Groundwater is characterized by a changing surface level, the mark rises in floods and rains. It is not very difficult to build a cellar with your own hands with a high level of groundwater, but you need to provide a drainage system. The basement walls are insulated from moisture, the work is performed using a special technology. Certain methods are used to determine GWL.
- Design options for high groundwater levels
- Wall-mounted above-ground cellar
- Semi-buried cellar
- Bulk basement
- Metal cellar-caisson
- Monolithic concrete structure
- Determination of the groundwater level
- Site preparation, tools and materials
- Building recommendations
- Base and recessed part
- Wastewater disposal
- External drainage
- Internal drainage
- Ventilation device
Design options for high groundwater levels

The basement must be built in such a way as to reduce the effect of the soil liquid on the walls of the structure. The waters inside the soil are acidic, alkaline, sulfate, magnesian, carbon dioxide.
The types of cellars are used:
- wall-mounted;
- semi-recessed;
- bulk;
- a caisson in the form of a capsule;
- monolithic concrete.
Each type of water acts on the material in its own way, but chemicals react with the components of concrete and brick. As a result, the base swells and collapses.
Wall-mounted above-ground cellar

A basement built against the wall of a house, a barn saves space on the site of a summer cottage, a private house. The dimensions of the building are chosen individually in each case.
Features of the wall-mounted design:
- the masonry of the walls is made of bricks or monolithic fences are made of concrete;
- inside the surface they are plastered;
- on the floor - concrete base and cement screed.
The roof is made multi-layered, a slab, clay-sand mortar and several layers of roofing material are used. They roll over the building with fertile soil, sow grass and stunted plants on the surface.
Semi-buried cellar
Use the construction method if the raised water does not exceed 1.5 m to the surface. The construction technology is similar to a wall basement, but the floor in the underground part is made 70 - 80 cm lower.
Construction characteristics:
- the base can be built from concrete or red brick, slag concrete (in dry soil);
- build with insulation with bitumen, clay, roofing material;
- a ventilation hole is made in the overlap of the ground part.
The entrance to the semi-buried basement is made from the ground, the door is placed not in the ceiling, but in the wall, combined with a staircase, and insulated.
Bulk basement

A freestanding storage facility is equipped under difficult hydrogeological circumstances on a land plot. This includes the proximity of a river, a lake from the yard, if the GWL distance approaches 50 cm.
Construction features:
- the floor is buried half a meter, and the frame of the structure is covered with soil to reduce heating in summer;
- additives are added to concrete to increase moisture resistance;
- the base and the underground part of the walls are insulated outside and inside.
The building is made of an interesting design in the form of a hemisphere, a pointed tower, in order to fit it into the landscape ensemble.
Metal cellar-caisson

The storage capsule is made of metal or plastic. The product is a one-piece container with carefully welded or welded seams to keep water out.
Description of caissons:
- the reservoir is rectangular, square, cylindrical, in the form of a ring;
- thickness of plastic on the walls up to 15 mm, metal - 4 - 12 mm;
- the hatch is performed on the side or on top.
Metal containers are treated with Kuzbasslak on the outside, and a heat-insulating layer is placed on them inside. Use mineral wool in rolls, sheets of polystyrene, foam. The insulator is sewn up inside with moisture-resistant plywood.
Monolithic concrete structure
The structure is completely buried in the ground, therefore, the communications of the water supply, gas, sewage, electricity, which may be in the ground, are pre-checked. To dig a pit, mechanical transport is used, since it is difficult to manually dig a hole to a depth of more than three meters.
Internal dimensions are standardly made 2.5 x 4.0 m, they can be changed depending on needs. The walls are 25 - 40 cm thick, concrete is poured into the formwork with mandatory waterproofing.
Determination of the groundwater level
It is possible to officially confirm the standing point of the soil liquid by ordering a geological examination with a topographic survey. This option is used if at the same time they are building housing on the site and surveys are required not only for the basement.
Step-by-step instructions for finding the water level on your own:
- drill several holes with a drill 2.0 m deep;
- within three days, measure the level of water filling in each hole, use a plumb line, rods.
In rains and thaws, an overhead water is formed in clay and loam - a cavity with water. There is no constant pressure in it.
Site preparation, tools and materials
It is better to make a cellar if the water is close, on the slope of a hillock, ideally, you need to use this feature of the relief. The driest place in the yard is chosen for storage.
Materials for the construction of the cellar:
- fired ceramic bricks are used for the walls, silicate bricks are not suitable;
- the concrete base is made with concrete, for which you will need medium fraction crushed stone, sifted sand, M400 cement;
- oily clay is taken for coating;
- the formwork is made of boards;
- two asbestos-cement or plastic pipes are prepared for ventilation;
- you will need steel reinforcement and a corner, a channel.
The concrete and mortar are mixed with a concrete mixer, the ingredients are poured with shovels, buckets. A hammer, tape measure, carpentry corner, plumb line are prepared for work. The horizontalness of the floor and rows is measured by the level.
The bottom of the pit is cleaned with bayonet shovels using scrap. For masonry, you will need a trowel, a brick pickaxe, a wooden or metal ordering with divisions.
Building recommendations

If one-piece storage containers are installed, protrusions-handles are provided on the walls to mount the box. The outer surface of the steel box is coated with phosphoric acid, then painted with red lead for metal.
If there is a high groundwater level in the area, the edges of the walls of a solid or monolithic concrete box must be higher than this mark, otherwise the upper end will soon collapse from moisture. A metal pipe with a crane welded to it is placed in the corner of the structure.
The depth of the pit is performed 30 cm below the estimated mark in order to make a crushed stone-sand cushion. The formwork for monolithic walls is not made immediately to the full height, so that it is more convenient to pour the mixture. It is gradually being added.
Base and recessed part
Sand 110 - 12 cm is poured at the bottom, then crushed stone, each layer is rammed, spilled with water for compaction. Concrete is poured with a thickness of 17 - 20 cm, before laying, a reinforcing mesh is placed from rods with a diameter of 6 - 8 mm. The joints are welded or connected with knitting wire.
Masonry features:
- prepare a solution in a ratio of 1: 3 (cement, sand, respectively);
- the gap between the wall and the ground is filled with a solution of sand and liquid clay at a concentration of 1: 2 (clay, sand); at large distances, a broken brick is added;
- the laying is carried out in 1 - ½ bricks with bandaging of horizontal and vertical joints.
Clay is not allowed to enter the masonry joints. It is convenient to use the ordering - a long bar, where there are marks along the length of the brick with a seam.
Wastewater disposal

In some construction options, they do not make a drainage system, preferring a thorough waterproofing of the contact surfaces. If the soil moisture does not rise above the base of the cellar base or the area is dry and without water bodies, such a risk is justified.
It is necessary to make drainage if the groundwater is close to the cellar:
- the basement is being erected in a risk zone, not far from the river bed;
- the ground moisture level rises above the basement base;
- the site is in a low place.
It is good if the surrounding earth from the basement contains loam and clay. The drainage device is not a complicated procedure, but it helps with an unexpected rise in moisture.
External drainage
A system of this type is built at the beginning of construction. The pipes are laid along the outer edge of the base, at the height of the sole. The system picks up most of the moisture before it passes through the floor and into the cellar. For additional protection against dripping moisture, sealing of all enclosing surfaces is used.
Materials used:
- perforated pipe 100 - 150 mm;
- for the inspection well, continuous pipes of 250 - 300 mm are taken;
- joined into a ring using corners, tees, straight connectors;
- insulate under the bottom with geotextiles.
After installing the pipes, the trench is filled with a mixture of gravel, sand and soil. Together with insulation, drainage protects the walls and interior from dampness.
Internal drainage

Such a scheme is used if it is difficult to dig out the soil outside, destroy the blind area, paths. The internal system collects liquid that has entered the basement. This is a less efficient arrangement compared to outdoor styling. It does not protect the floor and walls of the underground storage from mold.
With the device, work is performed:
- punch a trench in the basement basement (concrete) with a hammer drill or chipper;
- the laid pipes are covered with a decking, which reduces the useful height of the basement by 35 - 40 cm;
- try not to violate the integrity of the sand-crushed stone pillow.
Inspection hatches and wells are arranged along the perimeter of the floor.
Ventilation device
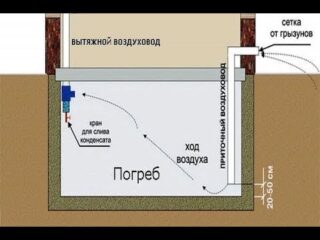
For vegetable stores, the creation of a standard microclimate is mandatory. The room should be free of stagnant odor and drafts.
Ventilation creates conditions:
- supplies fresh air;
- provides the required temperature;
- regulates humidity.
They make a system of inflow and outflow of streams. Air ducts are round or rectangular. The supply pipe is placed at the bottom, at a level of 60 cm from the floor surface. The hood is brought out to the roof of the cellar, raised by 1 m. Two pipes are placed in diagonally opposite corners to increase traction.








