Arrangement of the rafter system and laying of roofing material are the final stage in the construction of residential and utility buildings. This phase is no less important than the construction of the foundation and walls. The tightness, strength, stability and functionality of the entire structure depend on the correctness of its planning. The angle of inclination of the roof is not the least important in the design. This indicator determines the aesthetic side of the structure and its operational characteristics. To make the right decision, you should study the existing types of roof structures and the norms that are used when designing the angle of inclination of the roof.
Types of roofs and their dependence on the angle of inclination
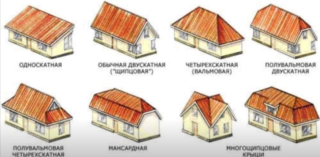
In terms of shape and steepness, these types of roofs are distinguished:
- Shed. It is an inclined plane without drops and kinks. It is the simplest design in terms of assembly, but limited in functionality. The slope of a flat roof is determined by the type of roofing and wind load.
- Gable. It is a classic and is considered the most popular among private developers. Consists of two surfaces connected at the top by a ridge beam. Vertical triangular walls - pediments - are arranged between the slopes.
- Tent. Consists of four isosceles triangles forming a regular pyramid. Provides a perfectly solid monolithic construction. The roof slope varies between 15-60 degrees, depending on climatic conditions and covering material.
- Hip. A four-slope pattern formed by trapezoidal and triangular surfaces. Differ in the complexity of the design of the frame and high aesthetic characteristics. The angle of the roof slope is steep due to the peculiarities of the project.
- Vaulted. It has complex curved slopes with smooth and sharp transitions. It is rarely used in construction, since several types of materials are used to create a support system - brick, reinforced concrete and wood. The slope of the roof is made large, since a flexible covering is used - soft tiles or welded roof.
- Multi-pliers. The most difficult to design and implement, but the most spectacular configuration. Consists of a set of sharp figures, assembled resembling the dome of a castle. The roof angle is maximum among analogs and starts from 50 degrees.
The slope of the slope directly depends on the design of the roof. Its configuration determines the choice of finishing material.
The influence of various factors on the choice of the angle of inclination

In most cases, the most spectacular and striking roof configuration is first selected with an assessment of the possibility of practical application of the attic space. After that, by the method of elimination, the optimal slope is selected, taking into account the analysis of the influence of various objective and subjective factors.
- Generally accepted building rules. It is necessary to choose the slope of the roof according to the standards established by GOST and SNIP. Otherwise, the building will not be put into operation and it will have to be remodeled.
- National traditions. In each locality, it is customary to follow one or another architecture that defines the local ethnos.
- The strength and direction of the prevailing winds.The greater the intensity of movement of air masses, the less should be the windage of the structure.
- Precipitation level. This applies to snow, which in large quantities can push through the roofing and break the rafters.
- The choice of topcoat. The range of the slope depends on it, ignoring which leads to emergency situations.
For each material, a maximum and minimum slope is set, which is calculated taking into account a lot of related data.
How to calculate
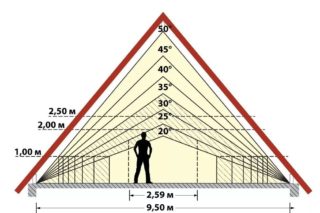
The roof slope is calculated individually for each dwelling. Initially, you need to decide on the functionality of the attic space - you need it for housekeeping or not.
Based on this parameter, the following types of roofs are distinguished:
- Flat (unexploited). They are structures where there is a minimum of space between the roof and the floor slab, where the movement of people is difficult or impossible. It is profitable to build such structures, since complex calculations are not required, the consumption of materials is minimal. The slope of the flat roof is from 3 to 15 degrees, depending on the cladding material and external factors.
- Pitched (operated). They are made with an angle of 30 degrees or more. Thanks to this solution, a spacious attic is formed, in which you can equip utility and even living quarters.
To correctly calculate the optimal slope angle, you should use the reference information set out in SNiP II-26-76. The document contains tables that contain data on regional coefficients: snow loads, wind indicators, recommended ranges of slope angles for finishing. It is recommended to count indicators in percent, but if desired, they can be converted into degrees using the table attached to the standards.
Influence of roof slope on the choice of roofing material

In order to correctly calculate the roof drawing, it is necessary to know and correctly apply in practice the norms established for each covering material:
- solid tiles made of metal, ceramics and cement - 6-30;
- bituminous tiles - 12-45;
- slate, profiled sheet - 7-40;
- folded metal covering - 15-60;
- roofing material and its analogues - 20-30.
Recommendations are given as a percentage. The figures are written taking into account such factors as the ability to withstand wind and snow loads, effective water drainage. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the degree of tightness of the roof, which is assembled from individual fragments. If the joints are not sealed with mastic, the slope must be increased. You can measure it with an electronic device, a protractor or by aspect ratio.
Minimum roof slope

These indicators are indicated in the installation instructions for all roofing materials on sale.
They are determined by the following factors:
- Leakage protection. Profiled sheeting, slate and hard tiles are placed in the overlay and with a slope of less than 20 degrees, water can penetrate into the joints.
- Snow load. If it does not come off on its own, there is a risk of deformation, breakage or rupture of the roofing, destruction of the support system. The recommended angle is 30 degrees.
- Stability of the material based on. If this does not apply to slate, profiled sheet and folded structures (they are nailed or screwed on), then in relation to strips and tiles, certain standards must be applied. Tiles can tear off too steep or gentle slopes, and overlays can slip.
The steeper the roof angle, the higher the roof. This leads to a high consumption of building materials and an increased risk of overturning the structure by a strong gust of wind. However, even gentle slopes are not a means of saving.They need to be made with a powerful rafter system in order to be guaranteed to withstand vertical snow and horizontal wind loads.
Climatic factors

Climatic conditions are the most important factor that influences the choice of roof structure and especially the slope of its slopes.
When the mass of precipitation after heavy snowfalls lingers on the roof, it absorbs moisture from the air and then freezes. The multi-ton layer is capable of crushing the most reliable and proven load-bearing structures and coatings. Based on this, it is necessary to observe the optimal roof angle for snow melting, which is recommended by the manufacturer. This indicator is influenced not only by the slope angle, but also by the smoothness and composition of the topcoat.
It is equally important to consider the wind load. Hurricanes are not uncommon in Russia and most often they destroy roofs. Streams of air masses knock down structures or tear them away from the base. To prevent this, it is necessary to carefully calculate the ratio of overhangs, steepness and windage of the roof. Experts say that the optimal roof slope is within 30-45 degrees. Structures of this type have proportions that ensure the rapid melting of snow, storm water and at the same time withstand gusts of wind, even of extreme force.









There is also bionic roofing, a very complex form for buildings with modern architecture, mostly public. there is a round roof for buildings with a strato-geodesic dome, or, in fact, its wall and roof at the same time.