Aerated concrete is a type of porous concrete. In the artificial material, interconnecting cells with a size of 1 - 3 mm are evenly distributed. It is easy to build a house from aerated concrete with your own hands, since the stones are large, have ideal parameters, they do not need to be adjusted. Lightweight buildings retain heat, subject to the construction technology.
Properties of aerated concrete

Ground sand, burnt carbonate rocks (lime) and water are taken as raw materials. Blocks are made in molds, they are not completely filled with the mixture, then a component is introduced to form a gas. Under pressure, the mass increases in size, bubbles form in it, in this form, aerated concrete hardens. Sometimes ground slag, gypsum, ash are added to the composition.
The blocks are obtained with the exact size and correct geometric shape. The density is coordinated by the volume of the blowing agent. The technology involves obtaining different grades of aerated concrete, the characteristics of which depend on the density, bearing capacity and thermal insulation qualities.
Low thermal conductivity is attributed to the main property of porous concrete, which is why the material is used as protection against cold and in the form of load-bearing elements. Aerated concrete conducts heat 4 times less than brick. The downside is that the moisture content of the material affects the insulating properties; it is able to absorb water from the surrounding space due to the bubbles in the mass communicating with each other.
By appointment, aerated concrete is classified:
- constructional;
- structural and heat-insulating;
- heat insulating.
The hardening conditions at release also cause subdivision. Autoclave types harden under the action of saturated steam, non-autoclave types harden in a normal environment.
An astringent is introduced into the composition:
- lime (boiling water) includes 50% or more of the mass, the remainder is gypsum, slag, cement;
- cement (Portland cement) add more than 50% of the total weight;
- slag is half, lime, alkali, gypsum are added;
- ash of the highly basic category is introduced into the volume of more than half.
Raw materials are natural or include wastes from the production of building materials, hydraulic removal, ore dressing.
Calculation and dimensions of the required quantity

Stones are produced rectangular or U-shaped. The second option is used to design wall openings and before laying floor slabs.
The size of gas blocks for building a house, standard:
- U-shaped - height 250 mm, width 200 - 400 mm, length 500, 600 mm;
- Rectangular - height 200 - 250 mm, width 100 - 400 mm, length 600, 625 mm.
When erecting internal partitions and walls, preference is given to stones with a thickness of 100 - 150 mm, and external vertical fences are built from blocks with a width of 400, 300, 240 mm.
To calculate the amount of material, the following methods are used:
- by the area of the outer walls;
- by the volume of the walls.
In the first method, a building plan is taken and the length of the outer fences is measured on it in individual areas, then the values are added. The perimeter is obtained, which is multiplied by the height from the basement to the roof, so the area of the outer walls is calculated. The quadrature of the internal partitions is calculated in a similar way. The area of openings for doors and windows is subtracted from the obtained value.
The next step is to count the number of stones in 1 m².For example, the area of a block is 0.12 m² (0.2 x 0.6 m), so there are 8.33 of them in the square (1: 0.12). The total square of the outer walls is divided by 8.33 and the number of stones is obtained. The parameters of the internal partitions are also used to obtain the number of aerated concrete blocks. For cutting to size add 3% to the number of blocks.
Another method is used if aerated concrete products are sold not in pieces, but in cubic meters. The accrued area of the outer walls and the quadrature of the partitions separately are divided by the thickness of the block as it will be laid in the structure. The total volume of the required material is obtained. If from this calculation it is necessary to select the number of stones, the cubic capacity of one stone is calculated.
Volumes of individual blocks:
- block 600 x 300 x 100 has a volume of 0.018 m³;
- 600 x 300 x 150 - 0.027 m³;
- 600 x 300 x 200 - 0.035 m³;
- 600 x 300 x 250 - 0.045 m³;
- 600 x 300 x 300 - 0.054 m³;
- 600 x 300 x 350 - 0.063 m³;
- 600 x 200 x 400 - 0.048 m³.
The resulting total volume of external fences and separately internal partitions is divided by the cubic capacity of the corresponding blocks, and the number of elements is found.
Advantages and disadvantages
Positive material characteristics:
- refers to light materials, so the load on the supporting base of the house is reduced;
- forms solid wall structures, despite the low density;
- keeps the house warm;
- easily processed, drilled, cut with a hacksaw;
- maintains a comfortable microclimate (when the humidity rises, it absorbs, when it decreases, it gives off);
- low cost;
- withstands from 35 to 100 cycles of freezing and thawing;
- reduces the complexity of the process, reduces the speed of masonry;
- invulnerable to climatic and biological influences of the surrounding space;
- belongs to the environmentally friendly group of building materials.
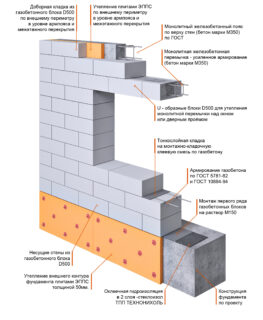
Aerated concrete is more saturated with water than other porous concretes, so it must be insulated from moisture. In this case, a ventilated gap is required so that condensation on the inside of the film does not wet the blocks. Because of this property, according to the instructions, it cannot be used for warming foundations, since there is direct contact with soil moisture. Aerated concrete blocks are fragile, therefore, they require caution during transportation and unloading.
Required tools and materials

The peculiarity of building a house from a gas block with your own hands is that you can use special electrical tools for processing stones, but cutting is easy to carry out with a hand tool.
Required tools:
- a band saw is prepared for cutting blocks, if the volume of construction is large or the complexity of the wall configuration is increased, there is a lot of cutting work;
- a hand saw or a hacksaw, preferably with victorious soldering on the teeth, is used directly at the construction site;
- a drill with different drills is taken to form structural holes in the blocks;
- grooves, grooves are made with a manual wall chaser to lay pipes, anchors, electrics, reinforcement elements;
- electromilling cutter is chosen with a large amount of chasing;
- a toothed trowel is used to apply glue to the surface of the block;
- use a 5 m tape measure, a construction or laser level, a plumb line, a carpenter's square;
- use a whisk for mixing the glue mixture, a trowel with a rubber or wooden tip;
- you need a hammer, chisel, metal grater.
Reinforcement is prepared from the materials, which is laid horizontally or placed vertically, depending on the masonry technology. Take corrugated or smooth rods with a diameter of 10 - 16 mm.
The glue is chosen depending on the manufacturer, quality and price.The maximum thickness of the seam is not more than 4 mm, and 1.5 - 2.0 kilograms of dry powder go to 1 square of masonry. You can prepare a mortar from sand and cement, but then the size of the seam will increase to 6 - 7 mm and the protective property of the wall from the cold will decrease.
Rules and features of laying aerated concrete
The first element is placed in the corner, which defines the highest point. Further, the stones are distributed in other corners of the future structure. A cord is pulled between the blocks, which gives a guideline in height for future masonry. The number of beacon stones can be increased and placed at intervals of 2 m, if there is a sagging of the cord.
For the masonry of the first row, a cement-sand mortar is used at a concentration of 1: 3 to enhance the adhesion of aerated concrete with a waterproofing layer on the surface of the foundation. For the installation of subsequent blocks, special glue is used, which is sold dry and mixed with water before use.
The second and subsequent rows are laid according to the pattern, starting from the corner, but so that the vertical seams between the blocks are displaced in relation to the bottom row. In the first 15 minutes after installation, the laid element can be corrected with a rubber mallet, then the solution will set.
Above the door and window wall openings, concrete or metal lintels are laid, the type and section of which is determined by calculation during the development of the project. The surrounding aerated concrete stones are trimmed so that they stand next to the lintel without a gap. Above the window beam is supported at least 25 cm on the walls on both sides of the opening.
Aerated concrete elements most often have flawless geometry and standard dimensions, so the seam should be made as small as possible, ideally the layer should be 1.5 - 2.0 mm.
DIY house construction from aerated concrete
Before starting construction, they study the technology and determine the order of work. They start with the design of a residential building, the documentation is ordered from a design organization that has an appropriate license. In the process of preparation, the volume of material is calculated and the first purchases are made so as not to store a large amount of material at the construction site.
Step-by-step stages of construction:
- preparation of the construction site;
- marking the axes of the structure on the ground in accordance with the plan;
- implementation of the zero cycle (soil development, foundation erection);
- insulation and waterproofing of the base;
- masonry of the basement, walls, decoration of openings for windows and doors;
- the device of a reinforced belt for the installation of coating slabs;
- installation of plates;
- roof structure device;
- roofing;
- installation of a water supply system, installation of a blind area;
- sewerage, plumbing, ventilation, electrical wiring, connection to general networks;
- external and internal finishing works.
A shallow strip foundation is chosen as the base, piles or individual pillars are placed. The plinth is made of red ceramic brick, which hardly gets wet and does not transfer moisture to the walls made of aerated concrete. Jumpers are purchased ready-made or welded from a corner, pipe or channel.
The length of the floor slab is chosen according to the width of the span, if necessary, perform monolithic concrete sections or cut the panels along the length using a grinder and a hammer. For communications, longitudinal cuts or through holes in the walls are made, observing safety rules.
Reinforcement of aerated concrete

The scheme for strengthening the walls of aerated concrete blocks is chosen at the design stage. There are options for vertical and horizontal masonry reinforcement.
The first type of bar insertion is not a mandatory procedure, it is used only in certain circumstances:
- the building is being erected in an earthquake-prone region;
- the house is located on a mountain slope;
- sharp and strong winds, hurricanes are expected in the area;
- the structure of the building is provided with tape glazing or large-scale openings are planned.
Horizontal reinforcement is always performed, while the rods are placed at the beginning and after 3 - 4 rows of masonry, which depends on the density of aerated concrete and its design ability to withstand loads.
Reinforcement materials are used:
- steel rods with a corrugated and smooth surface with a diameter of 6 - 10 mm, class A3;
- masonry wire mesh, which does not require grooving for installation;
- perforated galvanized strip 1 mm thick, 20 mm wide.
At the corners, an overlap of reinforcing rods or mesh is performed. For reinforcement, grooves are made in the body of the blocks, and after laying, the metal is sealed with mortar or glue.
Before laying the floor slabs, a reinforced concrete belt is made to support the reinforced concrete panels. It is made along the width of the wall to a height of 20 - 25 cm. For the belt, a reinforcing cage is made, the joints of which are knitted with wire or welded.









