mixer for preparing concrete;
- thermal insulation materials - the latter are recommended to be kept indoors for about a day before laying;
- waterproofing - roofing material, films, membranes, coating compounds;
- vapor barrier - not always required;
- materials for dry screed - chipboard, waterproof plywood, GPV sheet.
Other tools may be required to equip the sub-floor.
Styling features
The type of subfloor and the method of installation is determined not so much by the material of the walls as by the material of the floors or foundation, as well as the presence or absence of the basement.
- In a log house without an underground, the easiest way is to equip the floor on the ground. A dry screed, wet, bedding is used.
- If a wooden house stands on a slab foundation, a screed is made directly to the base.
- With an existing subfloor, the best option would be a floor on logs or beams. If the subfloor is ventilated, this option guarantees the durability of the floors and good insulation.
A reliable and even subfloor is the basis for the durability and reliability of the coating in the house. There are several design options. Choose a suitable one, taking into account the characteristics of a wooden building, foundation, subfloor.