The greenhouse is attached to the house so that the building and the garden under the polycarbonate have a common wall. The practical design includes a supporting frame and a translucent cover. The frame is made of materials with different properties. Wood, PVC, steel are chosen for construction in specific conditions. It is not difficult to build a wall-mounted polycarbonate greenhouse with your own hands if you know the construction features.
Technical features of wall greenhouses

Annexes for growing garden crops near the wall of the building save land space. The shape of the wall structures is made different, but the roof is most often covered with polycarbonate. Greenhouses are used as temporary beds under the roof or build a capital structure for a long time.
One of the load-bearing walls for the installation of arches, beams, inclined girders is the vertical fence of the house. The adjacent wall of the building is often warm, so energy will not leave the room through it.
Optimal dimensions of a polycarbonate greenhouse:
- to the ridge of the roof - 2.5 m;
- wall height - 1.5 m;
- room width - 3.5 m.
Dimensions can be changed upwards, it is not recommended to reduce them. Too long beds (more than 6 m) make it difficult to care for the plants. The door is made 2.0 - 2.1 m in height, and at least 1.0 m wide, so that a wheelbarrow or trolley can pass.
The entrance to the greenhouse is made from a house in the same wall, sometimes a separate opening from the street is provided. The first option allows you to use the entrance in frosty weather, since the opening will not admit cold streams. The door to the street is additionally sealed in winter, waterproofing is installed.
Characteristics of wall-mounted single-slope greenhouses

A roof with one slope is in demand, especially if it has a common wall with a residential building. The structure is a half of a gable polycarbonate house. The sun's rays fall inward at a right angle, therefore, they are evenly scattered, and they act effectively on crops.
Single-slope polycarbonate greenhouses attached to the house have a number of advantages:
- the volume of materials for the supporting elements of the roof and vertical fences is reduced, since one wall in fact already exists;
- no need to design complex trusses for overlapping;
- there is a significant glazing plane, where the maximum volume of light rays falls;
- quickly mounted in comparison with gable roofs, simplicity of the device;
- it is convenient to supply water, drain waste water, it is possible to conduct a heating circuit, there is no need to draw electricity over a long distance;
- less likelihood of being ruined by vandals and theft.
The disadvantage of attached lean-to greenhouses is the small volume of the room and the small area.
Design features

A girder made of metal and wood is mounted on an adjacent wall. Take corner No. 65, profile pipe 40x60, channel No. 8, 10. Bars with section 80x100 are used from sawn timber. The ends of the rafter legs or arched elements are supported on this beam, and with the second end they are fixed on the opposite wall. Vertical fencing can be solid in the form of a monolithic concrete structure, or frame with filling.
The location of the greenhouse in relation to the house:
- Butt. The building is adjoined by a narrow part of the greenhouse, the main structure is being built in the form of a greenhouse, directed from the house. At the end, they make an entrance to the greenhouse from housing. Such species may have a gable roof.
- Polygonal. An abutment is made to the wall along a complex line, such structures require accurate calculations and a lot of time to erect.
- Semi-arched. The roof structure belongs to the single-pitched category, but it is difficult to manufacture. Metal, plastic pipes need to be bent with a machine, it will not work manually.
Polycarbonate is used on all types of roofs, since the material is easy to cut and install. It can be bent to a certain radius depending on the thickness of the panel.
Erection of the foundation

Before construction, they clear the territory, remove a layer of fertile land. A line is marked on the territory along which a greenhouse will be built. Dig a trench or separate holes, depending on the type of foundation.
For greenhouses, varieties are used:
- Beam from a bar. In the ground, a trench is prepared for laying a girder from wood. The element is impregnated with linseed oil 3 times, then insulated with roofing material from soil moisture. Along the perimeter, they are joined with staples, self-tapping screws, pins.
- Columnar foundation. Individual supports are poured with concrete, or laid out of bricks. The supports are tied with a beam of metal, wood, so that the individual elements work together and are not pushed out when the soil heaves.
- Monolithic concrete tape. A base of this type is made for brick, concrete walls of the greenhouse, from shell rock, blocks. The depth is rarely made more than 50 cm, at the bottom they make a drainage cushion of sand and crushed stone, you can take gravel, slag.
A monolithic slab for a greenhouse is rarely equipped, since the structure weighs little. You can put piles if the soil is problematic and the main residential building also has this type of foundation.
Single-pitched wall greenhouse frame

For racks, metal, wood, PVC pipes, galvanized and aluminum profiles are used. Metal are connected by welding, corners are welded at critical joints. Aluminum are joined using embedded parts on self-tapping screws.
All materials have different characteristics:
- Metallic elements. The frame is strong, durable, and inexpensive. Metal is afraid of corrosion, so it is treated with special anti-rust agents. After the installation is completed, the steel parts are painted with oil compounds or pentaphthalic varnish to protect them from the atmosphere.
- Wooden will not last so long, but the life can be extended by impregnating the elements with antiseptics, fire retardants, anti-rot agents. It is not expensive.
- PVC pipes are the most durable material, it does not deteriorate from moisture and frost. Plastic does not need to be pre-impregnated with protective agents.
A galvanized profile from a plasterboard system is used. Profiles CW-60, 100, UW-60, 100 are taken from the wall system. For joining, straight and cross parts are used. Assembling such a frame is simple and quick. Aluminum profiles are expensive and rarely used. In terms of performance, they are most suitable - lightweight, strong, durable.
Installation of a wooden frame
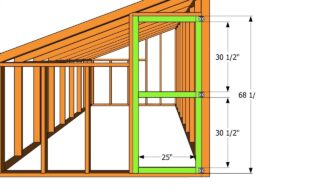
The frame of the attached greenhouse has three full-fledged walls for which the frame is made. In some cases, the racks are also placed near the wall of the house in order to fasten the floor beams to them, and not on the vertical plane of the building.
Between the racks, horizontal benches and girders are reinforced. Slopes are placed diagonally for strength, and corner braces are additionally placed at the corners for stability. Wooden elements are joined in a half-tree (connection with slaughtered quarters).
Deaf sections of the walls are sewn up with boards, shields, chipboard panels, OSB. In the summer version, the walls are not insulated, but for the winter they put waterproofing, an insulator outside, and sheathing is made on the crate.The rafters are placed at an angle so that the ramp is turned away from the house.
Opening transoms are provided in the construction of the roof and wall frame. Automation with temperature sensors is used to control the opening. The vents are placed on opposite ends to increase the speed of air flows.
Polycarbonate coating

The thickness of the sheets is referred to as the determining properties when choosing a material. The value depends on the climate, the strength of the wind, the material of the frame of the greenhouse. For seasonal construction, 4, 6 mm are used, and from 8 mm and more are used for heated buildings.
Polycarbonate characteristics:
- light weight, therefore, reduced efforts on the frame;
- strength, resistance to stress;
- in the event of a fire, it does not burn, but melts, while it does not flow down;
- cracks appear from a strong blow, but the fragments do not fly away;
- insulation from cold, noise;
- resistance to sudden temperature changes;
- resistance to aggressive atmospheric components, ultraviolet light.
Only transparent polycarbonate is placed on the roof and openings of the greenhouse, the colored one sharply reduces the transmission capacity of infrared rays. The sheets are mounted with the protective side out. On the walls, the slabs are placed so that the honeycomb is in an upright position.
A special connecting profile is used for joining. The holes for the screws are made slightly larger than the diameter of the hardware so that the material can move when expanding. Polycarbonate is not fastened with nails. When installing, the film is removed, the honeycomb cavities are blown with air from dust in order to increase the permeability to the rays. The ends with open honeycombs are covered with a sealant or special strips are placed.
Tools and materials for work

Wooden beams are prepared from the materials for the foundation or the strapping of the columnar base. Lumber is placed on the frame of walls and roofs. They buy polycarbonate sheets according to the calculation; for fastening to the wall, they purchase anchors or plastic dowels with self-tapping screws. The wood is fastened together with self-tapping screws, staples, steel corners are used.
Tool for work:
- tape measure from 5 m, carpenter's square for right angles, miter box, pencil;
- plumb bob, construction laser or bubble level;
- for wood - a hacksaw, jigsaw, circular;
- for metal - a grinder with a cutting and cleaning disc.
Polycarbonate is cut with a circular saw or knife on drywall. Use Phillips screwdrivers, drill, hammer drill, screwdriver.








